Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
adt-overview
What is an abstract data type (ADT)?
-
An abstract data type (ADT) is a collection of data and a set of operations on that data
-
Three common ADT’s are:
-
Stacks
-
Queues
-
Linked lists
-
Stack operations
What is a stack?
-
A stack is an abstract data type that stores data using the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle
-
A stack is like a pile of plates, the last item you put on is the first one you take off
-
PUSH: Add an item to the top of the stack
-
POP: Remove the item from the top
-
-
The first item pushed onto the stack will be the last one popped off
-
A stack uses two pointers:
-
A base pointer – points to the first item in the stack
-
A top pointer – points to the last item in the stack
-
Main operations
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
isEmpty() |
This checks is the stack is empty by checking the value of the top pointer |
|
push(value) |
This adds a new value to the end of the list, it will need to check the stack is not full before pushing to the stack. |
|
peek() |
This returns the top value of the stack. First check the stack is not empty by looking at the value of the top pointer. |
|
pop() |
This removes and returns the top value of the stack. This first checks if the stack is not empty by looking at the value of the top pointer. |
|
size() |
Returns the size of the stack |
|
isFull() |
Checks if the stack is full and returns the Boolean value, this compares the stack size to the top pointer. |
-
Stacks use a pointer which points to the top of the stack, where the next piece of data will be added (pushed) or the current piece of data can be removed (popped)
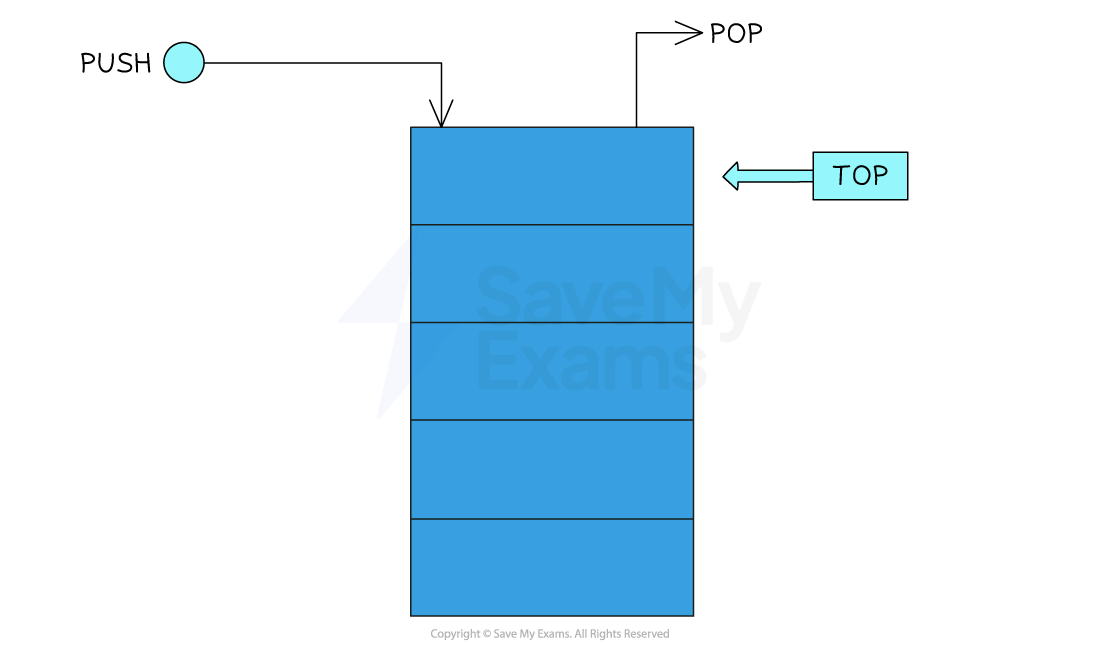
Pushing data to a stack
-
When pushing (adding) data to a stack, the data is pushed to the position of the pointer
-
Once pushed, the pointer will increment by 1, signifying the top of the stack
-
Since the stack is a static data structure, an attempt to push an item on to a full stack is called a stack overflow
-
This would push ‘Bunny’ onto the empty stack

-
This would push ‘Dog’ to the top of the stack

-
This would push ‘Ant’ to the top of the stack

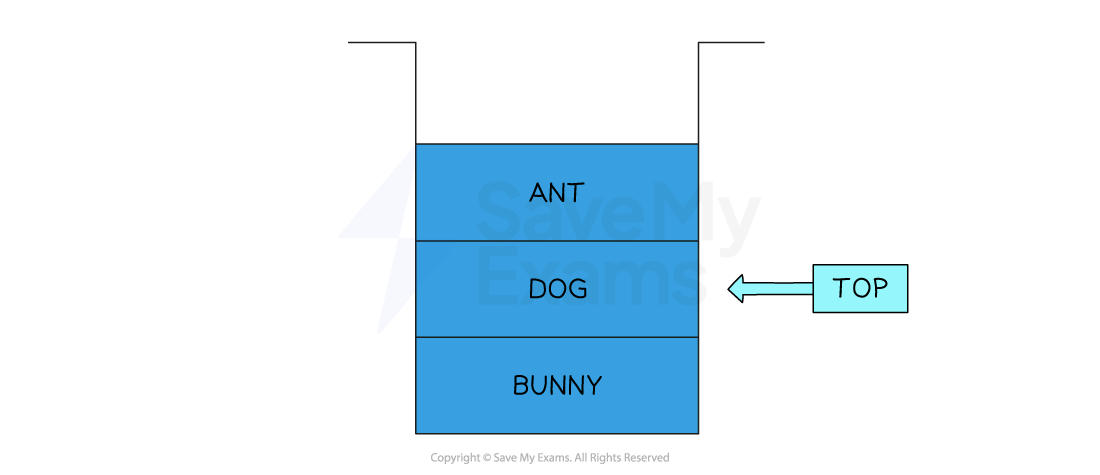
Popping data from a stack
-
When popping (removing) data from a stack, the data is popped from the position of the pointer
-
Once popped, the pointer will decrement by 1, to point at the new top of the stack
-
Since the stack is a static data structure, an attempt to pop an item from an empty stack is called a stack underflow
-
This would pop ‘Ant’ from the top of the stack
-
The new top of the stack would become ‘Dog’
-
Note that the data that is ‘popped’ isn’t necessarily erased
-
The pointer ‘top’ moves to show that ‘Ant’ is no longer in the stack and depending on the implementation, ‘Ant’ can be deleted or replaced with a null value, or left to be overwritten
Queue operations
What is a queue?
-
A queue is an abstract data type that stores data in the order it arrives, using the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle
-
A queue works like a line of people waiting at a shop, the first one in is the first one served
-
ENQUEUE: Add an item to the back of the queue
-
DEQUEUE: Remove the item from the front
-
-
The first item added to the queue is the first one removed
Main operations
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
enQueue(value) |
Adding an element to the back of the queue |
|
deQueue() |
Returning an element from the front of the queue |
|
peek() |
Return the value of the item from the front of the queue without removing it from the queue |
|
isEmpty() |
Check whether the queue is empty |
|
isFull() |
Check whether the queue is full (if the size has a constraint) |
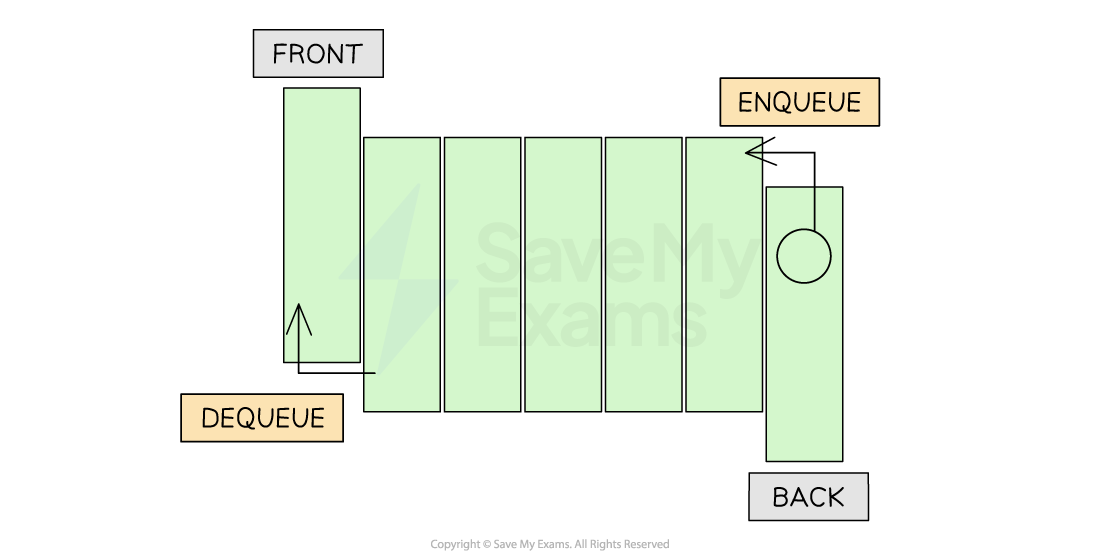
Linear queues
-
A linear queue is a data structure that consists of an array
-
Items are added to the next available space in the queue starting from the front
-
Items are then removed from the front of the queue
-
Before adding an item to the queue you need to check that the queue is not full
-
If the end of the array has not been reached, the rear index pointer is incremented and the new item is added to the queue
-
In the example below, you can see the queue as the data Adam, Brian and Linda are enqueued.

Responses