Exam code:8291
Renewable Energy Sources
What Are Renewable Energy Sources?
-
Renewable energy comes from energy sources that will not run out and includes:
-
Biofuels (biomass including wood, bioethanol and biogas)
-
Geothermal energy
-
Hydroelectric dams
-
Tidal energy
-
Wave energy
-
Solar energy
-
Wind energy
-
-
Once in place, these renewable energy sources do not produce any greenhouse gas emissions (with the exception of biomass):
-
However, it is important to note that greenhouse gases may be emitted in the production, construction and transport of the equipment required for the above renewable energy sources
-
Renewable Energy Sources Examples
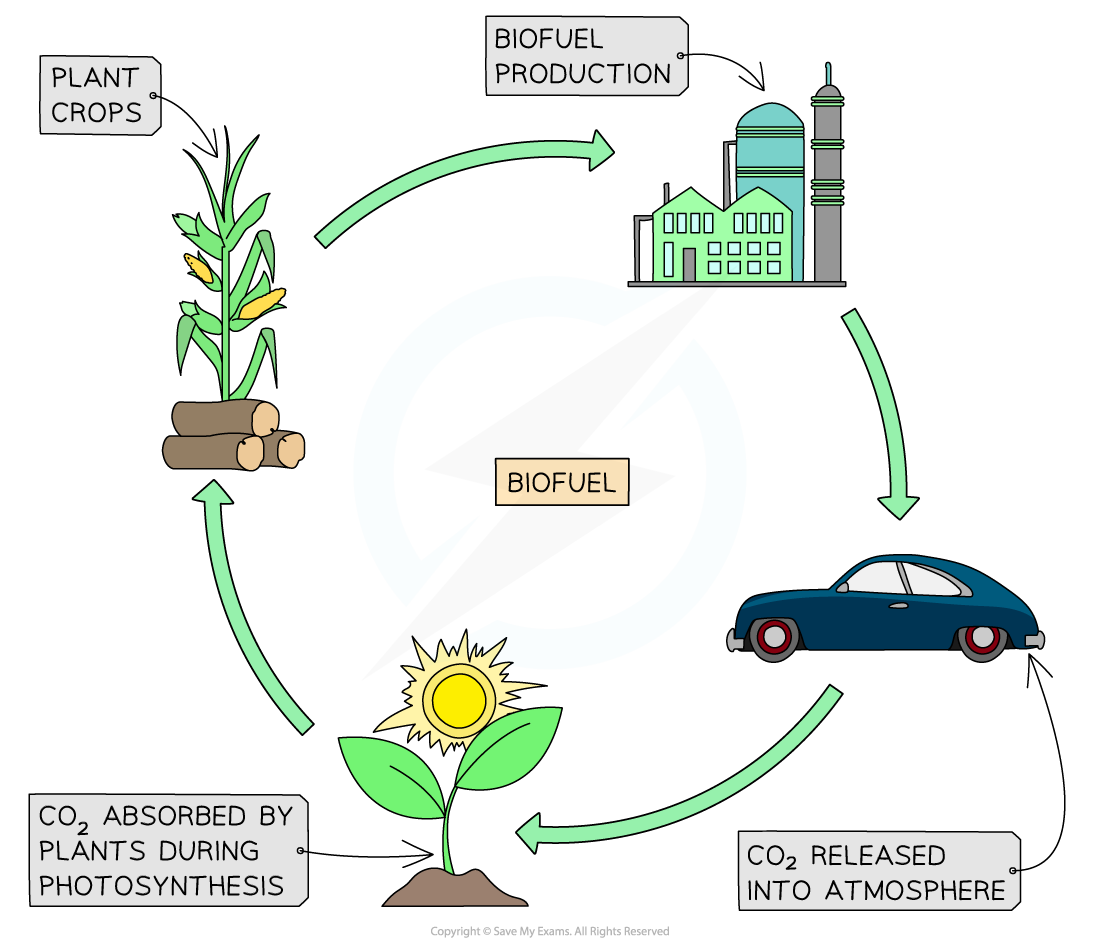
Biofuels
-
Biofuels (also known as biomass fuels) are renewable fuels derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, that can be used as an alternative to fossil fuels:
-
However, they have only half the energy density of fossil fuels
-
-
The three main biofuels are:
-
Biodiesel – made by refining renewable fats and oils (e.g. vegetable oils, animal fats or recycled cooking oil)
-
Bioethanol – made by fermentation (of crops rich in sugars or starches, such as corn or sugarcane)
-
Biogas – released when organic waste products decompose
-
Advantages
-
Biofuel is a renewable resource – uses waste or bioproducts that can be regrown
-
Some vehicles can be powered by biofuel rather than using fossil fuels
-
Biofuel is considered to be carbon neutral
-
No sulfur dioxide is produced
Disadvantages
-
Crops of biofuel producing plants must be grown, which takes time
-
Growing the crops takes a lot of land, and takes resources needed for food production
-
Burning biofuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (however, it is considered carbon neutral because plants take in carbon dioxide when they photosynthesise)
Geothermal Energy
-
Geothermal energy is caused by the heat that is generated from within the Earth:
-
The Earth’s interior is extremely hot, partly due to radioactive elements deep in the Earth that release energy as they decay
-
-
This geothermal energy heats up rocks in the Earth’s crust, sometimes to an extremely high temperature:
-
Water can be poured into shafts below the Earth’s surface
-
The water is heated and returned via another shaft as steam or hot water
-
Steam can be used to turn a turbine and generate electricity, and the hot water can also be used to heat homes
-
Advantages
-
Renewable resource
-
Reliable source of energy
-
Geothermal power stations are usually small compared to nuclear or fossil fuel power stations
Disadvantages
-
Few suitable locations on Earth, so only viable for small scale electricity production in many countries
-
Can result in the release of greenhouse gases from underground
-
Expensive to build and maintain

Hydroelectric Dams
-
When water is stored above ground level it has gravitational potential energy
-
This energy can be transferred to kinetic energy if the water is allowed to flow down the slope
-
Flowing water turns the turbine to generate electricity
Advantages
-
Can respond to demand quickly so is reliable and available
-
Can generate large-scale amounts of electricity in a short period of time
-
Often in sparsely populated areas
Disadvantages
-
Expensive to build and maintain
-
Creating reservoirs sometimes results in the need to flood valleys, which destroys habitats, towns and villages
-
The pumping systems (used if water needs to be pumped up to the reservoir) often rely on fossil fuels, releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases
-
Dam traps sediment which can affect ecosystems downstream
-
Visual pollution
-
Can prevent fish movement and migration upstream

Wave & Tidal Energy
-
The rise and fall of waves or the tide can be used to turn a turbine and generate electricity
Advantages
-
No pollution
-
Reliable and can produce a large amount of electricity at short notice
-
Renewable energy resource
-
Small systems are being developed to provide electricity for small islands
Disadvantages
-
Expensive to build and maintain
-
Damages fragile habitats
-
Very few suitable locations
-
The technology is not advanced enough for large-scale electricity production


Solar Energy
-
The energy from the Sun that falls on the Earth is transferred by radiation:
-
Mostly visible light and infrared radiation
-
-
The amount of energy transferred from the Sun to the Earth each hour is roughly equal to the energy use of the world for one year
-
Therefore, scientists are working hard to find methods of harnessing this energy:
-
Solar energy has a low energy density, which means large collecting devices are required
-
Collecting solar energy is expensive (due to the equipment required) and inefficient
-
Solar PV panels
-
Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels transfer energy from sunlight electrically producing a current and therefore generating electrical power:
-
Solar cells, sometimes called photovoltaic cells, are made of semiconducting materials
-
A number of photovoltaic cells or panels connected together can supply electricity to homes, small-scale businesses, communication devices and satellites
-
Energy generated can be stored in batteries for later use
-
Advantages
-
Solar energy is a renewable resource
-
In many places on Earth sunlight is a reliable energy resource (this means that the sun shines most of the time)
-
Solar farms produce no greenhouse gases or pollution
-
Solar energy can be generated in remote places where they don’t have electricity (e.g. to power solar street signs in rural areas)
-
Can be small- or large-scale
-
Can be incorporated into building design
-
Technology is improving and reducing the cost
Disadvantages
-
Solar farms need to be large-scale to produce large amounts of electricity, which is expensive to set up
-
Uses large areas of land
-
People often don’t like the appearance of large solar farms; this is known as visual pollution
-
In many places on Earth sunlight is not a reliable energy resource (there are not enough sunshine-hours to justify the set-up costs)

Wind Energy
-
Wind energy is a renewable form of energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity
-
It involves the use of wind turbines, which have large blades that spin when the wind blows
-
The rotating blades transfer kinetic energy to a generator, which converts it into electrical energy
Advantages
-
Wind is an abundant resource that will never run out, making wind energy a sustainable and renewable source of power
-
Wind energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation, helping to reduce the negative impact on climate change and air quality
-
Wind energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels and foreign energy sources, promoting energy independence and security
-
The wind energy industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, operation and maintenance of wind turbines
-
Can be small- or large-scale
-
Can be on land or offshore
-
Cheap to run
Disadvantages
-
Wind is not constant, and the availability of wind energy fluctuates
-
Electricity generation from wind turbines depends on wind speed and consistency
-
Wind turbines can be visually intrusive, especially when installed in large numbers
-
Some people may find the noise generated by wind turbines to be disruptive
-
Wind farms require large areas of land, which can have an impact on agricultural or natural landscapes
-
Birds and bats may occasionally collide with wind turbines, causing some

Responses