Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Introduction Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Introduction to sequences
What are sequences?
-
A sequence is an ordered set of numbers that follow a rule
-
For example 3, 6, 9, 12…
-
The rule is to add 3 each time
-
-
-
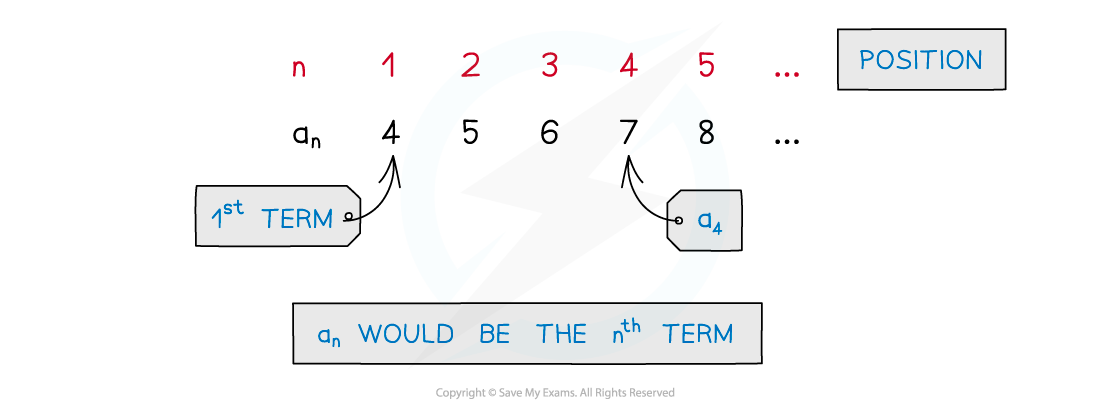
Each number in a sequence is called a term
-
The location of a term within a sequence is called its position
-
The letter n is used for position
-
n = 1 refers to the 1st term
-
n = 2 refers to the 2nd term
-
If you do not know its position, you can say the n th term
-
-
-
Another way to show the position of a term is using subscripts
-
A general sequence is given by a1, a2, a3, …
-
a1 represents the 1st term
-
a2 represents the 2nd term
-
an represents the nth term
-
-
How do I write out a sequence using a term-to-term rule?
-
Term-to-term rules tell you how to get the next term from the term you are on
-
It is what you do each time
-
For example, starting on 4, add 10 each time
-
4, 14, 24, 34, …
-
-
How do I write out a sequence using a position-to-term rule?
-
A position-to-term rule is an algebraic expression in n that lets you find any term in the sequence
-
This is also called the n th term formula
-
-
You need to know what position in the sequence you are looking for
-
To get the 1st term, substitute in n = 1
-
To get the 2nd term, substitute in n = 2
-
-
You can jump straight to the 100th term by substituting in n = 100
-
You do not need to find all 99 previous terms
-
-
For example, the n th term is 8n + 2
-
The 1st term is 8×1 + 2 = 10
-
The 2nd term is 8×2 + 2 = 18
-
The 100th term is 8×100 + 2 = 802
-
How do I know if a value belongs to a sequence?
-
If you know the n th term formula, set the value equal to the formula
-
This creates an equation to solve for n
-
-
For example, a sequence has the n th term formula 8n + 2
-
Is 98 in the sequence?
-
It is in the sequence, it is the 12th term
-
-
Is 124 in the sequence?
-
n is not a whole number, so it is not in the sequence
-
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
In the exam, it helps to write the position number (the value of n) above each term in the sequence.
Worked Example
</head

Responses