Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
inheritance-oop
Inheritance (OOP)
What is inheritance?
-
Inheritance is a key concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows a class to inherit the properties and behaviours (methods and attributes) of another class
-
Inheritance promotes code reuse by allowing derived classes to inherit and utilise the existing code from the base class. This avoids duplicating code and promotes better organization and maintainability
-
Inheritance establishes an “IS-A” relationship between the base class and the derived class
-
For example, if you have a base class called Vehicle and a derived class called Car, you can say that “a Car is a Vehicle.”
-
The car class inherits the properties and behaviours associated with being a vehicle
-
Inheritance involves two main entities:
-
The base class (also known as the parent class or superclass) and the derived class (also known as the child class or subclass)
-
The derived class inherits the characteristics of the base class, meaning it can access and use the methods and attributes defined in the base class
-

Example of a base class and derived classes
-
Base Class: The base class serves as the blueprint or template from which the derived class inherits
-
It defines common properties and behaviours that can be shared among multiple derived classes
-
-
Derived Class: The derived class inherits the attributes and methods of the base class
-
It can add additional attributes and methods
-
-
If a car object was to be created, it may have the following attributes:
-
Manufacturer – The company that makes the car
-
Make -The model of the car
-
Cost – The price of the car to purchase
-
IsInsured – Whether or not the car is insured
-
EngineCapacity – The size of the engine for the car
-
-
It may also have access to the following methods:
-
TurnEngineOn()– To start the car engine -
TurnEngineOff()– To turn off the car engine -
SteerLeft()– To turn the car to the left -
SteerRight()– To steer the car to the left -
GearChange()– To change the gear of the car -
UnlockDoors()– To unlock the doors to the car
-
-
The above methods are only a select few and there could be many more added for extra functionality
-
In the following code, the super keyword is used in inheritance to refer to the superclass (Base class: Vehicles) and access its members (methods, attributes, or constructors) from within the subclass (Derived Class: Cars)
Programming inheritance
How do you program inheritance?
Pseudocode
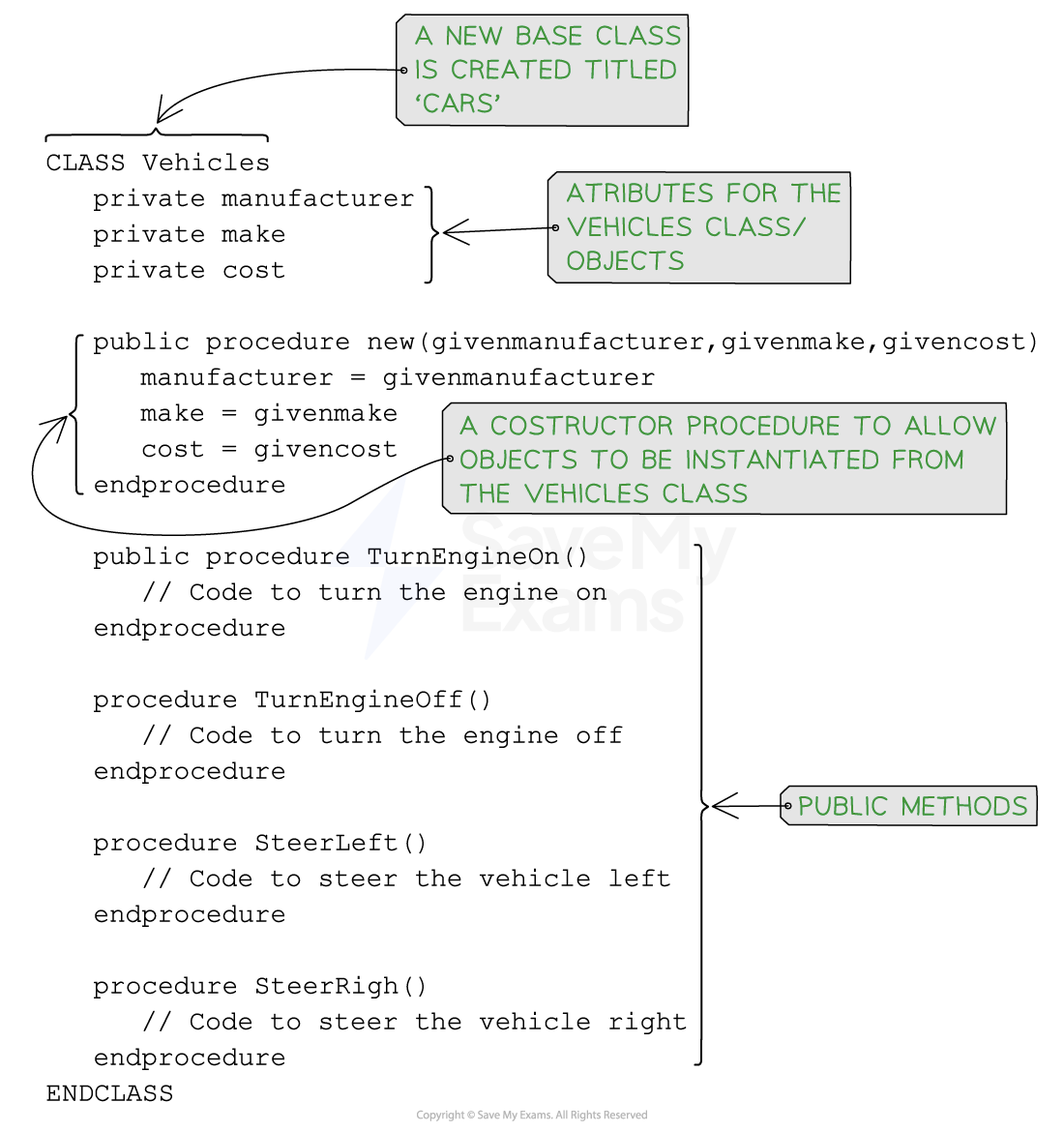
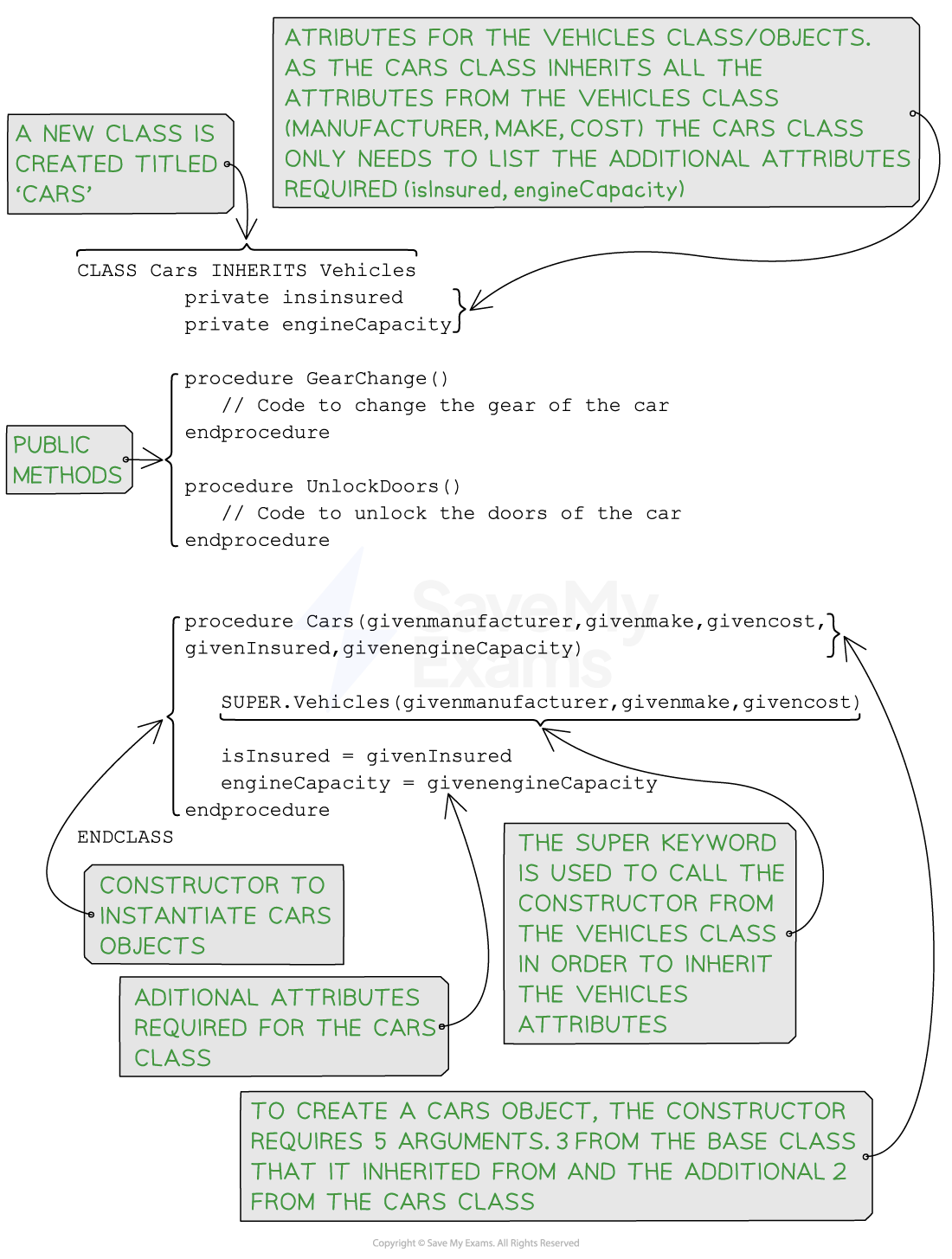
Pseudocode for a class created using inheritance
Java
//vehicle class created public class Vehicle { //attributes created for the vehicle class private String manufacturer; private String make; private double cost; //constructor to create objects of type vehicle public Vehicle(String manufacturer, String make, double cost) { this.manufacturer = manufacturer; this.make = make; this.cost = cost; } //method to start the engine of the car public void turnEngineOn() { //code to turn the engine on } //method to stop the engine of the car public void turnEngineOff() { //code to turn the engine off } //method to steer the car to the left public void steerLeft() { // code to steer the vehicle left } //method to steer the car to the right public void steerRight() { // code to steer the vehicle right } } //Derived Class (Car) //the Car class uses the keyword 'extends' to inherit from the Vehicle class public class Car extends Vehicle { private boolean isInsured; private double engineCapacity; // Constructor to create objects of type Car public Car(String manufacturer, String make, double cost, boolean isInsured, double engineCapacity) { //the super keyword is used to inherit the attributes from the base class super(manufacturer, make, cost); this.isInsured = isInsured; this.engineCapacity = engineCapacity; } //method to change gear public void gearChange() { //code to change the gear of the car } //method to unlock the vehicle doors public void unlockDoors() { //code to unlock the doors of the car } }Python
#Base class (Vehicle) #Vehicle class created class Vehicle: #attributes created for the Vehicle class def __init__(self, manufacturer, make, cost): self.manufacturer = manufacturer self.make = make self.cost = cost #method to start the engine of the car def turn_engine_on(self): # Code to turn the engine on #method to stop the engine of the car def turn_engine_off(self): # Code to turn the engine off #method to steer the car to the left def steer_left(self): # Code to steer the vehicle left #method to steer the car to the right def steer_right(self): # Code to steer the vehicle right #Derived Class (Car) #the Car class uses the keyword parent class name in parenthesis to inherit from the Vehicle class class Car(Vehicle): def __init__(self, manufacturer, make, cost, is_insured, engine_capacity): #the super keyword is used to inherit the attributes from the base class super().__init__(manufacturer, make, cost) self.is_insured = is_insured self.engine_capacity = engine_capacity #method to change gear def gear_change(self): # Code to change the gear of the car #method to steer the car to the right def unlock_doors(self): # Code to unlock the doors of the carWorked Example
The child class Helicopter inherits from the parent class Vehicle. A helicopter also has a vertical position and changes the vertical position when it increases speed.

Write program code to declare the class Helicopter. You only need to declare the class and its constructor. You do not need to declare the other methods.
Use your programming language’s appropriate constructor.
All attributes must be private.
If you are writing in Python, include attribute declarations using comments. [5]
Answer
-
Class header (and end where appropriate) inheriting from Vehicle [1 mark]
-
3 (private) attribute declarations with data types [1 mark]
-
Constructor (and end where appropriate) with (min) 5 parameters [1 mark]
-
Calling parent constructor with appropriate parameters [1 mark]
-
Initialising
VerticalPositionto 0 andVerticalChangeandMaxHeightto attributes [1 mark]
Example program code:
VB.NET
Class Helicopter Inherits Vehicle Private VerticalPosition As Integer Private VerticalChange As Integer Private MaxHeight As Integer Sub New(IDP, MaxSpeedP, IncreaseAmountP, VertChangeP, MaxHeightP) MyBase.New(IDP, MaxSpeedP, IncreaseAmountP) VerticalPosition = 0 VerticalChange = VertChangeP MaxHeight = MaxHeightP End Sub
End ClassJava
class Helicopter extends Vehicle{ private Integer VerticalPosition; private Integer VerticalChange; private Integer MaxHeight; public Helicopter(String IDP, Integer MaxSpeedP, Integer IncreaseAmountP, Integer VertChangeP, Integer MaxHeightP){ super(IDP, MaxSpeedP, IncreaseAmountP); VerticalPosition = 0; VerticalChange = VertChangeP; MaxHeight = MaxHeightP; }}Python
class Helicopter(Vehicle): #VerticalPosition Integer #VerticalChange Integer #MaxHeight Integer def __init__(self, IDP, MaxSpeedP, IncreaseAmountP, VertChangeP, MaxHeightP): Vehicle.__init__(self,IDP, MaxSpeedP, IncreaseAmountP) self.__VerticalPosition = 0 self.__VerticalChange = VertChangeP self.__MaxHeight = MaxHeightP
Responses