Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Types-Of-Sequences Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Types of sequences
What types of sequences are there?
-
Linear sequences are the sequences that you are most likely to see in an exam question
-
These are sometimes called arithmetic sequences or progressions
-
A common difference is added to or subtracted from one term to get to the next term
-
-
Other types of sequences that you may also come across include
-
Quadratic sequences (square numbers)
-
Cube numbers
-
Triangular numbers
-
Geometric sequences
-
Fibonacci sequences
-
-
Another common type of sequence in exam questions, is fractions with combinations of the above
-
Look for anything that makes the position-to-term and/or the term-to-term rule easy to spot
-
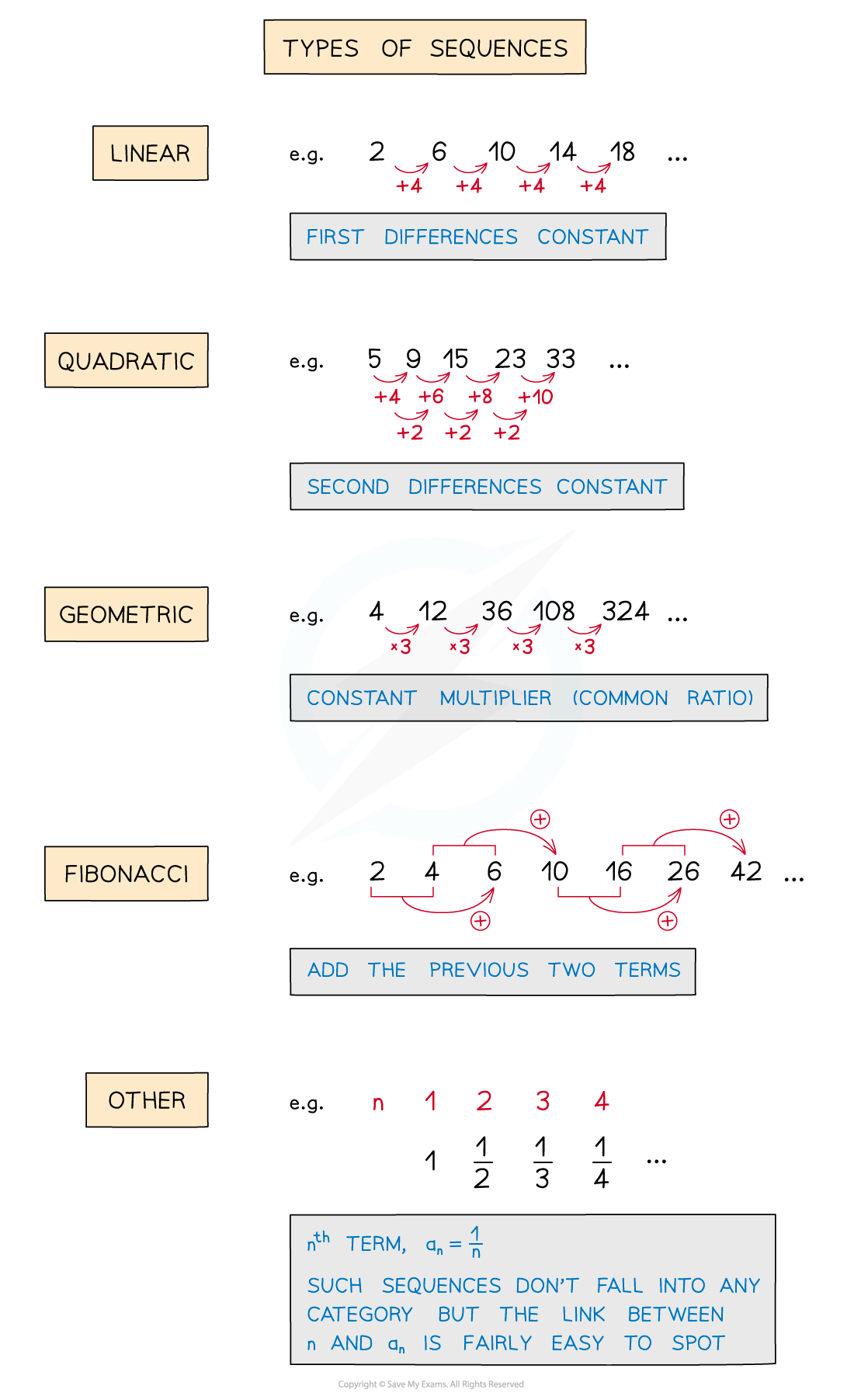
What is a quadratic sequence?
-
A quadratic sequence is based around square numbers
-
The second differences are constant (the same)
-
Second differences are the differences between the first differences
-
For example, 2, 3, 6, 11, 18, …
1st Differences: 1 3 5 72nd Differences: 2 2 2
-
What is a geometric sequence?
-
A geometric sequence can also be referred to as a geometric progression and sometimes as an exponential sequence
-
In a geometric sequence, the term-to-term rule would be to multiply by a constant
-
This multiplier is called the common ratio and can be found by dividing any two consecutive terms
-
Consider the sequence 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, …
The common ratio would be x2 (8 ÷ 4 or 16 ÷ 8 or 32 ÷ 16 and so on)
-
What is a Fibonacci sequence?
-
THE Fibonacci sequence is 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, …
-
The sequence starts with the first two terms as 1
-
Each subsequent term is the sum of the previous two
-
Notice that two terms are needed to start a Fibonacci sequence
-
-
Any sequence that has the term-to-term rule of adding the previous two terms is called a Fibonacci sequence but the first two terms will not both be 1
-
Fibonacci sequences occur a lot in nature such as the number of petals of flowers
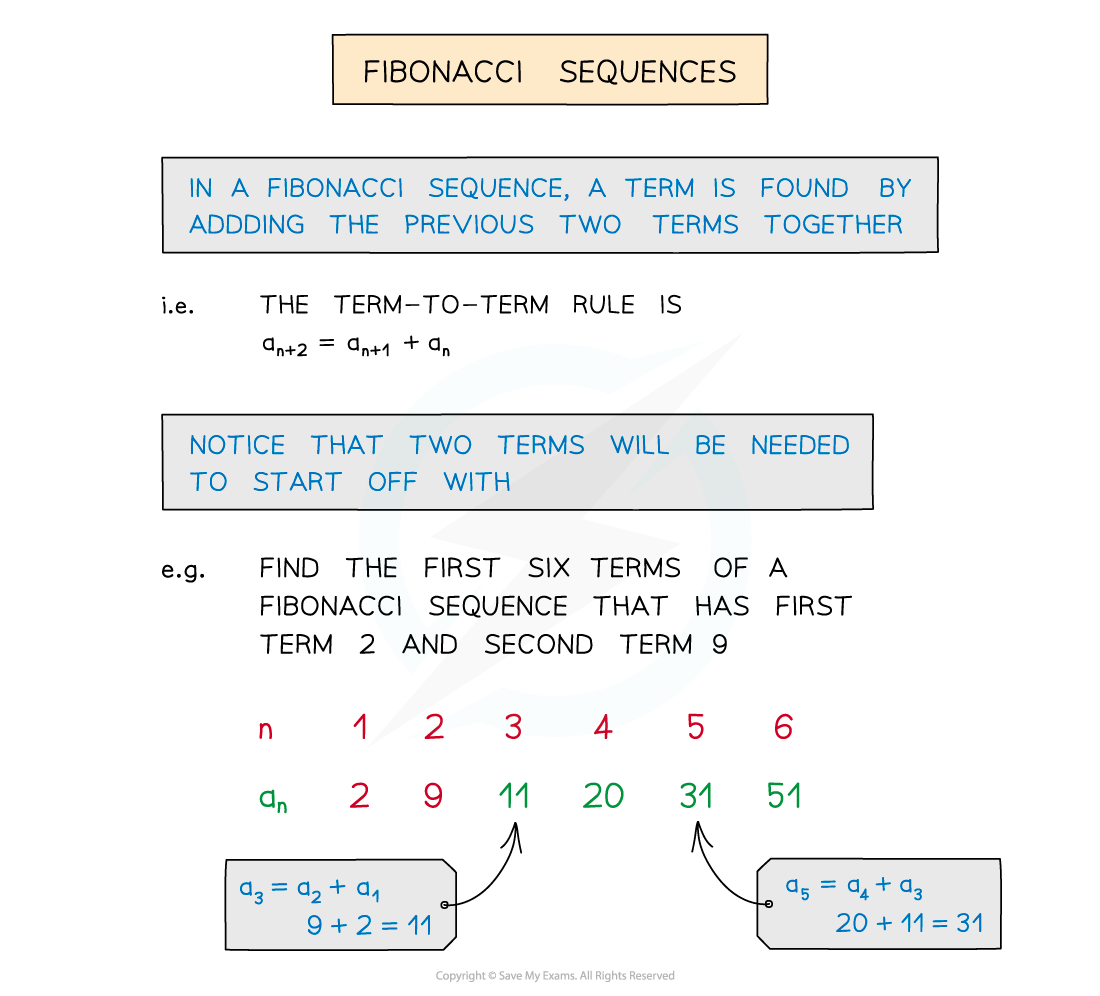
Problem solving with sequences
-
When the type of sequence is known it is possible to find unknown terms within the sequence
-
Possibly simultaneous equationsThis can lead to problems involving setting up and solving equations
-
Other problems may involve sequences that are related to common number sequences such as square numbers, cube numbers and triangular numbers
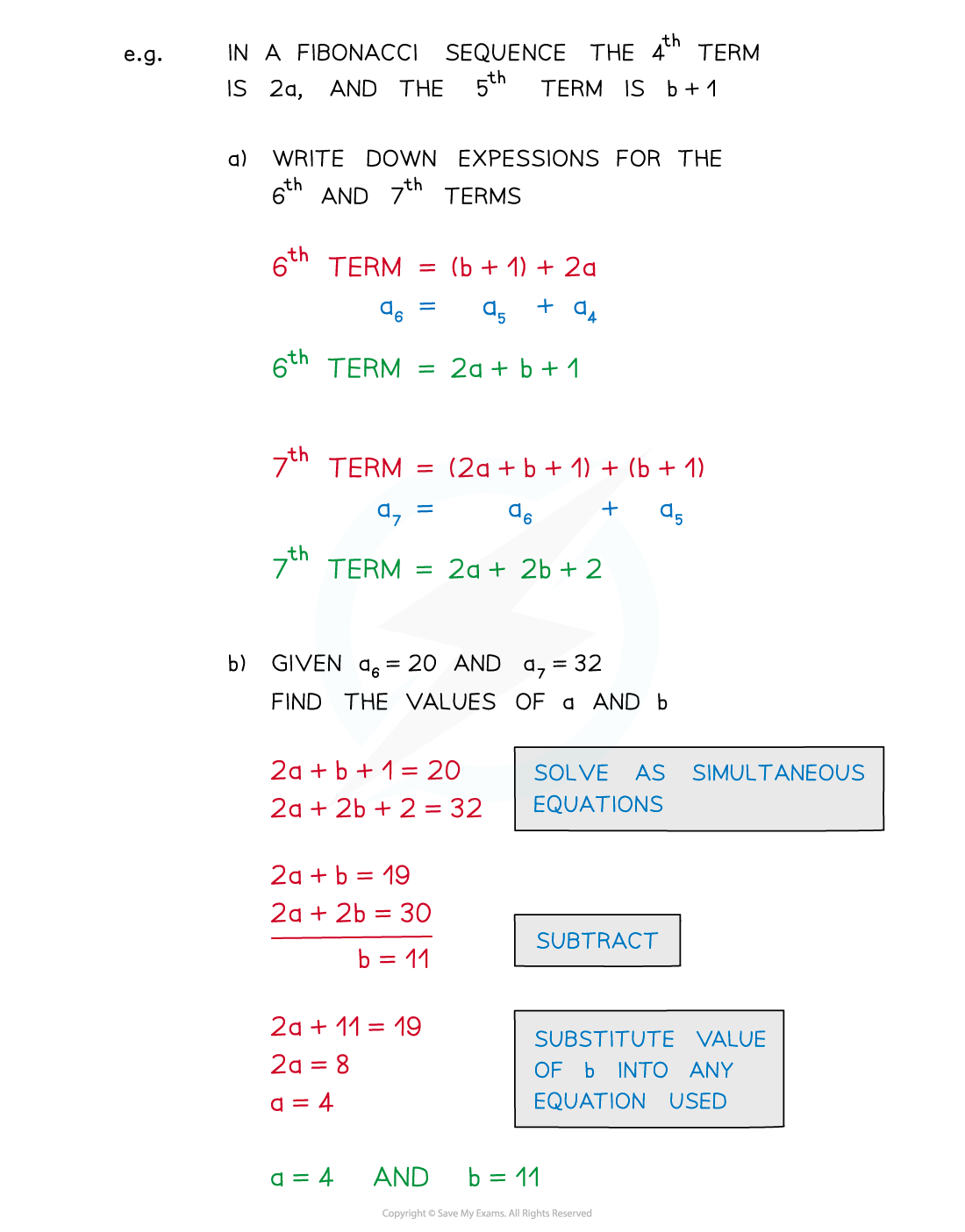
Worked Example
(a)
Identify the types of sequence below;
i) 4, 5, 9, 14, 23, 37, 60, …
There is no common second difference so it is not quadratic
There is no common ratio so it is not geometric
Two terms add together to give the next term in the sequence
4 + 5 = 9
5 + 9 = 14 etc.
Fibonacci sequence
ii) 6, 10, 16, 24, 34, …
First differences are not equal so it is not linear
Second differences are equal
6, 10, 16, 24, 34, …
4 6 8 10
2 2 2
Quadratic sequence
iii) 12, 7, 2, -3, …
There is a common first difference
12, 7, 2, -3, …
-5 -5 -5
Linear sequence
(b) The 3rd and 6th terms in a Fibonacci sequence are 7 and 31 respectively.
Find the 1st and 2nd terms of the sequence.
Write down the terms of the sequence that you know in their correct position
|
n |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
an |
|
|
7 |
|
|
31 |
We’re told that this is a Fibonacci sequence, so two consecutive terms added together give the next term
Let the second term, a2 be x
We can write an expression for the 4th term by adding together the second and 3rd terms
We can write an expression for the 5th term by adding together the 3rd and 4th terms
|
n |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
an |
|
x |
7 |
x + 7 |
(x + 7) + 7 |
31 |
We know that the 6th term in the sequence is 31
Add together the expressions for the 4th and the 5th term and set it equal to 31
(x + 7) + (x + 7) + 7 = 31
Simplify
2x + 21 = 31
Solve for x
2x = 10
x = 5
Substitute the value for x into the terms of the sequence that you have expressions for
|
n |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |

Responses