Economics-A-level-Aqa
-
1-economic-methodology-and-the-economic-problem4 主题
-
2-individual-economic-decision-making4 主题
-
3-price-determination-in-competitive-markets10 主题
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
protectionist-policies-quotas-and-export-subsidies
-
protectionist-policies-tariffs
-
protectionist-policies-an-introduction
-
the-benefits-and-costs-of-trade
-
international-trade
-
globalisation
-
types-of-supply-side-policies
-
an-introduction-to-supply-side-policies
-
fiscal-policy-budget-balances-and-national-debt
-
types-of-economic-integration
-
4-production-costs-and-revenue11 主题
-
Production & Productivity
-
fiscal-policy-types-of-public-expenditure-and-taxation
-
fiscal-policy-an-introduction
-
regulating-the-financial-system
-
monetary-policy-transmission-mechanisms
-
central-banks-and-monetary-policy
-
commercial-and-investment-banks
-
financial-assets
-
financial-markets
-
conflicts-between-the-macroeconomic-objectives
-
price-level-global-influences
-
Production & Productivity
-
5-perfect-and-imperfectly-competitive-markets-and-monopolies12 主题
-
price-level-deflation
-
price-level-inflation
-
employment-and-unemployment
-
the-economic-cycle
-
the-impact-of-economic-growth
-
economic-growth
-
the-multiplier-and-basic-accelerator-process
-
macroeconomic-equilibrium
-
long-run-aggregate-supply-lras
-
short-run-aggregate-supply-sras
-
aggregate-demand-ad
-
injections-and-withdrawals-into-the-circular-flow
-
price-level-deflation
-
6-the-labour-market7 主题
-
7-income-and-wealth-distribution4 主题
-
8-the-market-mechanism-market-failure-and-government-intervention16 主题
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
government-intervention-indirect-taxation-and-subsidies
-
government-intervention-an-introduction
-
market-failure-market-imperfections
-
market-failure-merit-and-demerit-goods
-
market-failure-tragedy-of-the-commons
-
market-failure-positive-externalities
-
market-failure-negative-externalities
-
market-failure-public-private-and-quasi-public-goods
-
an-introduction-to-market-failure
-
the-market-price-mechanism
-
government-policies-to-reduce-poverty-and-inequity
-
the-problem-of-poverty
-
the-lorenz-curve-and-gini-coefficient
-
income-and-wealth-distribution
-
discrimination-in-the-labour-market
-
government-intervention-price-controls
-
9-measuring-macroeconomic-performance5 主题
-
10-how-the-macroeconomy-works6 主题
-
11-economic-performance8 主题
-
12-financial-markets-and-monetary-policy6 主题
-
13-fiscal-and-supply-side-policies5 主题
-
14-the-international-economy16 主题
-
using-index-numbers
-
analysing-changes-to-market-equilibrium
-
the-determination-of-market-equilibrium
-
supply-curves-real-world-analysis
-
supply-curves
-
demand-curves-real-world-analysis
-
demand-curves
-
using-behavioural-economics
-
behavioural-economics
-
imperfect-information
-
consumer-behaviour
-
production-possibility-diagrams
-
scarcity-choice-and-the-allocation-of-resources
-
economic-resources
-
economic-activity
-
economic-methodology
-
using-index-numbers
price-level-deflation
The Consequences of Deflation
-
Deflation occurs when there is a fall in the average price level of goods/services in an economy, as measured by the consumer price index (CPI)
-
Deflation only occurs when the percentage change in prices falls below zero %
-
-
Deflation can be caused by either demand-side or supply-side factors
-
The two different causes of deflation have very different consequences for the economy
-
1. Demand-side deflation (bad deflation)
-
Demand-side deflation is caused by a fall in total (aggregate) demand in the economy
-
Aggregate demand is the sum of all expenditures in the economy as measured by the real gross domestic product (rGDP)
-
rGDP = Consumption (C) + Investment (I) + Government spending (G) + Net Exports (X-M)
-
-
If any of the four components of rGDP decrease, there will possibly be a decrease in aggregate demand in the economy, leading to a decrease in the general price level
-
Demand-side deflation has occurred
-
Diagram: Demand Side Deflation

Diagram analysis
-
The initial macroeconomic equilibrium is at AP Y
-
Any factor which causes a reduction in one or more of the determinants of real GDP may cause the AD curve to shift left from AD1 → AD2
-
This shift causes a fall in average price levels from AP to AP1
-
The new macroeconomic equilibrium is now at AP1 Y1
-
Demand-side deflation has occurred
The Consequences of Demand-side Deflation
|
Government Challenges |
Consumers Lose Confidence |
Debt |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Firms Lose Confidence |
Bankruptcies |
Export |
|
|
|
2. Supply-side Deflation
-
Supply-side deflation is caused by increases in the productive capacity of the economy
-
This is brought about by any increase in the quantity/quality of the factors of production
-
It effectively creates a condition of excess supply in the economy
-
Average price levels fall
-
National output (rGDP) increases
-
Diagram: Supply Side Deflation
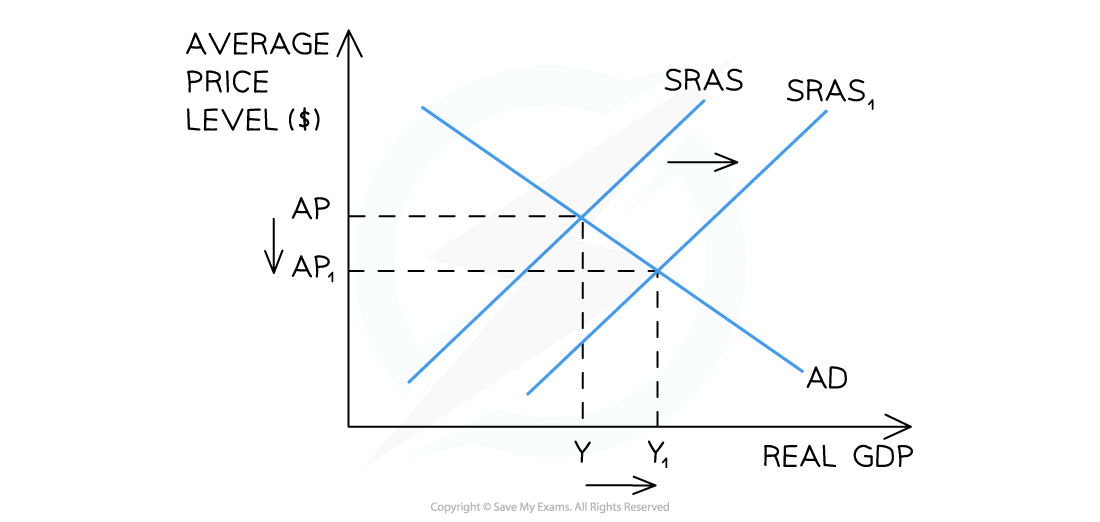
Diagram analysis
-
The initial macroeconomic equilibrium is at AP Y
-
Any factor which causes an increase in the SRAS will result in the SRAS curve shifting right from SRAS → SRAS1
-
This shift causes a fall in average price levels from AP → AP1
-
The new macroeconomic equilibrium is now at AP1 Y1
-
Supply-side deflation has occurred
The Consequences of Supply-side Deflation
|
Unemployment |
Consumers Gain Confidence |
Debt |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Firms Gain Confidence |
Exports |
|
|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Understanding the cause of deflation is vital to analysing the consequences of it.
Falling prices caused by a recession are not good for an economy. In this scenario, national output is falling, which means that fewer workers will be required to produce goods and services, so unemployment will increase.
Falling prices caused by an increase in supply are good for an economy. In this scenario, national output is rising, which means that more workers will be required to produce goods and services, so unemployment will decrease.

Responses