Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
translation-process
Interpreter execution
What is an interpreter?
-
An interpreter is a type of translator that executes high-level code line by line
-
It does not convert the entire program into a separate machine code file
How does it work?
-
The source code is read, analysed, and executed one line at a time
-
No complete machine code file is produced, only immediate execution happens
-
If there is an error in a line, execution stops, and the error is reported immediately
|
Feature |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
No output file |
It does not generate a standalone |
|
Immediate execution |
Runs the code as it is interpreted |
|
Slower execution |
Each line is translated every time the program runs |
|
Useful for development |
Good for testing and debugging during coding |
|
Stops on first error |
Detects and reports errors as they occur |
Example use cases
-
Used in educational tools, like Python shells or BASIC interpreters
-
Helpful for rapid prototyping or when frequent changes are made
Compilation stages
What is compilation?
-
Compilation is a process that translates a program written in a high-level programming language into machine code
-
Only machine code can be executed by a computer
-
There are four stages involved in this process:
-
Lexical Analysis
-
Syntax Analysis
-
Code Generation
-
Optimisation
-
Lexical analysis
-
In A Level Computer Science, lexical analysis means studying the words or vocabulary of a language
-
This stage involves identifying lexical ‘tokens’ in the code
-
Tokens represent small meaningful units in the programming language, such as:
-
Keywords
-
var, const, function, for, while, if
-
-
Identifiers
-
Variable names, function names
-
-
Operators
-
‘+’, ‘++’, ‘-‘, ‘*’
-
-
Separators
-
‘,’ ‘;’, ‘{‘, ‘}’, ‘(‘, ‘)’
-
-
-
During this stage, unnecessary elements like comments and whitespace are ignored
-
For example, if the following code is being compiled:
var x = function(x,y) {
if(x>2) {
return x*y;
}
return x+y;}
-
The result of lexical analysis is a token table
|
|
Token |
Type |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
var |
Keyword |
|
2 |
x |
Identifier |
|
3 |
= |
Operator |
|
4 |
function |
Keyword |
|
5 |
( |
Separator |
|
6 |
x |
Identifier |
|
7 |
, |
Separators |
|
8 |
y |
Identifier |
|
9 |
) |
Separator |
|
10 |
{ |
Separator |
|
11 |
return |
Keyword |
|
12 |
x |
Identifier |
|
13 |
* |
Operator |
|
14 |
y |
Identifier |
|
15 |
; |
Separator |
|
16 |
} |
Separator |
Syntax analysis
-
Now that tokens have been identified, syntax analysis makes sure they all adhere to the syntax rules of the programming language
-
A symbol, e.g. ‘$’ could be a valid token but not a valid character according to particular programming languages
-
The dollar symbol would be flagged as breaking the syntax rules
-
Other syntax errors programmers commonly make include mismatched parentheses or missing semicolons
-
If the code passes the syntax analysis, the compiler can create an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)
-
An AST is a graph-based representation of the code being compiled
-
An AST is an efficient way to represent the code for the next step
Example abstract syntax tree
-
For the same code as above, the following abstract syntax tree can be created
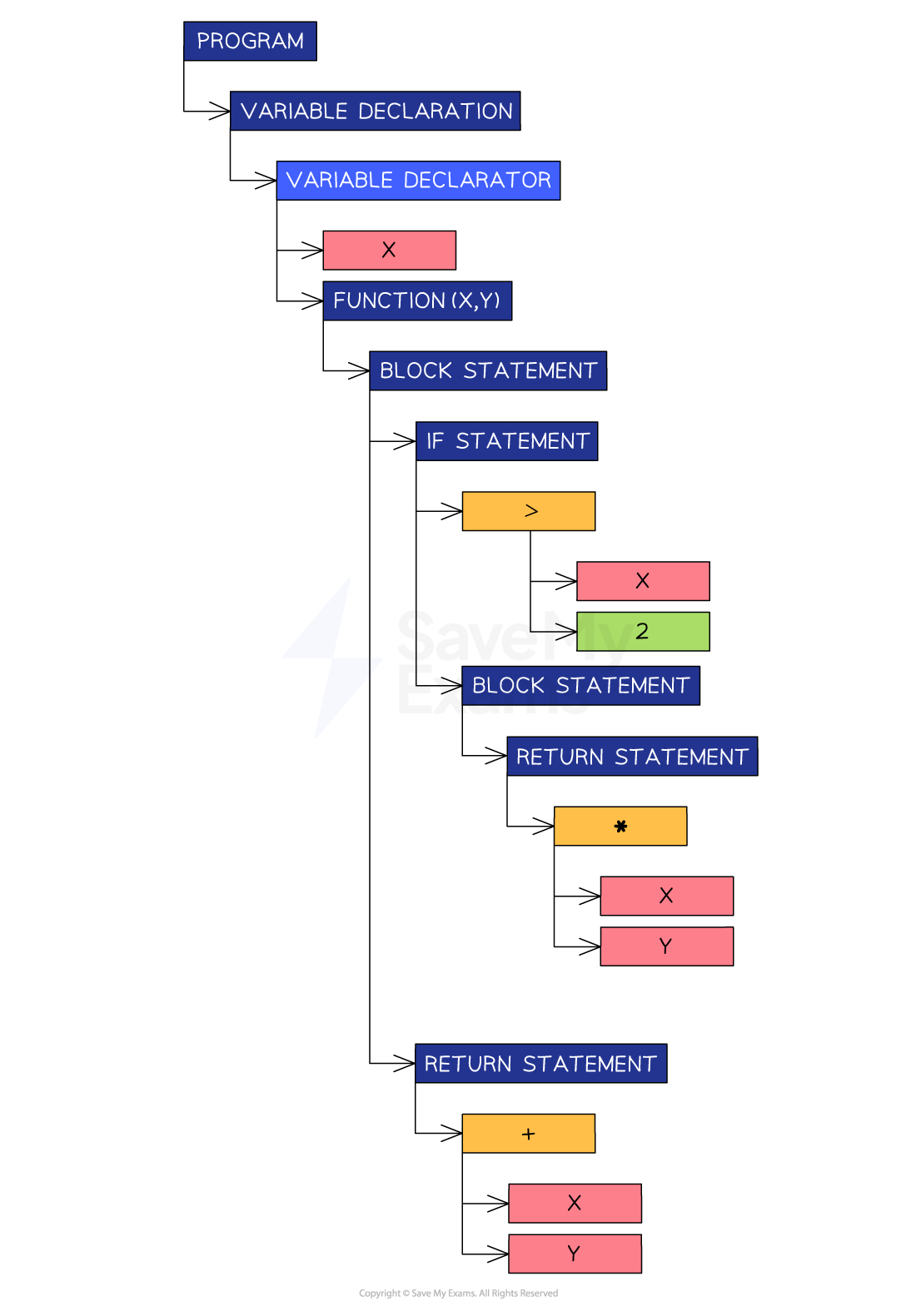
Abstract syntax tree
Code generation
-
This step takes the AST and traverses it to generate object code that can be executed by the computer
Optimisation
-
This step modifies the code to make it more efficient without changing its functionality
-
This is important to attempt because it reduces the memory required to run the code, which leads to faster execution
-
A common optimisation action is removing duplicate code
-
If an ‘add’ function is written twice in the source code, a sophisticated compiler will notice this and include it only once in the object code

Responses