Maths Gcse Aqa Foundation
-
Scatter-Graphs-And-Correlation Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Statistical-Diagrams Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Averages-Ranges-And-Data Aqa Foundation7 主题
-
Tree-Diagrams-And-Combined-Probability Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-Probability-Diagrams Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Transformations Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Vectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Pythagoras-And-Trigonometry Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Congruence-Similarity-And-Geometrical-Proof Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Volume-And-Surface-Area Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Circles-Arcs-And-Sectors Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Area-And-Perimeter Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Bearings-Scale-Drawing-Constructions-And-Loci Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
2D-And-3D-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Angles-In-Polygons-And-Parallel-Lines Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Symmetry-And-Shapes Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Exchange-Rates-And-Best-Buys Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Standard-And-Compound-Units Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Direct-And-Inverse-Proportion Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Ratio-Problem-Solving Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Sequences Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Solving-Inequalities Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Real-Life-Graphs Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Graphs-Of-Functions Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Linear-Graphs Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Coordinate-Geometry Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Functions Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Forming-And-Solving-Equations Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simultaneous-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Solving-Quadratic-Equations Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Linear-Equations Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Algebraic-Reasoning Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rearranging-Formulas Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Introduction Aqa Foundation10 主题
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Sample-Space-Diagrams Aqa Foundation
-
Basic-Probability Aqa Foundation
-
Sharing-In-A-Ratio Aqa Foundation
-
Equivalent-And-Simplified-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Introduction-To-Ratios Aqa Foundation
-
Collecting-Like-Terms Aqa Foundation
-
Substitution Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Vocabulary Aqa Foundation
-
Algebraic-Notation Aqa Foundation
-
Relative-And-Expected-Frequency Aqa Foundation
-
Factorising Aqa Foundation3 主题
-
Expanding-Brackets Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Algebraic-Roots-And-Indices Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Using-A-Calculator Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Exact-Values Aqa Foundation1 主题
-
Rounding-Estimation-And-Error-Intervals Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Fractions-Decimals-And-Percentages Aqa Foundation2 主题
-
Simple-And-Compound-Interest-Growth-And-Decay Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Percentages Aqa Foundation5 主题
-
Fractions Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Powers-Roots-And-Standard-Form Aqa Foundation4 主题
-
Types-Of-Number-Prime-Factors-Hcf-And-Lcm Aqa Foundation6 主题
-
Number-Operations Aqa Foundation9 主题
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
-
Related-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Multiplication-And-Division Aqa Foundation
-
Addition-And-Subtraction Aqa Foundation
-
Money-Calculations Aqa Foundation
-
Negative-Numbers Aqa Foundation
-
Place-Value Aqa Foundation
-
Order-Of-Operations-Bidmasbodmas Aqa Foundation
-
Mathematical-Operations Aqa Foundation
-
Counting-Principles Aqa Foundation
Types-Of-Graphs Aqa Foundation
Exam code:8300
Types of graphs
What graphs do I need to know?
-
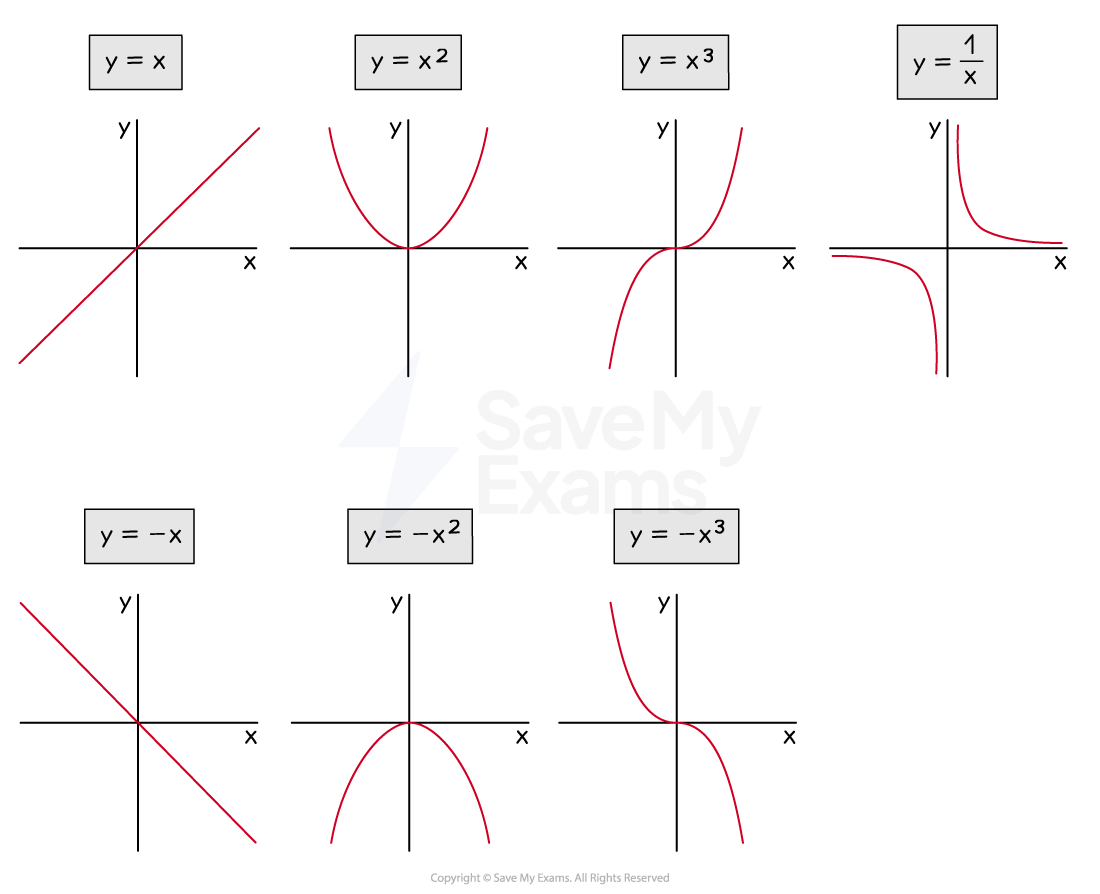
You need to be able to recognise the following lines:
-
Straight lines
-
y = mx + c
-
Such as y = 3x + 2, y = 5x – 1, …
-
Two important ones are y = x and y = –x
-
-
Horizontal lines
-
y = c
-
Such as y = 4, y = -10, …
-
-
Vertical lines
-
x = k
-
Such as x = 2, x = -1, …
-
-
-
You need to be able to recognise quadratic graphs
-
y = x2
-
y = –x2
-
y = ax2 + bx + c
-
-
You need to be able to recognise simple cubic graphs
-
y = x3
-
y = –x3
-
y = ax3 + bx2 + x + c
-
-
You also need to be able to recognise reciprocal graphs
-
, where
-
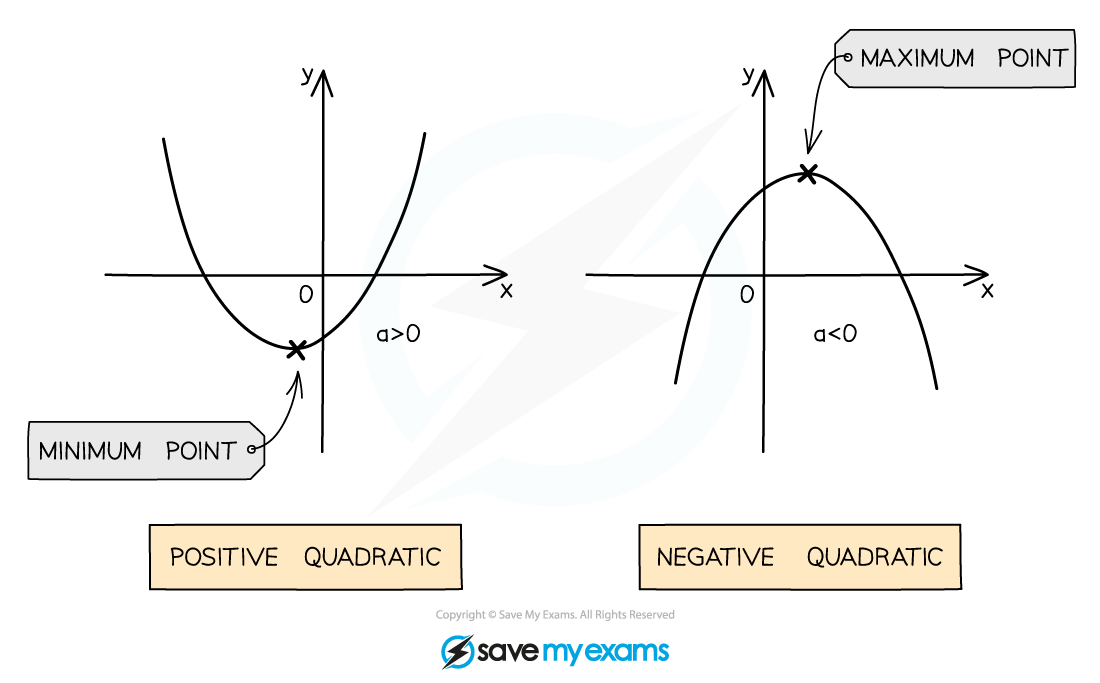
What does a quadratic graph look like?
-
The equation of a quadratic graph is y = ax2 + bx + c
-
A quadratic graph has either a u-shape or an n-shape
-
This type of shape is called a parabola
-
-
u-shapes are called positive quadratics
-
because the number in front of x2 is positive
-
For example, y = 2x2 + 3x + 4
-
-
-
n-shapes are called negative quadratics
-
because the number in front of x2 is negative
-
For example, y = -3x2 + 2x + 4
-
-
-
You can plot quadratic graphs using a table of values
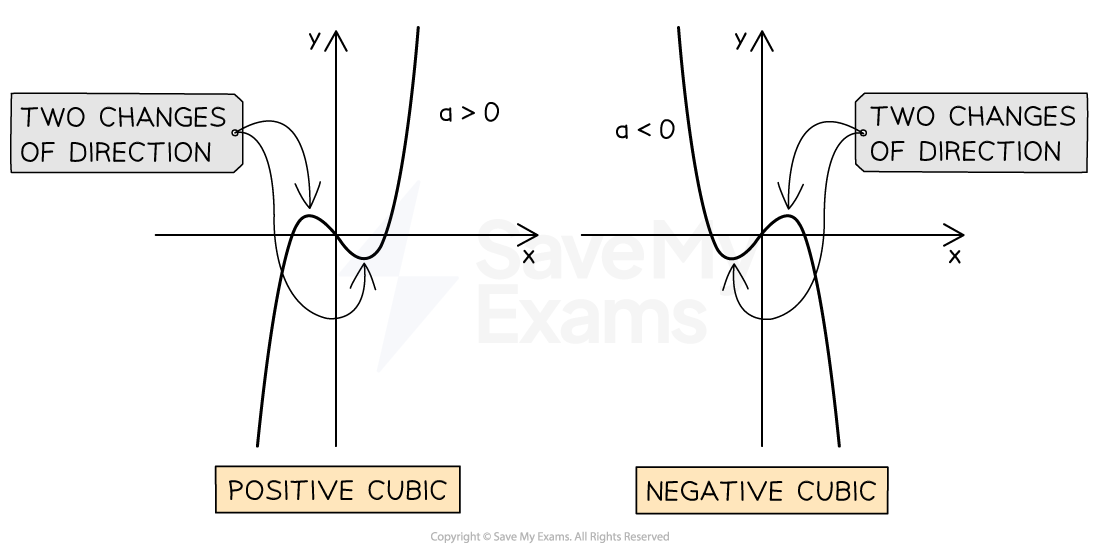
What does a cubic graph look like?
-
The equation of a cubic graph is y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d
-
A cubic graph can have two points where it changes direction (turning points)
-
A positive cubic goes uphill (from the bottom left to the top right)
-
The number in front of x3 is positive
-
For example, y = x3 – 3x2 + 2x + 1
-
-
-
A negative cubic goes downhill (from the top left to the bottom right)
-
The number in front of x3 is negative
-
For example, y = –x3 + 2x2 – x + 5
-
-
-
You can plot cubic graphs using a table of values
What does a reciprocal graph look like?
-
The equation of the basic reciprocal graph is
-
You cannot substitute in x = 0 (division by zero is not allowed)
-
<img alt=”x not equal to 0″ data-mathml='<math ><semantics><mrow><mi>x</mi><mo>≠</mo><mn>0</mn></mrow><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“language”:”en”,”fontFamily”:”Times New Roman”,”fontSize”:”18″,”autoformat”:true}</annotation></semantics></math>’ height=”22″ role=”math” src=”data:image/svg+xml;charset=utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%20xmlns%3Awrs%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wiris.com%2Fxml%2Fmathml-extension%22%20height%3D%2222%22%20width
-
-

Responses