Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Basic probability
What is probability?
-
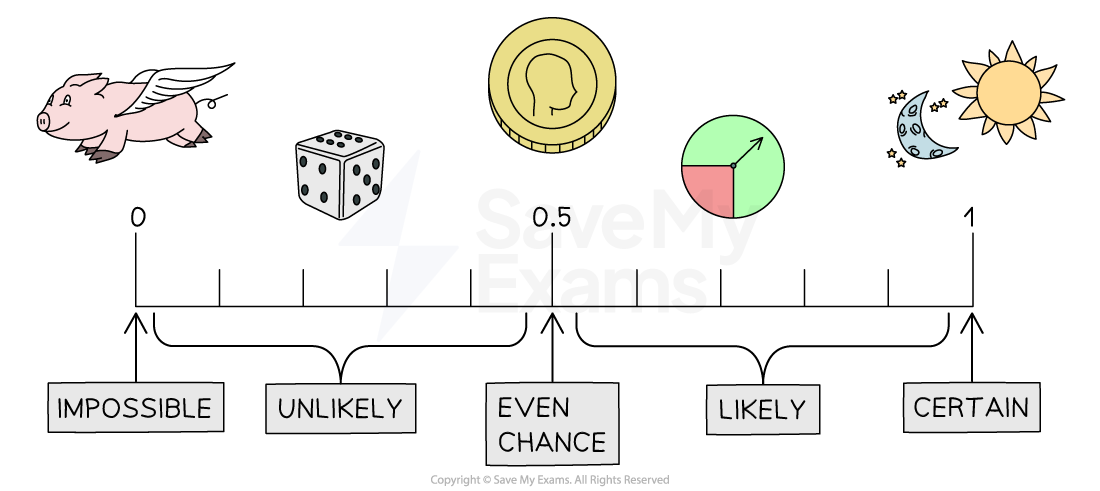
Probability describes the likelihood of something happening
-
In real-life you might use words such as impossible, unlikely and certain
-
-
In maths we use the probability scale to describe probability
-
This means giving it a number between 0 and 1
-
0 means impossible
-
Between 0 and 0.5 means unlikely
-
0.5 means even chance
-
Between 0.5 and 1 means likely
-
1 means certain
-
-
-
Probabilities can be given as fractions, decimals or percentages
What key words and terminology are used in probability?
-
An experiment is an activity that is repeated to produce a set of results
-
Results can be observed (seen) or recorded
-
Each repeat is called a trial
-
-
An outcome is a possible result of a trial
-
An event is an outcome (or a collection of outcomes)
-
For example:
-
a dice lands on a six
-
a dice lands on an even number
-
-
Events are usually given capital letters
-
n(A) is the number of possible outcomes from event A
-
A = a dice lands on an even number (2, 4 or 6)
-
n(A) = 3
-
-
-
A sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment
-
It can be represented as a list or a table
-
-
The probability of event A is written P(A)
-
An event is said to be fair if there is an equal chance of achieving each outcome
-
If there is not an equal chance, the event is biased
-
For example, a fair coin has an equal chance of landing on heads or tails
-
How do I calculate basic probabilities?
-
If all outcomes are equally likely then the probability for each outcome is the same
-
The probability for each outcome is
-
If there are 50 marbles in a bag then the probability of selecting a specific one is
-
-
-
The theoretical probability of an event can be calculated by dividing the number of outcomes of that event by the total number of outcomes
-
-
This can be calculated without actually doing the experiment
-
-
If there are 50 marbles in a bag and 20 are blue, then the probability of selecting a blue marble is
How do I find missing probabilities?
-
The probabilities of all the outcomes add up to 1
-
If you have a table of probabilities with one missing, find it by making them all add up to 1
-
-
The complement of event A is the event where A does not happen
-
This can be thought of as not A
-
P(event does not happen) = 1 – P(event does happen)
-
For example, if the probability of rain is 0.3, then the probability of not rain is 1 – 0.3 = 0.7
-
-
What are mutually exclusive events?
-
Two events are mutually exclusive if they cannot both happen at once
-
When rolling a dice, the events “getting a prime number” and “getting a 6” are mutually exclusive
-
-
If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then the probability of either A or B happening is P(A) + P(B)
-
Complementary events are mutually exclusive
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
If you are not told in the question how to leave your answer, then fractions are best for probabilities.
Worked Example
Emilia is using a spinner that has outcomes and probabilities as shown in the table.

Responses