Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Using a calculator
Why are calculator skills important?
-
There are many special functions on a scientific calculator
-
To answer questions successfully you need to be able to use your calculator effectively
-
-
You may need to use some of the functions on the calculator in other subjects such as Science
-
There are many different models of calculator
-
Any scientific calculator will have the functions you need but may be accessed in different ways
-
You need to know how to use the features on your specific model
-
-
If you have an old or very basic scientific calculator the functions may be used backwards
-
To find the sine of an angle on a newer calculator, type sin (57)
-
On an older calculator you may need to type 57 then press the sin button
-
-
The notes below apply to most if not all scientific calculators but the images are based on the Casio fx-83GT

The Casio fx-83GTX Classwiz
How do I make sure that I have the correct settings on the calculator?
-
Check you know how change the mode of your calculator
-
There is usually a button marked ‘MODE’
-
Most calculators default to ‘MATH’ mode with the word MATH written across the top of the display or using a symbol
-
-
The ‘Angle Unit’ needs to be degrees
-
There is usually a button marked ‘SETUP’ where you can find the angle unit options
-
A ‘D’ symbol at the top of the display is used to indicate that the calculator is in the degrees setting
-
-
Make sure you can switch between ‘exact’ answers (e.g. fractions) and ‘approximate’ answers (e.g. decimals)
-
When in ‘MATH’ mode press the ‘S
D’ button to switch between answer types
-
What are the shortcut buttons on the calculator?
-
There are several very useful shortcut buttons on the calculator that you should know
-
The fraction, square, cube, power and square root buttons are all frequently used
-
Use the ‘SHIFT’ (2nd or INV) button to access functions including mixed numbers, cube roots, and nth roots
-
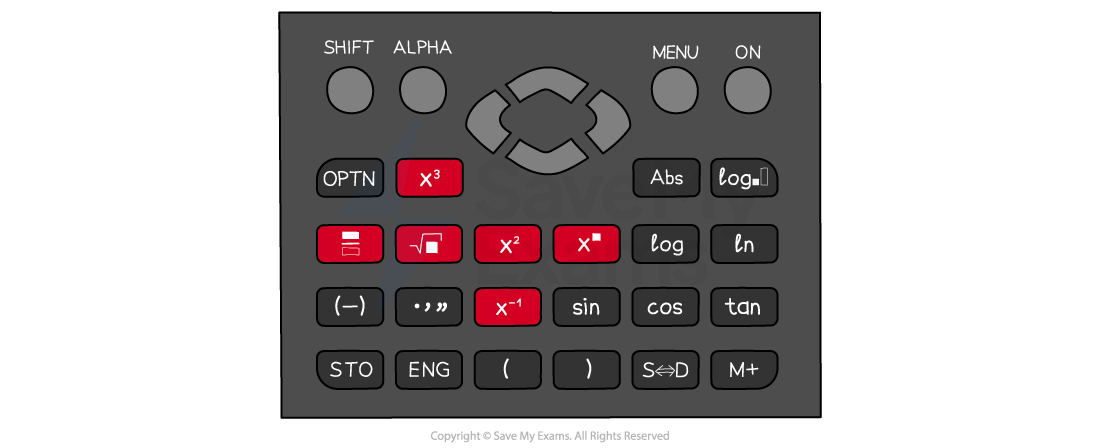
Why is using brackets important?
-
Applying brackets correctly on your calculator helps you to avoid errors in your calculations
-
Use brackets as you would in written mathematics
-
Put brackets around negative numbers in calculations
-
Remember,
gives you a different result to
-
Use the ‘(-)’ button for negative values, not the minus button
-
-
Which buttons are useful for trigonometry?
-
Use the sin, cos and tan buttons when finding missing sides of a triangle
-
Remember to make sure that your calculator is in degrees mode
-
-
Use sin-1, cos-1 and tan-1 when finding missing angles of a triangle
-
Access these by using the ‘SHIFT’ button
-
-
When using a trig function, the calculator gives you an open bracket ‘(‘
-
Remember to use a closed bracket ‘)’ after typing the angle in
-
Which buttons are useful for standard form and calculations involving π?
-
To write a number in standard form on the calculator, use the ×10x
-
Modern calculators display standard form in the way it is written, e.g., 2 x 105
-
Older models may use a small capital letter ‘E’ in place of ×10x, e.g., 2E5
-
-
<img alt=”bold italic pi” data-mathml='<math ><semantics><mi mathvariant=”bold-italic”>π</mi><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“language”:”en”,”fontFamily”:”Times New Roman”,”fontSize”:”18″,”autoformat”:true}</annotation></semantics></math>’ height=”19″ role=”math” src=”data:image/svg+xml;charset=utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%20xmlns%3Awrs%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wiris.com%2Fxml%2Fmathml-extension%22%20height%3D%2219%22%20width%3D%2215%22%20wrs%3Abaseline%3D%2216%22%3E%3C!–MathML%3A%20%3Cmath%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F1998%2FMath%2FMathML%22%3E%3Cmi%20mathvariant%3D%22bold-italic%22%3E%26%23x3C0%3B%3C%2Fmi%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E–%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A’math1437d7d1d97917cd627a34a6a0f’%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAt2hlYWQQC2qxAAACRAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAnwAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKgAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACqAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAArQAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALUAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEdAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABJQAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAA8D%2F%2FwAAA8D%2F%2F%2FxBAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAAD

Responses