Maths Gcse Aqa Higher
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Cumulative-Frequency-And-Box-Plots Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Histograms Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Combined-And-Conditional-Probability Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Higher6 主题
-
3D-Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Sine-Cosine-Rule-And-Area-Of-Triangles Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Area-And-Volume-Of-Similar-Shapes Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Circle-Theorems Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Higher5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Problem-Solving-With-Ratios Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Ratios Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Transformations-Of-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Graphing-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Estimating-Gradients-And-Areas-Under-Graphs Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Equation-Of-A-Circle Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Functions Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Iteration Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Quadratic-Equations Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Algebraic-Proof Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Algebraic-Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Completing-The-Square Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Factorising Aqa Higher6 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Higher1 主题
-
Surds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Bounds Aqa Higher2 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Higher7 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Higher3 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Higher4 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Higher10 主题
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
-
Systematic-Lists Aqa Higher
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Higher
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Higher
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Higher
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Irrational-Numbers Aqa Higher
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmas-Bodmas Aqa Higher
-
Mathematical-Symbols Aqa Higher
-
Product-Rule-For-Counting Aqa Higher
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Higher
Exam code:8300
Multiplication
How do I multiply two numbers without a calculator?
-
There are a variety of written methods that can be used to add large numbers
-
You only need to know one method, but be able to use it confidently
-
Four common methods are described below, but there are many other valid methods
-
How do I use the column method?
-
This is an efficient method if you are confident with multiplication
-
To use the column method:
-
Write one number above the other lining up the digits using place value columns
-
Multiply the first digit (on the right) from the bottom value by each digit in the top value
-
Write the result under the line with the digits in the correct place value columns
-
-
Multiply the next digit in the bottom value by each digit in the top value
-
Always work from right to left
-
Use 0s as place holders when multiplying digits in columns other than the ones column
-
-
For example, 87 × 426 = 37 062
-
How do I use the lattice method?
-
The lattice method is good for numbers with two or more digits
-
This method allows you to work with individual digits
-
-
To use the lattice method:
-
Draw a grid
-
The number of rows should be the same as the number of digits in one number
-
The number of columns should be the same as the number of digits in the other number
-
Draw diagonal lines through the boxes
-
-
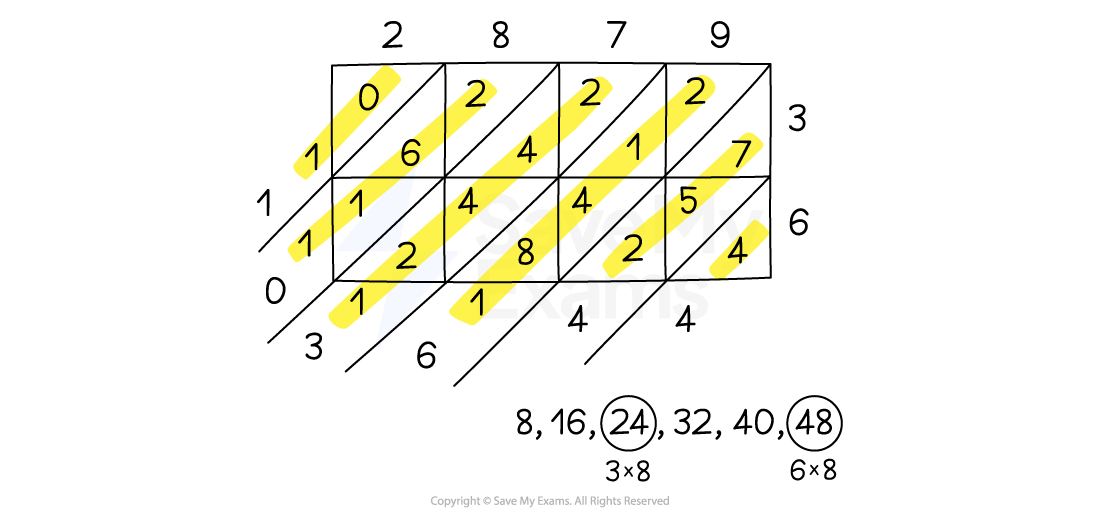
Multiply each pair of digits, writing the result in the relevant box
-
Ones should be written in the bottom half of the box and tens in the top half of the box
-
-
Add the digits along the diagonals and write the result in the diagonal outside the grid
-
Carry the tens of any 2 digit result into the next diagonal
-
-
-
For example, 3516 × 23 = 80 868
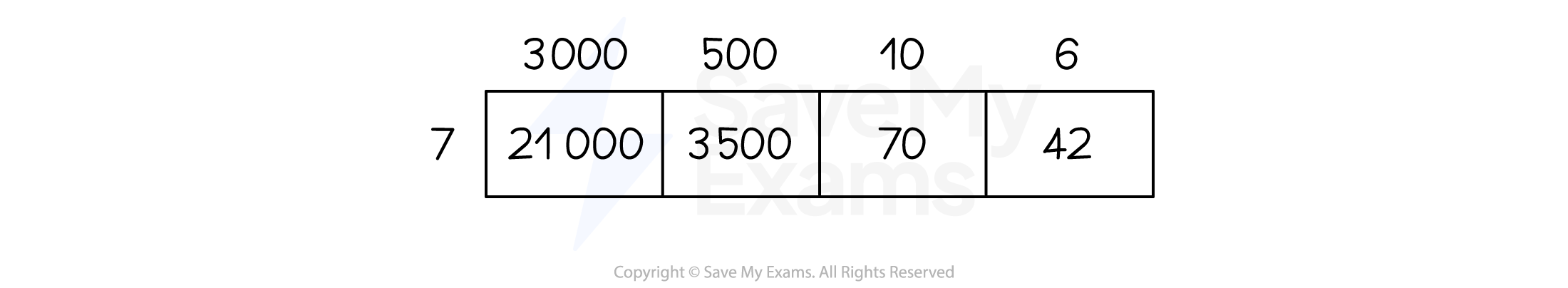
How do I use the grid method?
-
This method keeps the value of the larger number intact
-
It may take longer with two larger numbers
-
Be careful lining up numbers with lots of zeros!
-
-
To use the grid method
-
Draw a grid
-
The number of rows should be the same as the number of digits in one number
-
The number of columns should be the same as the number of digits in the other number
-
-
Label the rows and columns with the values of each digit
-
E.g. For 3516 you would use 3000, 500, 10 and 6
-
-
Multiply together the relevant values and put the results in the boxes
-
Add up all of the cells in the boxes
-
-
For example, 3516 × 7 = 24 612
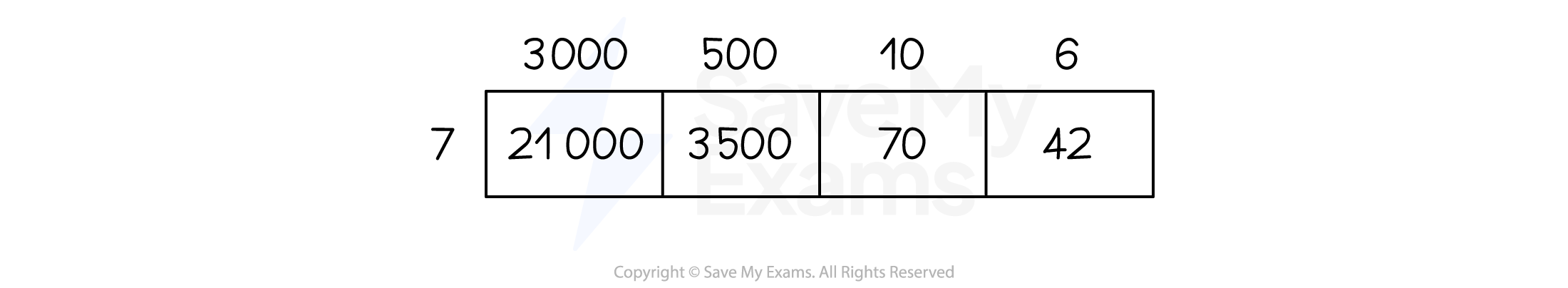
How do I use the repeated addition method?
-
This is best for smaller, simpler cases
-
You may have seen this called ‘chunking’
-
-
To use the repeated addition method
-
Build up to the answer using simple multiplication facts that can be worked out easily
-
To find 13 × 23 :
1 × 23 = 232 × 23 = 46
4 × 23 = 92
8 × 23 =184
-
So, 13 × 23 = 1 × 23 + 4 × 23 + 8 × 23 = 23 + 92 + 184 = 299
-
What words are used for multiplication and division?
-
Multiplication may be phrased using the words lots of, times or product
-
Division may be phrased using the words quotient, share and per

Responses