Further Maths: Core Pure -Edexcel-A Level
-
complex-numbers-and-argand-diagrams6 主题
-
exponential-form-and-de-moivres-theorem4 主题
-
properties-of-matrices3 主题
-
transformations-using-matrices3 主题
-
roots-of-polynomials2 主题
-
series2 主题
-
maclaurin-series1 主题
-
hyperbolic-functions4 主题
-
volumes-of-revolution2 主题
-
methods-in-calculus5 主题
-
vector-lines4 主题
-
vector-planes4 主题
-
polar-coordinates2 主题
-
first-order-differential-equations3 主题
-
second-order-differential-equations2 主题
-
simple-harmonic-motion2 主题
-
proof-by-induction2 主题
intro-to-differential-equations
General solutions
What is a differential equation?

-
Any equation, involving a derivative term, is a differential equation
-
Equations involving only first derivative terms are called first order differential equations
-
Equations involving second derivative terms are called second order differential equations
What is a general solution?

-
Integration will be involved in solving the differential equation
-
ie working back to “y = f(x)”
-
-
A constant of integration, c is produced
-
This gives an infinite number of solutions to the differential equation, each of the form y = g(x) + c (ie y = f(x) where f(x) = g(x) + c)
-
… and the solution y= g(x) + c is called the general solutionThese are often called a family of solutions …
Worked Example
Find the general solution to the differential equation .

Particular solutions
What is a particular solution?
-
Ensure you are familiar with General Solutions first
-
With extra information, the constant of integration, c, can be found
-
This means the particular solution (from the family of solutions) can be found
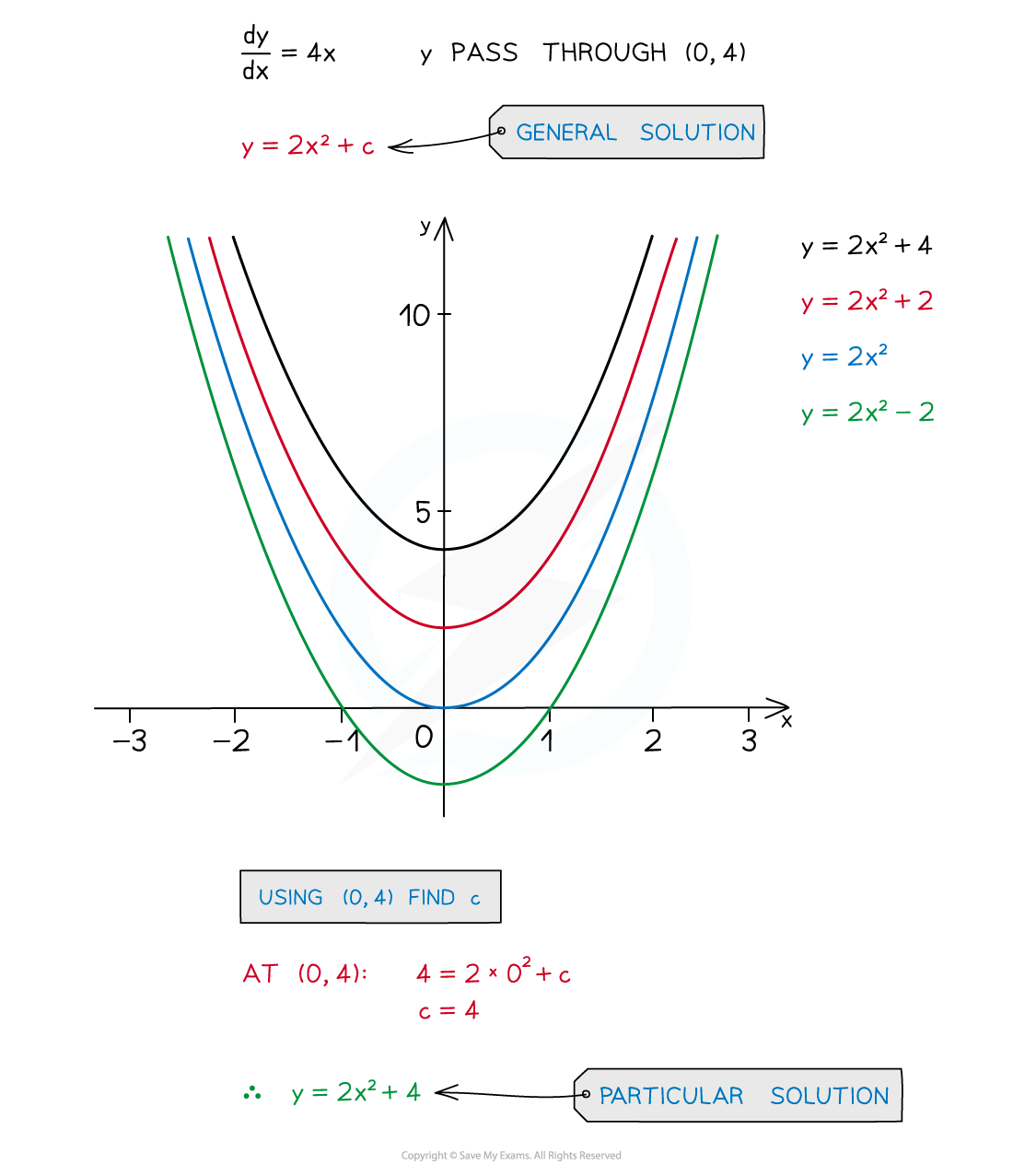
What is a boundary condition/initial condition?
A boundary condition is a piece of extra information that lets you find the particular solution
-
For example knowing y = 4 when x = 0 in the preceding example
-
In a model this could be a particle coming to rest after a certain time, ie v = 0 at time t
-
Differential equations are used in modelling, experiments and real-life situations
-
A boundary condition is often called an initial condition when it gives the situation at the start of the model or experiment
-
This is often linked to time, so t = 0
-
It is possible to have two boundary conditions
-
eg a particle initially at rest has velocity, v = 0 and acceleration, a = 0 at time, t = 0
-
for a second order differential equation you need two boundary conditions to find the particular solution
-
Worked Example
The velocity of a particle, initially at rest, is modelled by the differential equation , where <img alt=”v” data-mathml='<math ><semantics><mi>v</mi><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“language”:”en”,”fontFamily”:”T

Responses