Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Rates-Of-Change-Of-Graphs Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Rates of change of graphs
What is a rate-of-change graph?
-
A rate-of-change graph usually shows how a variable changes with time
-
The following are examples of rates-of-change graphs:
-
Speed against time
-
Speed is the rate of change of distance as time increases
-
-
Acceleration against time
-
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity as time increases
-
-
The depth of water against time (e.g. in a container as it is filled with water)
-
Can rates-of-change graphs not be against time?
-
More generally, rate-of-change graphs can show any two different variables plotted against each other, not just time
-
E.g. the volume of air inside an inflating balloon plotted against the balloon’s radius
-
This shows the rate of change of volume as radius increases
-
-
E.g. the number of ice-creams sold plotted against the weather temperature
-
This shows the rate of change of number of ice-creams as temperature increases
-
-
How can I use gradients to find rates of change?
-
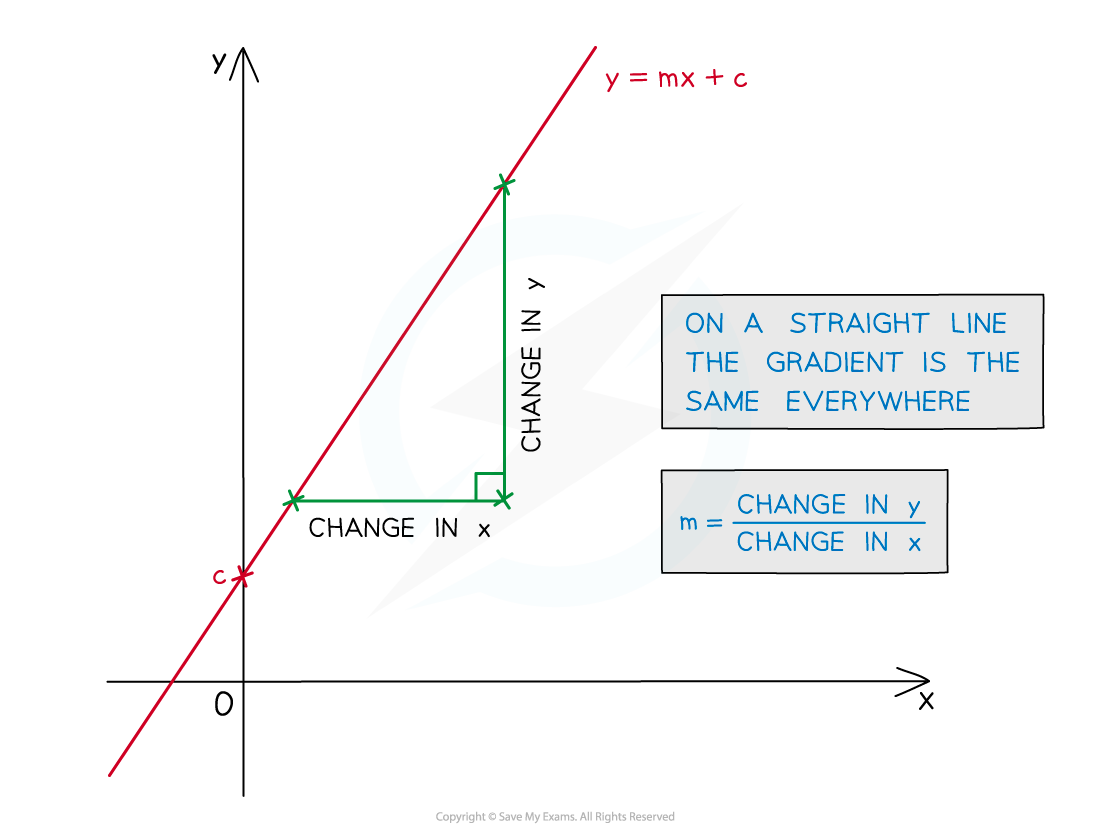
The gradient of the graph of y against x represents:
-
the amount of change in y for every 1 unit of increase in the x-direction
-
This is the amount of y per unit of x
-
-
This is called the rate of change of y against x
-
-
The units of gradients are the units of the y-axis, divided by the units of the x-axis
-
E.g. If the graph shows volume in cm3 on the y-axis and time in seconds on the x-axis, the rate of change is measured in cm3/s (or cm3s-1)
-
-
If the graph is a straight line the rate of change is constant
-
If the graph is horizontal, the rate of change is zero
-
y is not changing as x changes
-
-
How can I use tangents to find rates of change?
-
If the graph is a curve, you can draw a tangent at a point on the graph and find its gradient
-
This will be an estimate of the rate of change of y against x
-
-
The rate of change is greater when the graph is steeper
-
In the below image
-
tangents drawn at points A and B show the graph is steeper at B
-
therefore the rate of change at B is greater
-
-

-
On a distance-time graph, a tangent at a point on the curve can be used to estimate the velocity at that particular time
-
On a speed-time graph, a tangent at a point on the curve can be used to estimate the acceleration at that particular time
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
The units of the gradient can help you understand what is happening in the context of an exam question
-
For example, if the y-axis is in dollars and the x-axis is in hours, the gradient represents the change in dollars per hour
-
Worked Example
(a) Each of the graphs below show the depth of water, d cm, in different containers that are being filled from a running tap of water.
Match each of the graphs 1, 2, 3, 4 with the containers A, B, C, D.
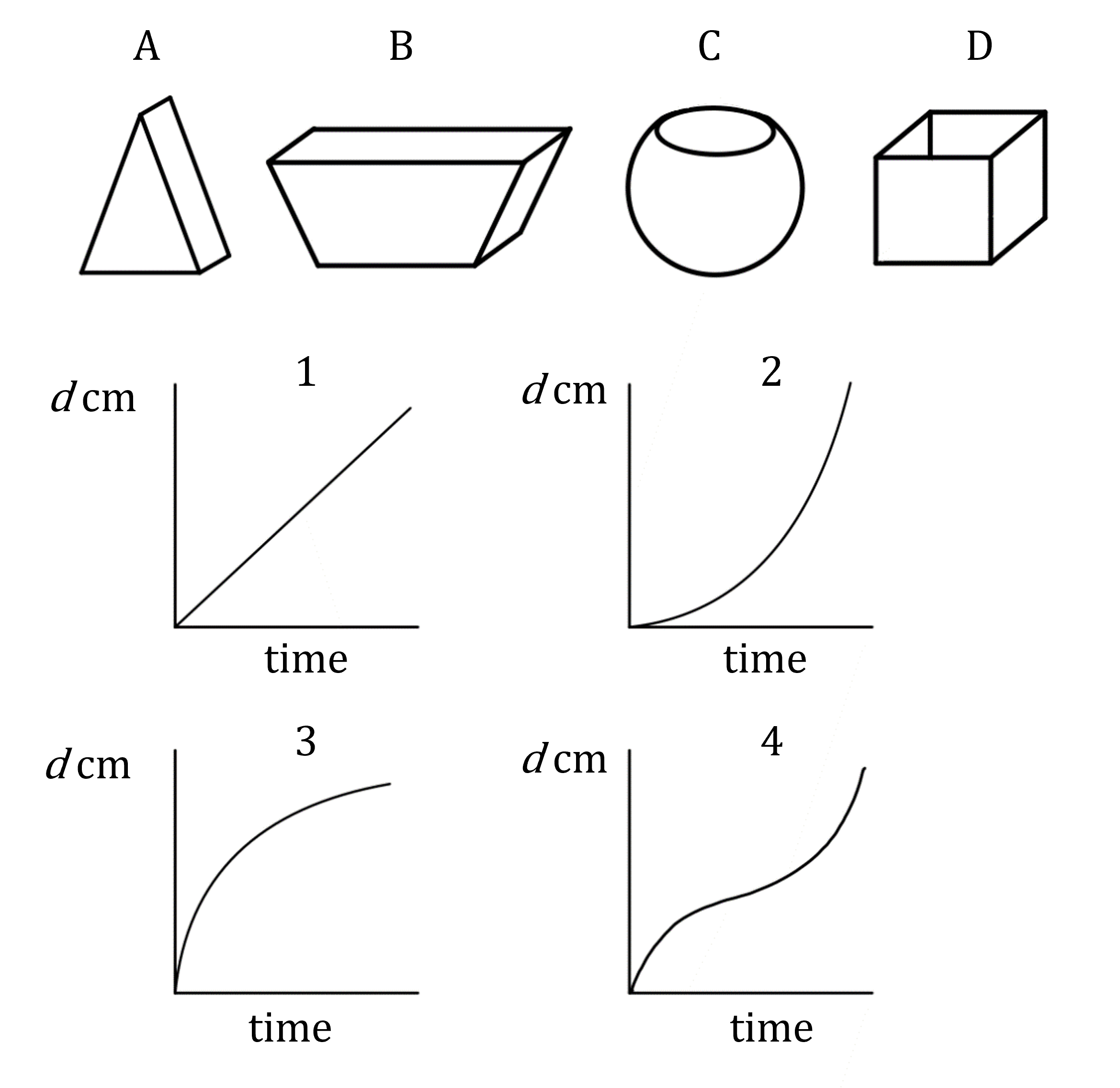
Considering graph 1: the gradient is constant
This means the rate of change is constant
So the depth increases at the same rate throughout
This matches container D which has vertical sides, so depth increases uniformly
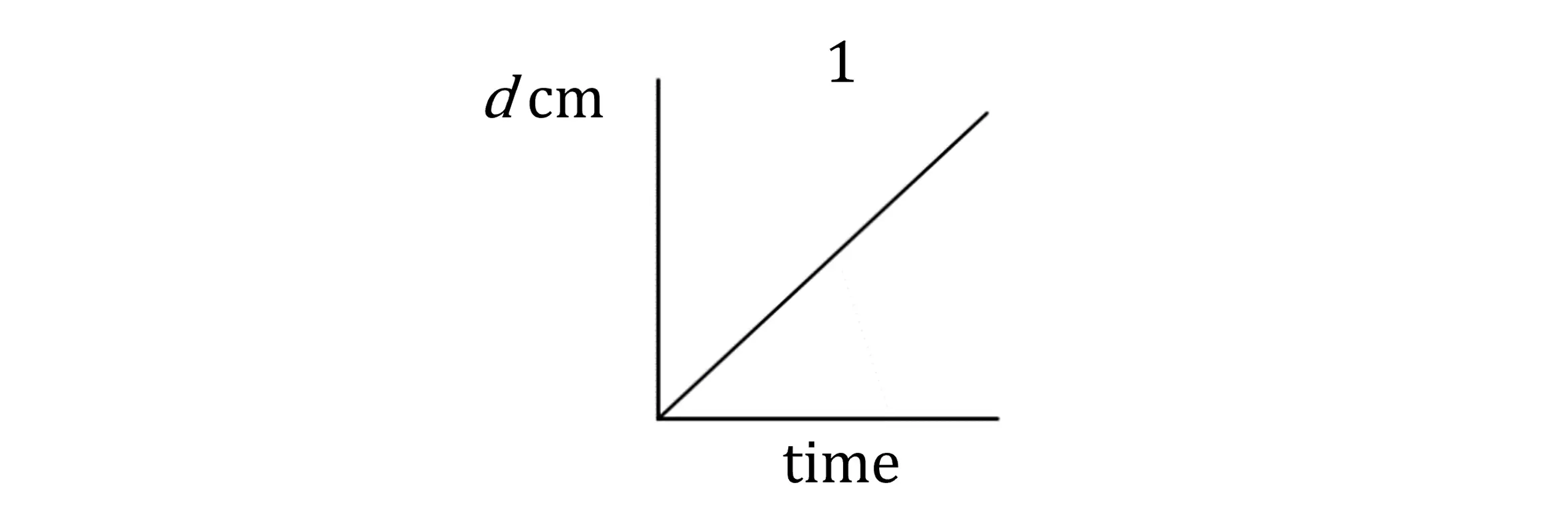
Graph 1 is container D
Considering graph 2: the gradient starts shallow and becomes steeper, meaning that the depth increases faster and faster at the end
This matches container A, which gets narrower towards the top, causing the depth to increase faster at the end
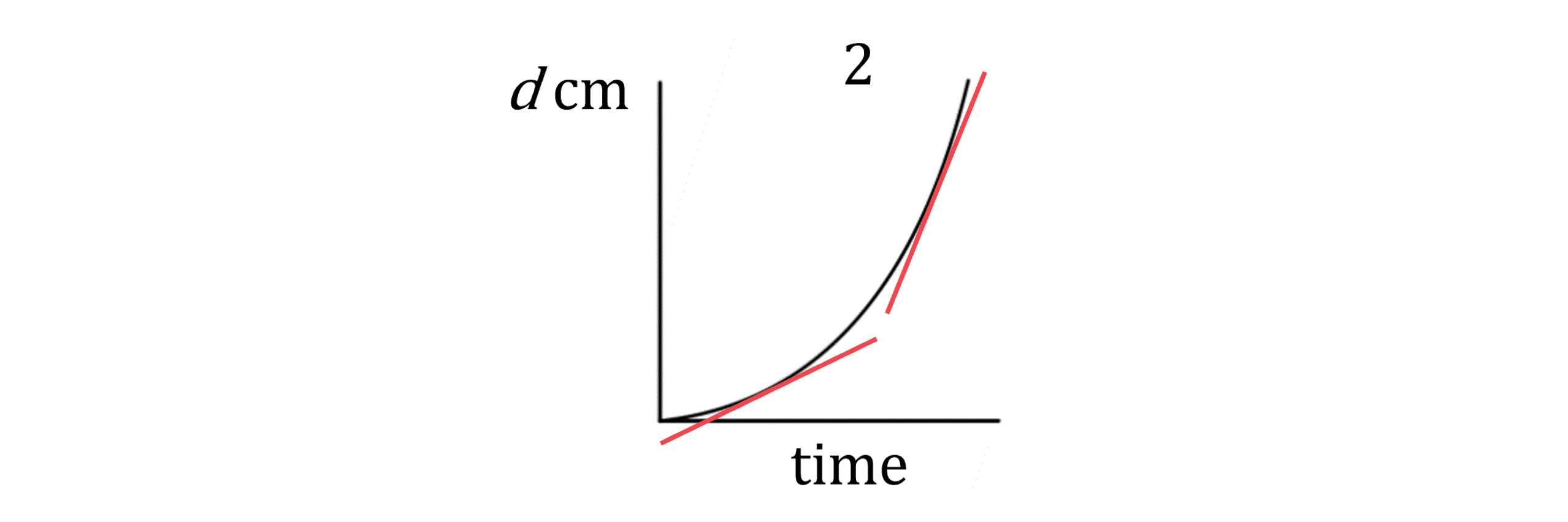
Graph 2 is container A
Considering graph 3: the gradient starts steep and becomes shallower, meaning that the depth increases at a slower and slower rate as time increases
This matches container B, which gets wider towards the top, causing the depth to increase more slowly at the end

Responses