Maths Gcse Aqa Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Functions Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Iteration Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Surds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Aqa Higher
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Higher
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Aqa Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Aqa Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
Bar-Charts-And-Pictograms Aqa Higher
Exam code:8300
Line charts, bar charts & pictograms
What is a line chart and what is it used for?
-
Sometimes called a vertical line chart, this a visual way to represent discrete data
-
Line charts are used for numerical data (rather than categorical data)
-
They are particularly useful when there are lots of different options to show
e.g. Results of a test where scores are given as percentages
-
-
-
The vertical axis shows the frequency
-
The scale should start at zero and increase in equal amounts
-
-
The horizontal axis shows the different outcomes
-
A vertical line is drawn for each outcome and its height is its frequency
-

-
You can easily identify the mode using a line chart
-
The mode is the most common outcome
-
This will be the outcome with the highest (tallest/longest) line
-
e.g. In the line chart above, 11 was the modal test score, with a frequency of 7
-
-
You can quickly see how the data is spread using a line chart
-
Lines may be crowded around a particular group of options with only a few elsewhere
-
This may help identify anomalies or outliers in the data
-
e.g. In the line chart above we can see
-
the majority of the test scores, out of 20, were between 7 and 12
-
one pupil scored 19 out of 20, much higher than anyone else in the class
-
-
What is a bar chart?
-
A bar chart is a visual way to represent discrete data
-
Discrete data is data that can be counted
-
This can be numerical like shoe sizes in a class
-
Or non-numerical (categorical) like colours of cars down a road
-
-
-
The horizontal axis shows the different outcomes
-
The vertical axis shows the frequency
-
The heights of the bars show the frequency
-
Bars should be separated by gaps
-
Bars should have equal widths
-
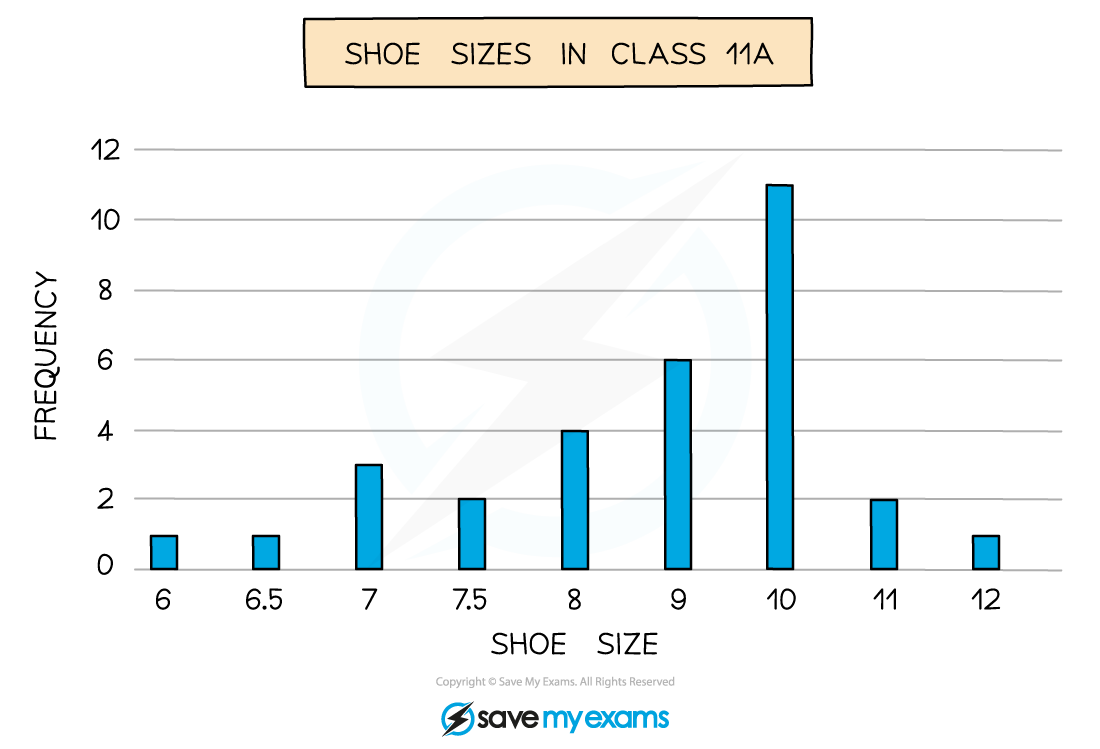
-
The mode is the outcome with the highest bar
-
You can also get dual bar charts to compare two data sets
-
Bars are in pairs (side-by-side) for each outcome
-
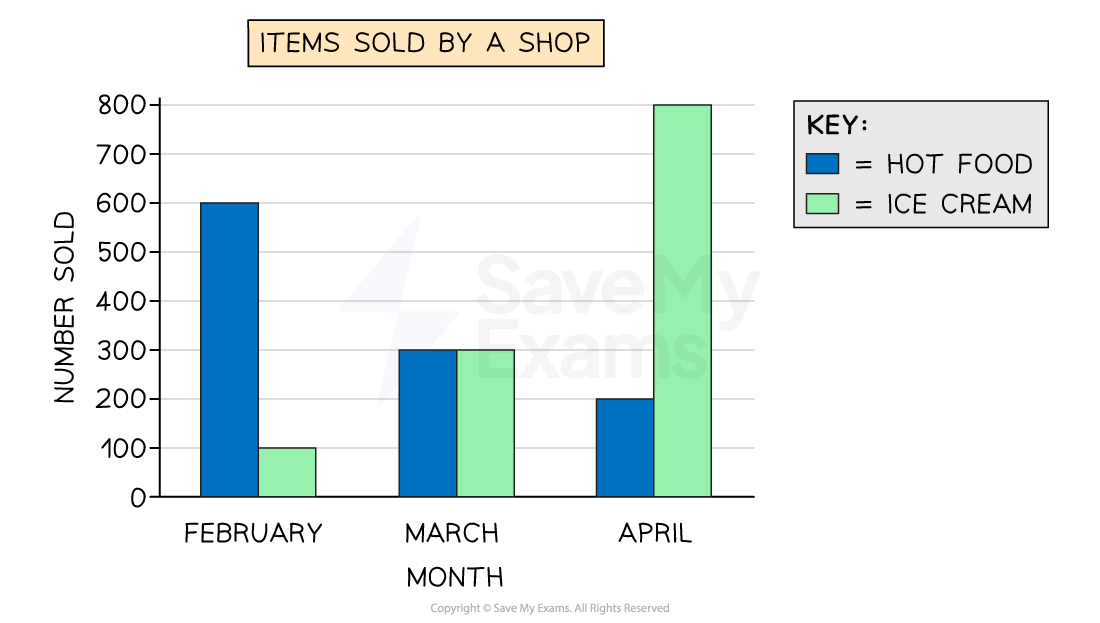
What is a pictogram?
-
A pictogram is an alternative to a bar chart
-
It is used in the same situations
-
-
There are no axes
-
Frequency is represented by symbols
-
A key shows the value of 1 symbol
-
For example, 1 symbol represents a frequency of 2
-
-
Half and quarter symbols are often used
-

-
The pictogram above shows the shoe sizes of students in a class
-
As 1 picture of a shoe represents 2 students
-
Half a shoe represents 1 student
-
-
The number of students with a shoe size of 7, is 3
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
If asked to draw a bar chart, find the largest frequency and choose a scale which makes that fit in the space provided
-
If asked to draw a pictogram, pick a symbol that is easy to duplicate and draw half (or quarter) of
Worked Example
Mr Barr teaches students in Year 7 and Year 8.
He records the number of pets that students in each year have.
His results are shown below.
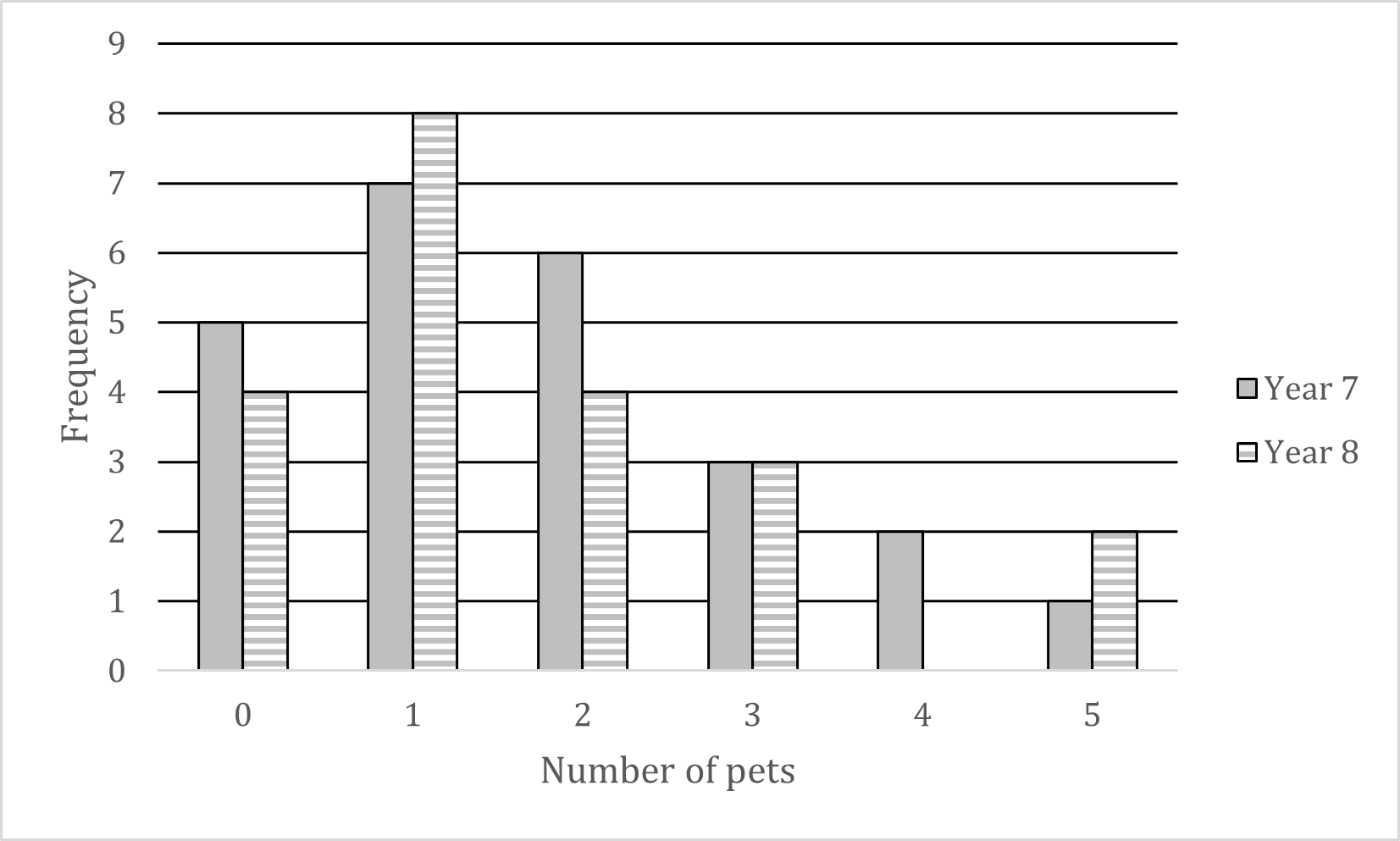
(a) Write down the modal number of pets for his Year 7 students.
The modal number (mode) is the number of pets that occurs the most
Visually, this will be the highest bar for Year 7s
The mode for Year 7 is 1 pet
(b) How many Year 8 students does he teach?
Add up all the heights (frequencies) of the Year 8 bars
4 + 8 + 4 + 3 + 0 + 2
He teaches 21 Year 8 students

Responses