Maths Gcse Aqa Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Functions Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Iteration Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Surds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Aqa Higher
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Higher
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Aqa Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Aqa Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
Types-Of-Sequences Aqa Higher
Exam code:8300
Types of sequences
What other sequences are there?
-
Linear and quadratic sequences are particular types of sequence covered in previous notes
-
Other sequences include geometric and Fibonacci sequences, which are looked at in more detail below
-
Other sequences include cube numbers and triangular numbers
-
Another common type of sequence in exam questions, is fractions with combinations of the above
-
Look for anything that makes the position-to-term and/or the term-to-term rule easy to spot
-
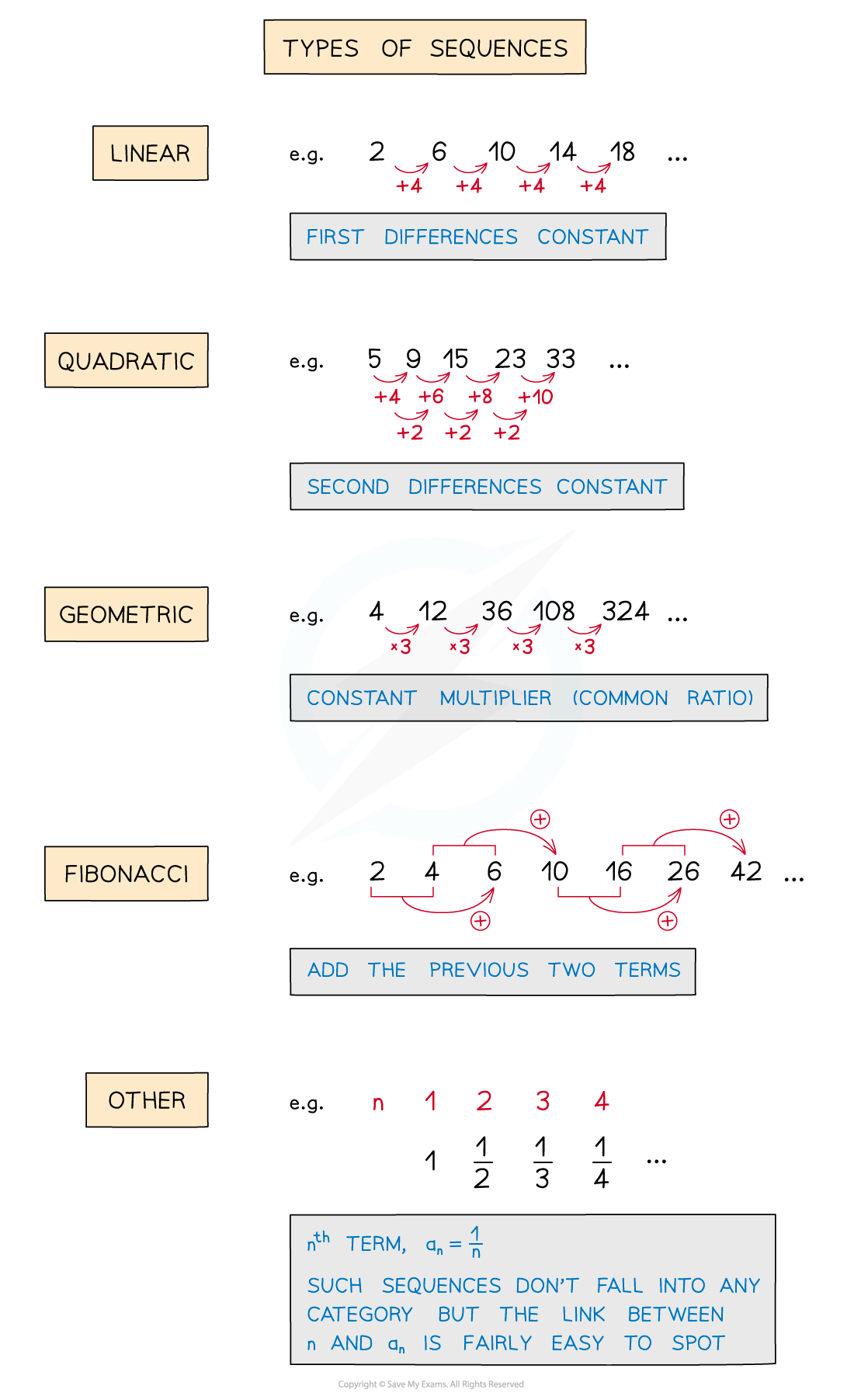
What is a geometric sequence?
-
A geometric sequence can also be referred to as a geometric progression and sometimes as an exponential sequence
-
In a geometric sequence, the term-to-term rule would be to multiply by a constant, r
-
an+1 = r.an
-
-
r is called the common ratio and can be found by dividing any two consecutive terms, or
-
r = an+1 / an
-
-
In the sequence 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, … the common ratio, r, would be 2 (8 ÷ 4 or 16 ÷ 8 or 32 ÷ 16 and so on)

What is a Fibonacci sequence?
-
The Fibonacci sequence is 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, …
-
The sequence starts with the first two terms as 1
-
Each subsequent term is the sum of the previous two
-
ie The term-to-term rule is an+2 = an+1 + an
-
Notice that two terms are needed to start a Fibonacci sequence
-
-
Any sequence that has the term-to-term rule of adding the previous two terms is called a Fibonacci sequence but the first two terms will not both be 1
-
Fibonacci sequences occur a lot in nature such as the number of petals of flowers
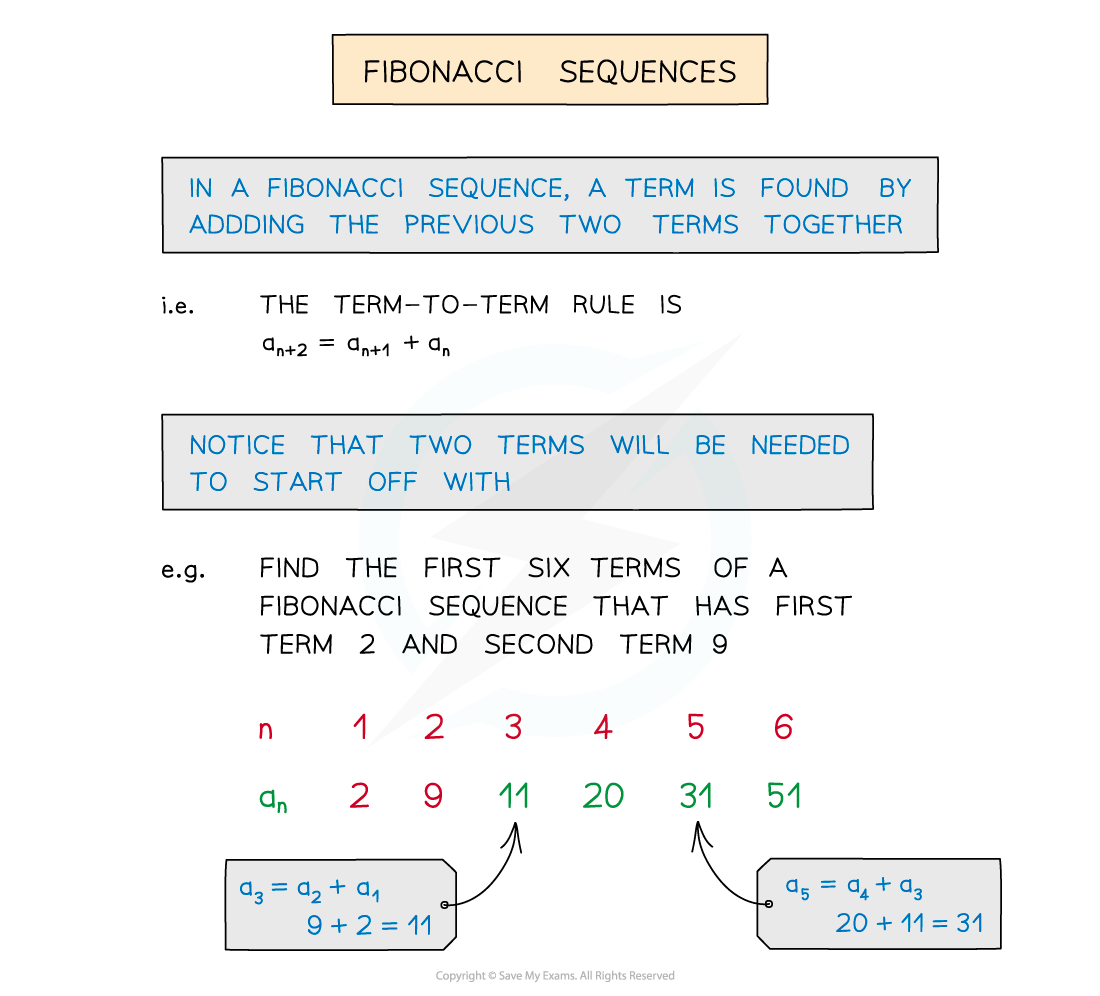
Problem solving and sequences
-
When the type of sequence is known it is possible to find unknown terms within the sequence
-
This can lead to problems involving setting up and solving equations
-
Possibly simultaneous equations
-
-
Other problems may involve sequences that are related to common number sequences such as square numbers, cube numbers and triangular numbers
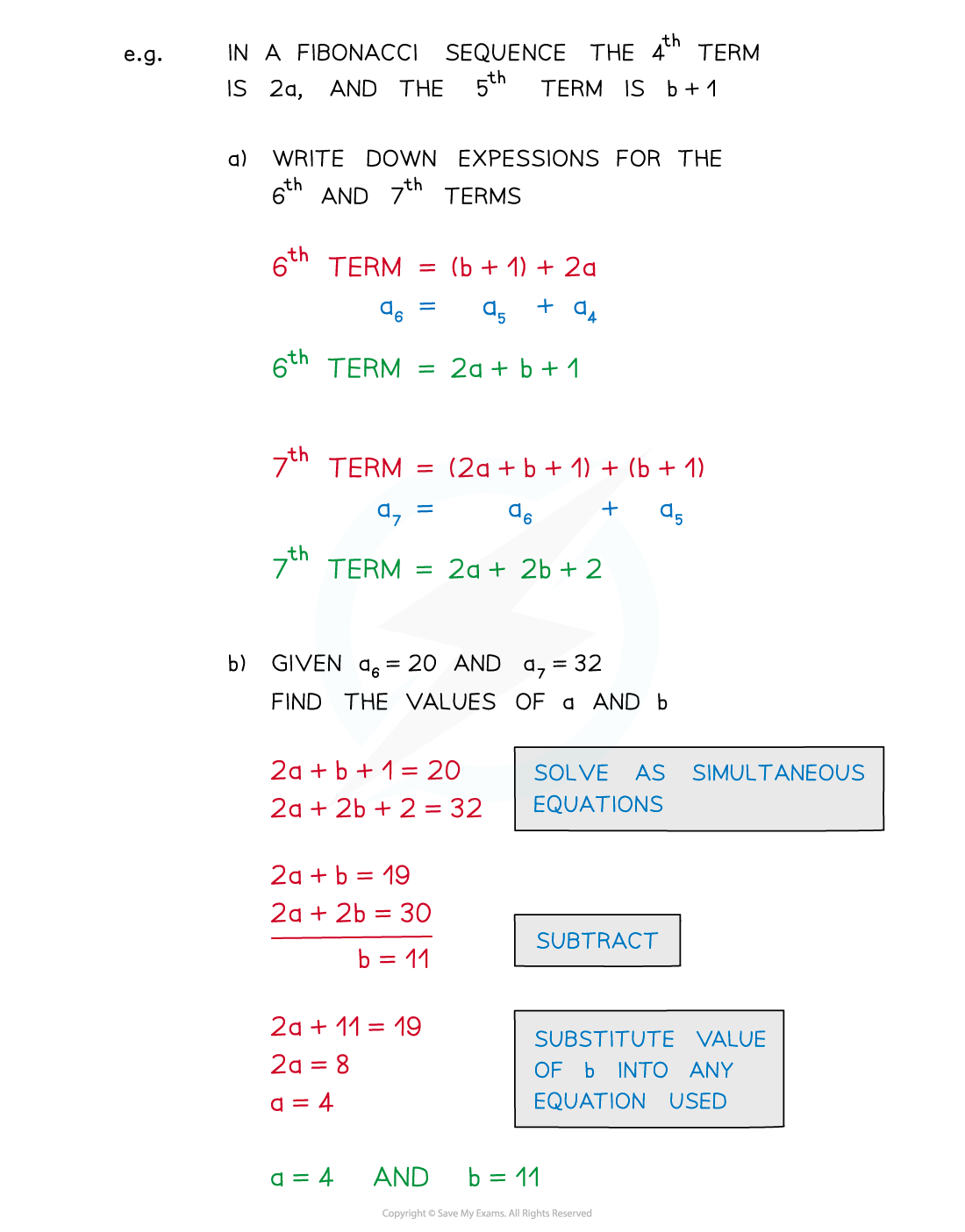
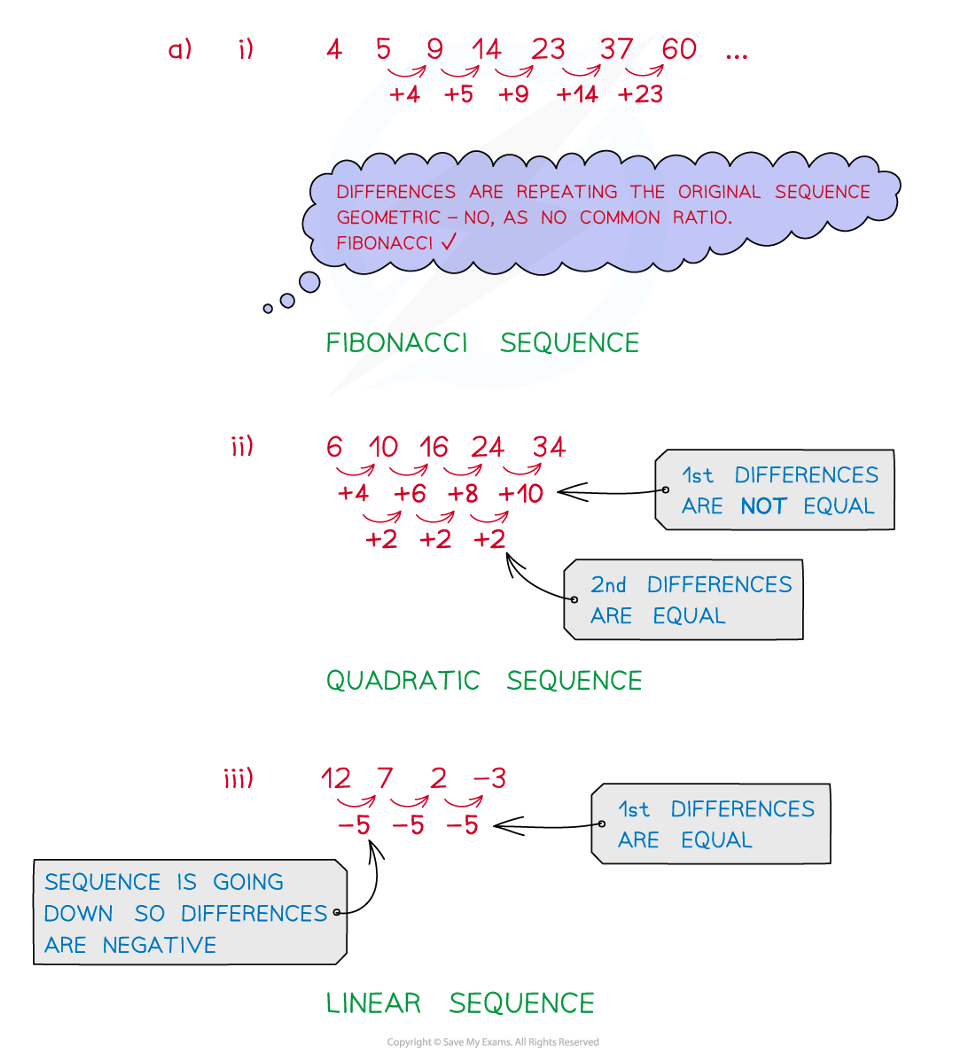
Worked Example
a)
Identify the types of sequence below;
i) 4, 5, 9, 14, 23, 37, 60, …
ii) 6, 10, 16, 24, 34, …
iii) 12, 7, 2, -3, …
b)
The 3rd and 6th terms in a Fibonacci sequence are 7 and 31 respectively.
Find the 1st and 2nd terms of the sequence.


Responses