Economics-A-level-Aqa
-
1-economic-methodology-and-the-economic-problem4 主题
-
2-individual-economic-decision-making4 主题
-
3-price-determination-in-competitive-markets10 主题
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
protectionist-policies-quotas-and-export-subsidies
-
protectionist-policies-tariffs
-
protectionist-policies-an-introduction
-
the-benefits-and-costs-of-trade
-
international-trade
-
globalisation
-
types-of-supply-side-policies
-
an-introduction-to-supply-side-policies
-
fiscal-policy-budget-balances-and-national-debt
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
4-production-costs-and-revenue11 主题
-
Production & Productivity
-
fiscal-policy-types-of-public-expenditure-and-taxation
-
fiscal-policy-an-introduction
-
regulating-the-financial-system
-
monetary-policy-transmission-mechanisms
-
central-banks-and-monetary-policy
-
commercial-and-investment-banks
-
financial-assets
-
financial-markets
-
conflicts-between-the-macroeconomic-objectives
-
price-level-global-influences
-
Production & Productivity
-
5-perfect-and-imperfectly-competitive-markets-and-monopolies12 主题
-
price-level-deflation
-
price-level-inflation
-
employment-and-unemployment
-
the-economic-cycle
-
the-impact-of-economic-growth
-
economic-growth
-
the-multiplier-and-basic-accelerator-process
-
macroeconomic-equilibrium
-
long-run-aggregate-supply-lras
-
short-run-aggregate-supply-sras
-
aggregate-demand-ad
-
injections-and-withdrawals-into-the-circular-flow
-
price-level-deflation
-
6-the-labour-market7 主题
-
7-income-and-wealth-distribution4 主题
-
8-the-market-mechanism-market-failure-and-government-intervention16 主题
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
government-intervention-indirect-taxation-and-subsidies
-
government-intervention-an-introduction
-
market-failure-market-imperfections
-
market-failure-merit-and-demerit-goods
-
market-failure-tragedy-of-the-commons
-
market-failure-positive-externalities
-
market-failure-negative-externalities
-
market-failure-public-private-and-quasi-public-goods
-
an-introduction-to-market-failure
-
the-market-price-mechanism
-
government-policies-to-reduce-poverty-and-inequity
-
the-problem-of-poverty
-
the-lorenz-curve-and-gini-coefficient
-
income-and-wealth-distribution
-
discrimination-in-the-labour-market
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
9-measuring-macroeconomic-performance5 主题
-
10-how-the-macroeconomy-works6 主题
-
11-economic-performance8 主题
-
12-financial-markets-and-monetary-policy6 主题
-
13-fiscal-and-supply-side-policies5 主题
-
14-the-international-economy16 主题
-
using-index-numbers
-
analysing-changes-to-market-equilibrium
-
the-determination-of-market-equilibrium
-
supply-curves-real-world-analysis
-
supply-curves
-
demand-curves-real-world-analysis
-
demand-curves
-
using-behavioural-economics
-
behavioural-economics
-
imperfect-information
-
consumer-behaviour
-
production-possibility-diagrams
-
scarcity-choice-and-the-allocation-of-resources
-
economic-resources
-
economic-activity
-
economic-methodology
-
using-index-numbers
government-policies-to-reduce-poverty-and-inequity
Policies to Alleviate Poverty & Address Income Inequity
-
The poverty cycle diagram (below) was introduced in the previous subtopic and helps to explain the causes of poverty
-
Any policy that helps to break the poverty cycle at any point will help to improve the standards of living within a country
-
Policies used to alleviate poverty include promoting economic growth, improving education, providing more generous state benefits, progressive taxation, and the establishment/increase of a national minimum wage
Diagram: Poverty Trap
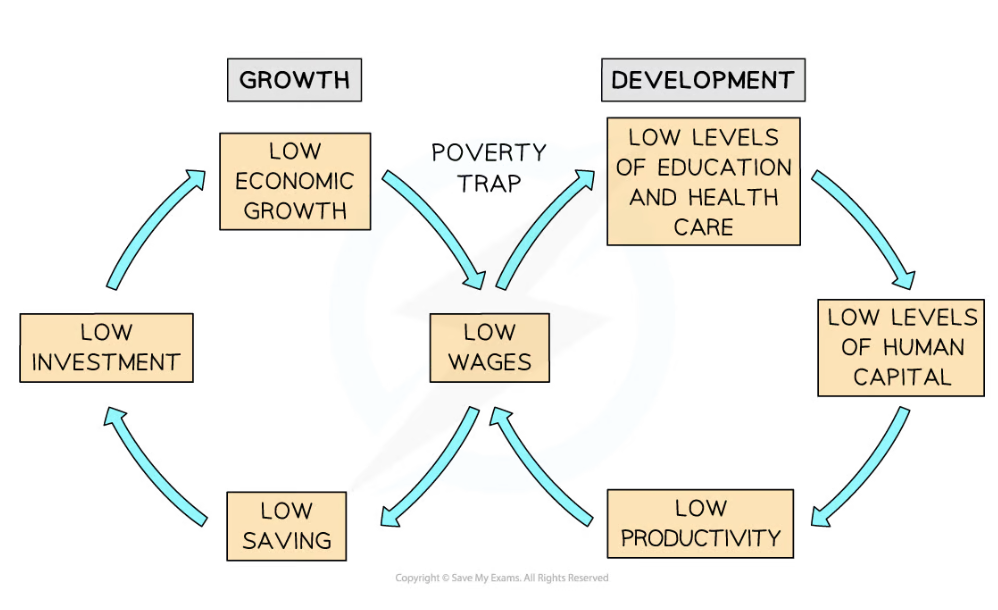
How Different Policies Alleviate Poverty
|
Policy |
Explanation |
Impact on Poverty Cycle |
|---|---|---|
|
Reducing the use of protectionist policies |
|
Higher growth → higher wages → better education/healthcare → better human capital → better productivity → higher income |
|
Education |
|
Higher education/skill levels → higher human capital → increased productivity → higher output → higher income |
|
State benefits |
|
More benefits → higher wages → better education/healthcare → better human capital → better productivity → higher wages |
|
Progressive taxation |
|
Higher redistribution → better education/healthcare → better human capital → better productivity → higher income |
|
Minimum wage |
|
Higher wages → better education/healthcare → better human capital → better productivity → higher wages |
Economic Consequences of Policies
-
Free market economists argue that any government intervention in the free market creates inefficiencies and reduces incentives
-
Reducing poverty and inequity can have both positive and negative economic consequence on:
-
Employment
-
Economic growth
-
Government finances
-
Economic Consequences of Policies
|
Consequence |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Employment |
|
|
Economic growth |
|
|
Government finances |
|

Responses