Economics-A-level-Aqa
-
1-economic-methodology-and-the-economic-problem4 主题
-
2-individual-economic-decision-making4 主题
-
3-price-determination-in-competitive-markets10 主题
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
protectionist-policies-quotas-and-export-subsidies
-
protectionist-policies-tariffs
-
protectionist-policies-an-introduction
-
the-benefits-and-costs-of-trade
-
international-trade
-
globalisation
-
types-of-supply-side-policies
-
an-introduction-to-supply-side-policies
-
fiscal-policy-budget-balances-and-national-debt
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
4-production-costs-and-revenue11 主题
-
Production & Productivity
-
fiscal-policy-types-of-public-expenditure-and-taxation
-
fiscal-policy-an-introduction
-
regulating-the-financial-system
-
monetary-policy-transmission-mechanisms
-
central-banks-and-monetary-policy
-
commercial-and-investment-banks
-
financial-assets
-
financial-markets
-
conflicts-between-the-macroeconomic-objectives
-
price-level-global-influences
-
Production & Productivity
-
5-perfect-and-imperfectly-competitive-markets-and-monopolies12 主题
-
price-level-deflation
-
price-level-inflation
-
employment-and-unemployment
-
the-economic-cycle
-
the-impact-of-economic-growth
-
economic-growth
-
the-multiplier-and-basic-accelerator-process
-
macroeconomic-equilibrium
-
long-run-aggregate-supply-lras
-
short-run-aggregate-supply-sras
-
aggregate-demand-ad
-
injections-and-withdrawals-into-the-circular-flow
-
price-level-deflation
-
6-the-labour-market7 主题
-
7-income-and-wealth-distribution4 主题
-
8-the-market-mechanism-market-failure-and-government-intervention16 主题
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
government-intervention-indirect-taxation-and-subsidies
-
government-intervention-an-introduction
-
market-failure-market-imperfections
-
market-failure-merit-and-demerit-goods
-
market-failure-tragedy-of-the-commons
-
market-failure-positive-externalities
-
market-failure-negative-externalities
-
market-failure-public-private-and-quasi-public-goods
-
an-introduction-to-market-failure
-
the-market-price-mechanism
-
government-policies-to-reduce-poverty-and-inequity
-
the-problem-of-poverty
-
the-lorenz-curve-and-gini-coefficient
-
income-and-wealth-distribution
-
discrimination-in-the-labour-market
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
9-measuring-macroeconomic-performance5 主题
-
10-how-the-macroeconomy-works6 主题
-
11-economic-performance8 主题
-
12-financial-markets-and-monetary-policy6 主题
-
13-fiscal-and-supply-side-policies5 主题
-
14-the-international-economy16 主题
-
using-index-numbers
-
analysing-changes-to-market-equilibrium
-
the-determination-of-market-equilibrium
-
supply-curves-real-world-analysis
-
supply-curves
-
demand-curves-real-world-analysis
-
demand-curves
-
using-behavioural-economics
-
behavioural-economics
-
imperfect-information
-
consumer-behaviour
-
production-possibility-diagrams
-
scarcity-choice-and-the-allocation-of-resources
-
economic-resources
-
economic-activity
-
economic-methodology
-
using-index-numbers
the-problem-of-poverty
The Difference Between Relative & Absolute Poverty
-
Absolute poverty is a situation where individuals cannot afford to acquire the basic necessities for a healthy and safe existence
-
These necessities include shelter, water, nutrition, clothing and healthcare
-
In 2022, the World Bank defined absolute poverty as anyone who was living on less than $1.90 a day (the so called international poverty line)
-
Absolute poverty is more prevalent in developing countries than in developed ones
-
-
Relative poverty is a situation where household income is a certain percentage less than the median household income in the economy
-
Poverty in a household is considered relative to income levels in other households
-
Households that are living with less than 50% of the median household income are considered to be in relative poverty
-
Relative poverty is the main form of poverty that occurs in developed countries
-
Causes & Effects of Poverty
-
There are many causes of poverty. However, poor countries have several common characteristics, which can be summarised in a poverty cycle
Diagram: Poverty Cycle Diagram
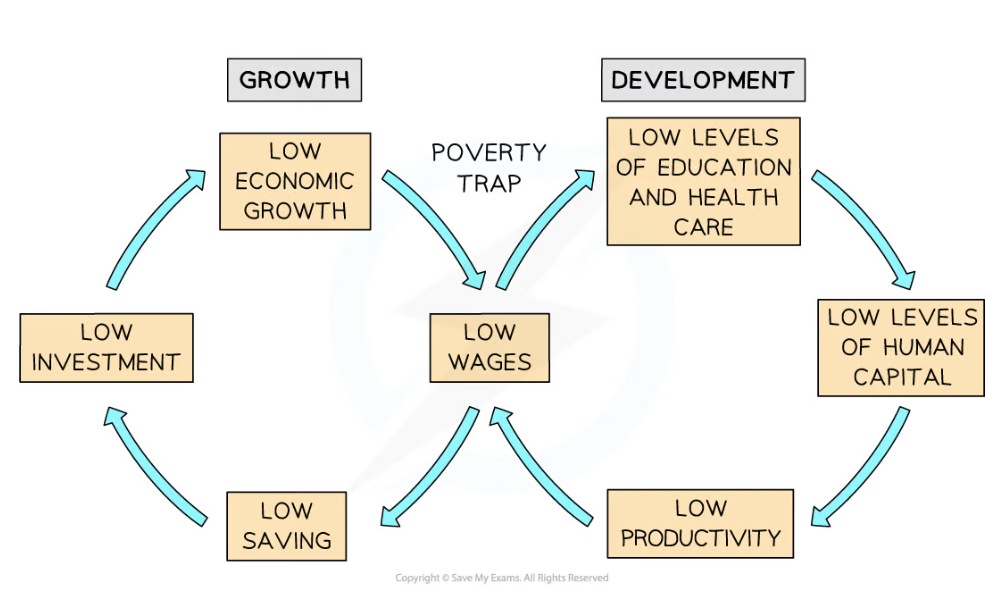
-
Low wages represent the intersection of economic growth and human development and are the major cause of poverty
-
Low wages are usually the result of unemployment, informal employment, a lack of skills, or a primary sector based economy
-
-
Education and healthcare cost money and with lower wage levels, these are not accessible, resulting in poor human capital
-
People find it harder to stay well or recover from illness, resulting in lower productivity and shorter life expectancy
-
-
Low productivity results in low wages, and the cycle continues
-
Populations with a large number of dependents (old people and children) for each working household tend to experience higher levels of poverty
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to know the poverty cycle diagram for your exams. However, it is an incredibly useful tool to understand and explain the causes of poverty.

Responses