Maths Gcse Edexcel Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation8 主题
-
Comparing-Statistical-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation
-
Reading-And-Interpreting-Statistical-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation
-
Time-Series-Graphs Edexcel Foundation
-
Pie-Charts Edexcel Foundation
-
Frequency-Polygons Edexcel Foundation
-
Bar-Charts-And-Pictograms Edexcel Foundation
-
Tally-Charts-And-Frequency-Tables Edexcel Foundation
-
Stem-And-Leaf-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation
-
Comparing-Statistical-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation
-
Statistics-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Probability-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Transformations Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
Geometry-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Ratio-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Sequences Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Factorising Edexcel Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Algebra-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Edexcel Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Edexcel Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Edexcel Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Edexcel Foundation6 主题
-
Multiplying-And-Dividing-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Adding-And-Subtracting-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Mixed-Numbers-And-Improper-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Fractions-Of-Amounts Edexcel Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Multiplying-And-Dividing-Fractions Edexcel Foundation
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Edexcel Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Edexcel Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Toolkit Edexcel Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Edexcel Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Edexcel Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Edexcel Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Edexcel Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Edexcel Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Edexcel Foundation
-
Place-Value Edexcel Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Edexcel Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Edexcel Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Edexcel Foundation
Conversion-Graphs Edexcel Foundation
Exam code:1MA1
Conversion graphs
What is a conversion graph?
-
A conversion graph is a straight-line graph relating two quantities
-
You can convert (change) between them by reading values off the graph
-
-
Common examples include
-
Temperature
-
degrees Celsius (°C) and degrees Fahrenheit (°F)
-
-
Currency
-
Dollars ($) and Yen (¥)
-
-
Volume
-
Litres and gallons
-
-
Prices
-
A taxi driver charging per kilometre driven
-
-
-
The gradient of a conversion graph represents the rate of change
-
If the y-axis is the cost of a taxi journey (£) and the x-axis is the distance travelled (mile) then the gradient represents the cost per mile
-
A gradient of 5 means the cost increases by £5 for each mile travelled
-
-
How do I use a conversion graph?
-
Find the cost of 20kg using the conversion graph below
-
Start at 20kg on the x-axis
-
Draw a vertical line to the graph
-
Then a horizontal line across to the y-axis
-
Read off the value
-
$12
-
-
-
Find how many kilograms can be bought with $30
-
Start at $30 on the y-axis
-
Draw a horizontal line to the graph
-
Then a vertical line down to the x-axis
-
Read off the value
-
50kg
-
-
-
You can use proportion to find values that on not on the axes
-
To find the cost of 120kg
-
120kg = 6 × 20kg costs 6 × $12 = $72
-
120kg = 50kg + 50kg + 20kg costs $30 + $30 + $12 = $72
-
-
You can only do this if the graph starts at the origin
-
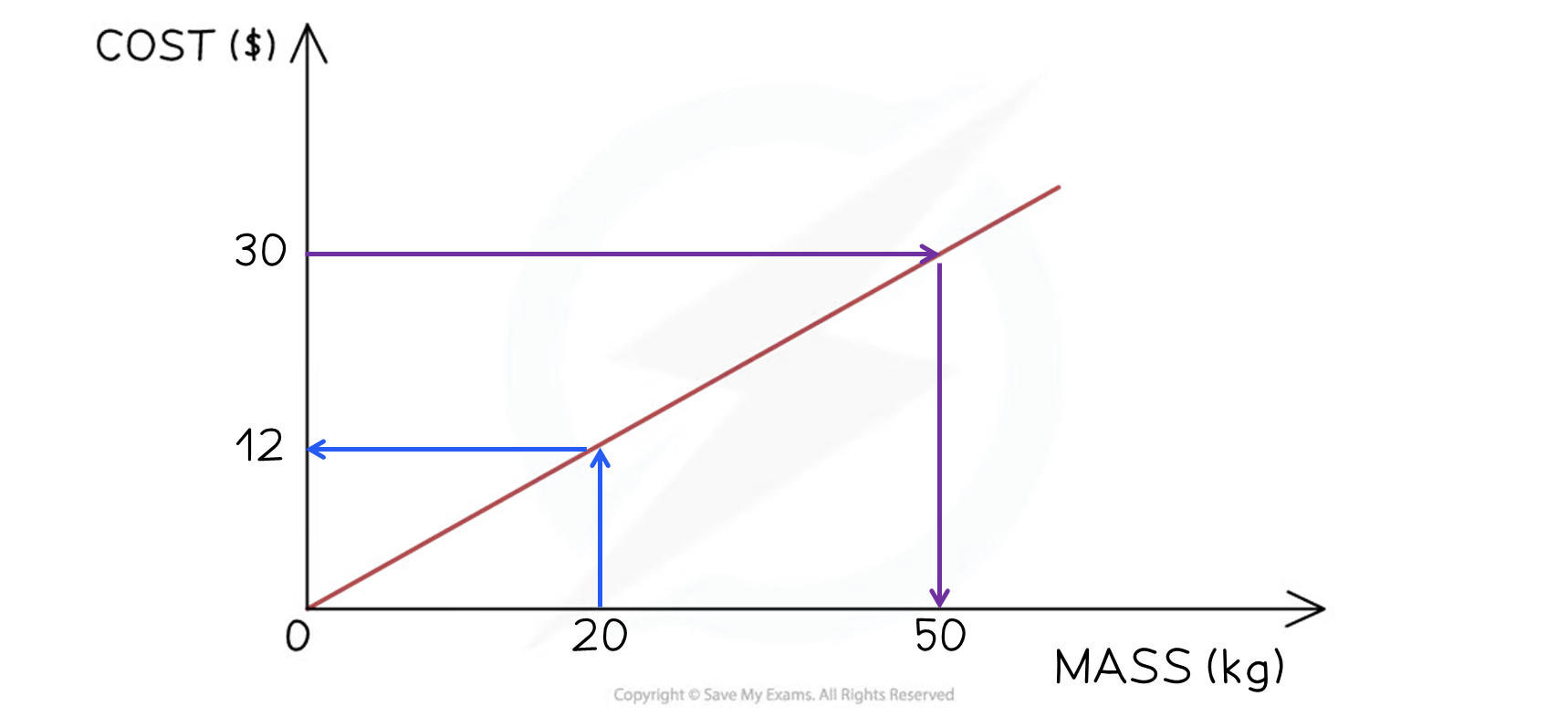
How do I use a conversion graph that does not start at the origin?
-
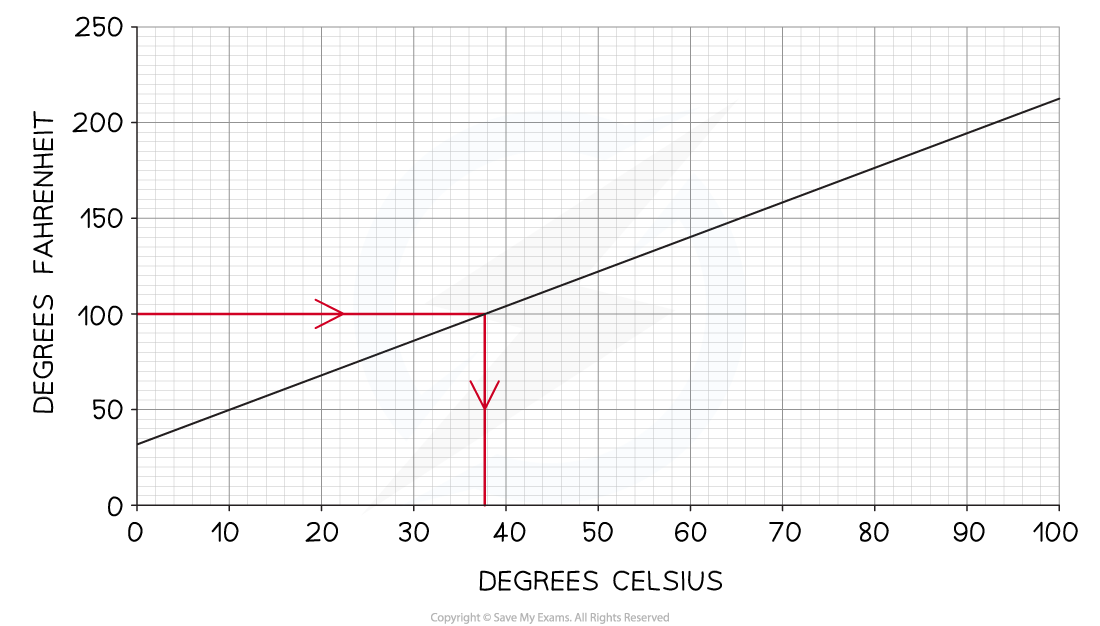
Convert 100°F into Celsius using the conversion graph below
-
Start at 100°F on the y-axis
-
Draw a horizontal line to the graph
-
Then a vertical line down to the x-axis
-
Read off the value
-
37.5°C
-
Answers between 37°C and 38°C would be accepted
-
(The true answer is 37.8°C to 1 decimal place)
-
-
-
The graph starts at 32 on the y-axis
-
This means that 0°C is 32°F
-
This starting value sometimes represents a fixed cost when money is involved
-
It could represent the fixed charge for the cost of a taxi fare
-
-
-
To convert values that are not on the axis
-
You would need to find an equation for the straight-line
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
Always check the scales of the axes!
Worked Example
The graph below shows the price (in dollars, $) charged by a plumber for the time spent (in hours) on a particular job.
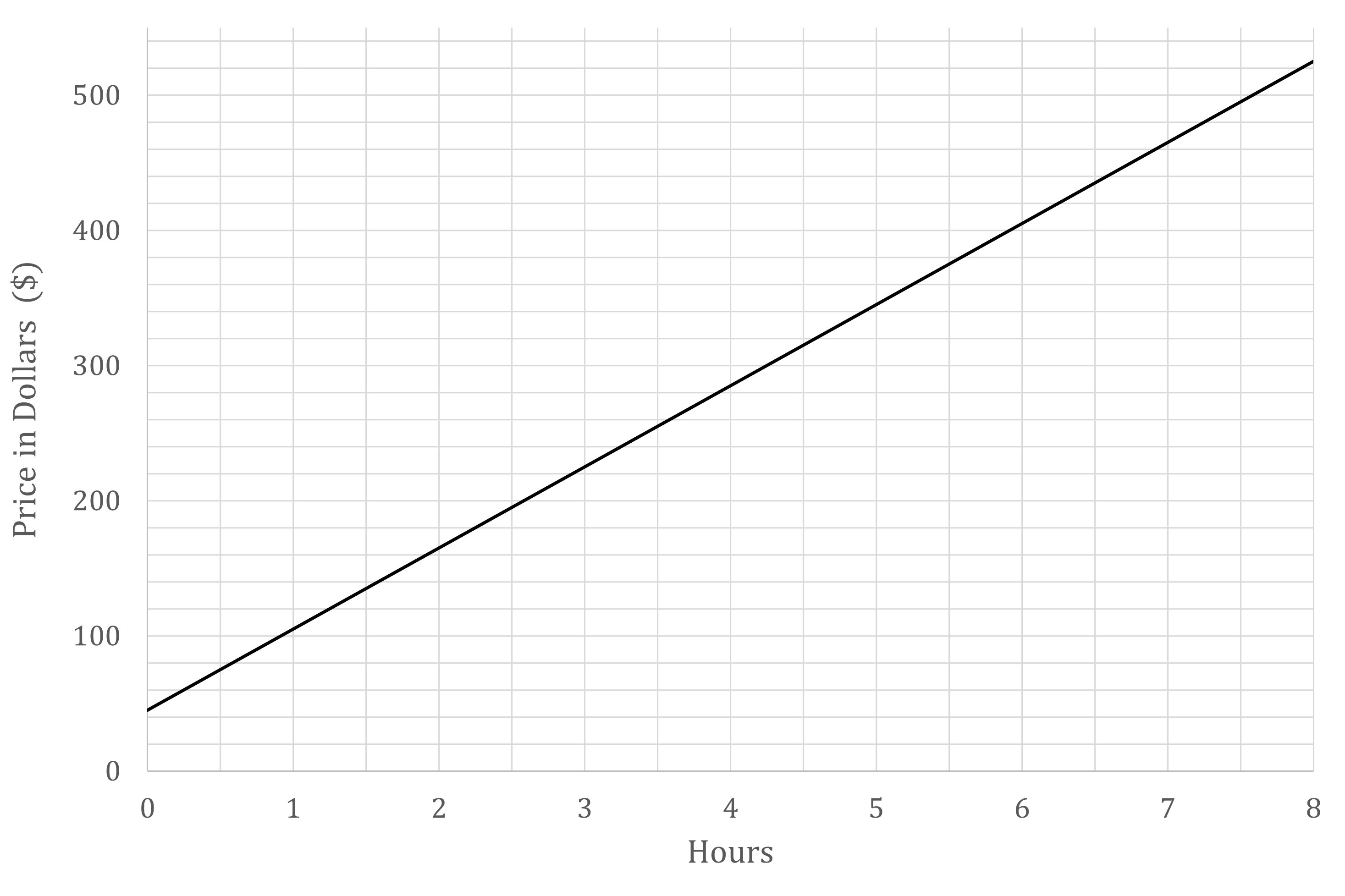
(a) Estimate the price charged for a job that takes 3 hours.
Draw a vertical line up from the x-axis at 3 hours
Then a horizontal line across to the y-axis
Read off the value
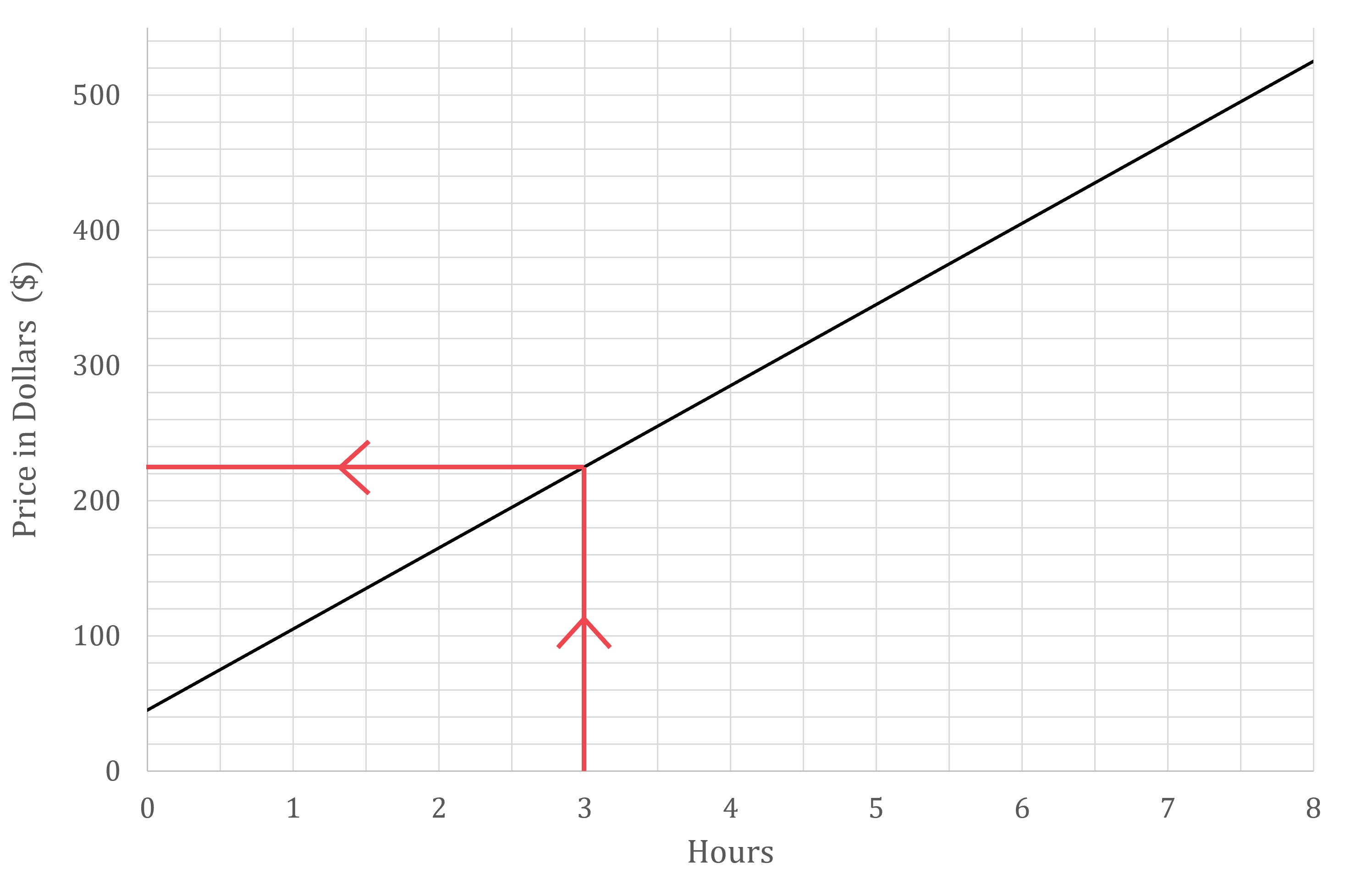
Approximately $225
Answers between $220 and £230 are accepted
(b) A particular job costs $320. Estimate, to the nearest half hour, how long this job took.
Draw a horizontal line across from the y-axis at $320
Draw a vertical line down to the x-axis
Read off the value to the nearest 0.5 hours
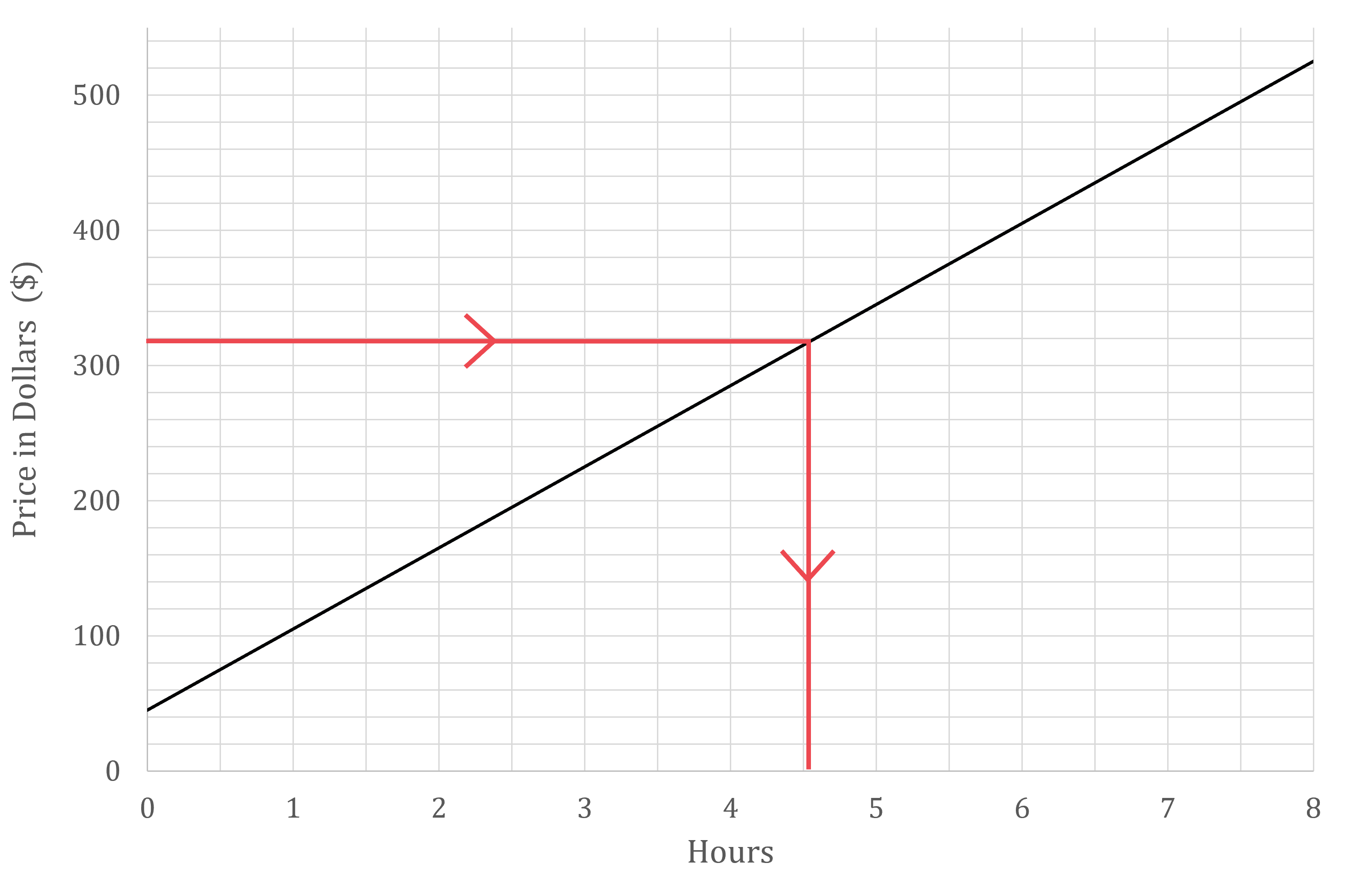
4.5 hours (to the nearest half hour)
(c) The plumber charges a fixed callout fee for travelling to the customer and inspecting the job before starting any work.
Find the price of the callout fee.
Before starting work means 0 hours of work has been done
Find the price charged for 0 hours
This is the y-intercept of the graph
Approximately $45
Answers between $40 and £50 are accepted

Responses