Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
attributes-oop
Attributes (OOP)
What is an attribute?
-
In object-oriented programming (OOP), an attribute refers to a data member or a property associated with an object or a class
-
They define the state of an object and can have different values for different instances of the same class
-
Attributes can be of various data types, such as integers, strings, Booleans, or even other objects
-
Attributes can have different access rights
-
The example below shows a Car class object with an attribute called manufacturer
-
It has a private access meaning that it can be accessed only by instances of the Car class
-
The data that this attribute will hold must be of the String data type
-
The image below gives a visual representation of an object of this class being instantiated with a data value of “Ford” :

An example instance of an object
-
In most cases each class has many different attributes
-
Below is an example of an object of class “person”:

Example of an object of class “person”
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
Attributes declared within methods (local variables) cannot have access modifiers because they are local to the method and have a limited scope
-
Local variables are only accessible within the block or method in which they are declared. They are not part of the class’s state and cannot be accessed from other methods or classes
Programming attributes (OOP)
How do you program attributes?
Pseudocode
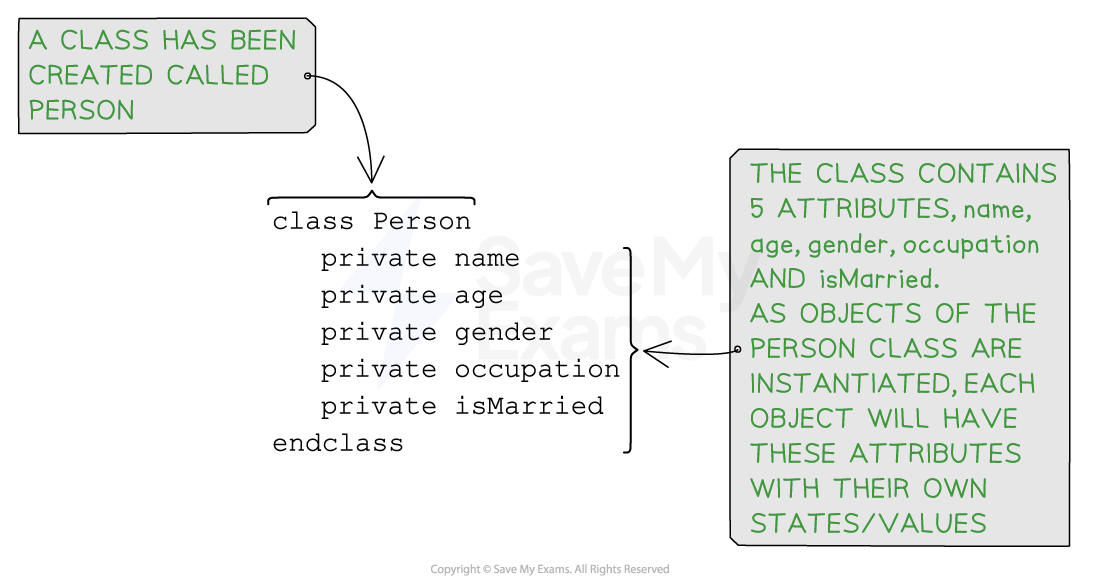
Example of a created class, “Person”, containing several attributes
Java
public class Person { // Attributes for the person class private String name; private int age; private String gender; private String occupation; private boolean isMarried; }Python
-
In Python attributes are defined using the
selfkeyword followed by the attribute name and its initial value
class MyClass: def __init__(self, attribute1, attribute2): # Define attributes self.attribute1 = attribute1 self.attribute2 = attribute2
Responses