Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
uses-of-number-systems
Applications of Binary Coded Decimal (BCD)
What are the uses of binary-coded decimal (BCD)?
|
Use Case |
Why BCD is used |
|---|---|
|
Electronic calculators |
Keeps numbers in decimal format for easier display and accuracy |
|
Digital clocks and watches |
Time is naturally decimal (e.g. 12:45), so BCD makes display logic simpler |
|
Banking and financial systems |
Avoids rounding errors when doing decimal calculations, especially with money |
|
Old digital systems / embedded systems |
Simpler to implement with hardware that displays digits individually |
-
Binary coded decimal is commonly used in systems that need to display decimal numbers clearly and accurately
-
BCD is ideal for applications like digital clocks, calculators, and financial systems where decimal precision matters
-
Using BCD avoids rounding errors that can occur in binary-based arithmetic, especially with money and time
-
It’s still found in older or embedded systems where simple hardware-based decimal output is needed
Applications of hexadecimal
Why is hexadecimal used?
-
In Computer Science hexadecimal is often preferred when working with large values
-
It takes fewer digits to represent a given value in hexadecimal than in binary
-
1 hexadecimal digit corresponds 4 bits and can represent 16 unique values (0-F)
-
-
It is beneficial to use hexadecimal over binary because:
-
The more bits there are in a binary number, the harder it makes for a human to read
-
Numbers with more bits are more prone to errors when being copied
-
-
Examples of where hexadecimal can be seen:
-
MAC addresses
-
Colour codes
-
URLs
-
MAC addresses
-
A typical MAC address consists of 12 hexadecimal digits, equivalent to 48 digits in in binary
-
AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF
-
10101010:10111011:11001100:11011101:11101110:11111111
-
-
Writing down or performing calculations with 48 binary digits makes it very easy to make a mistake
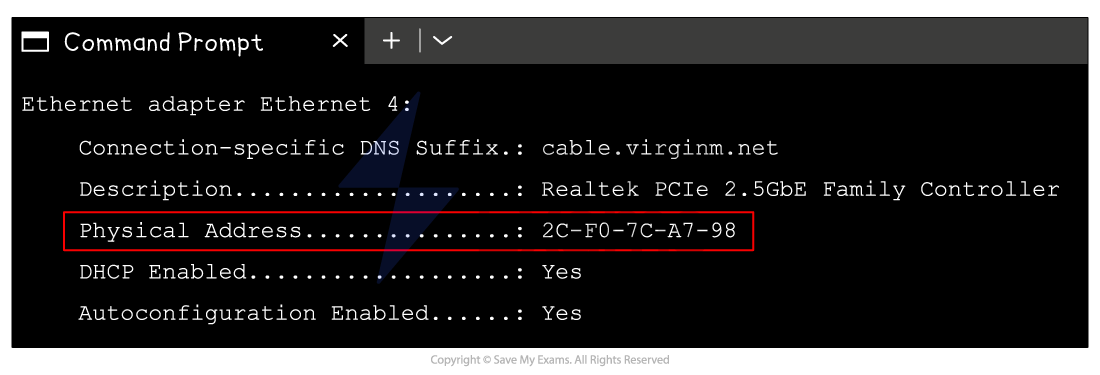
Colour codes
-
A typical hexadecimal colour code consists of 6 hexadecimal digits, equivalent to 24 digits in binary
-
#66FF33 (green)
-
01000010:11111111:00110011
-
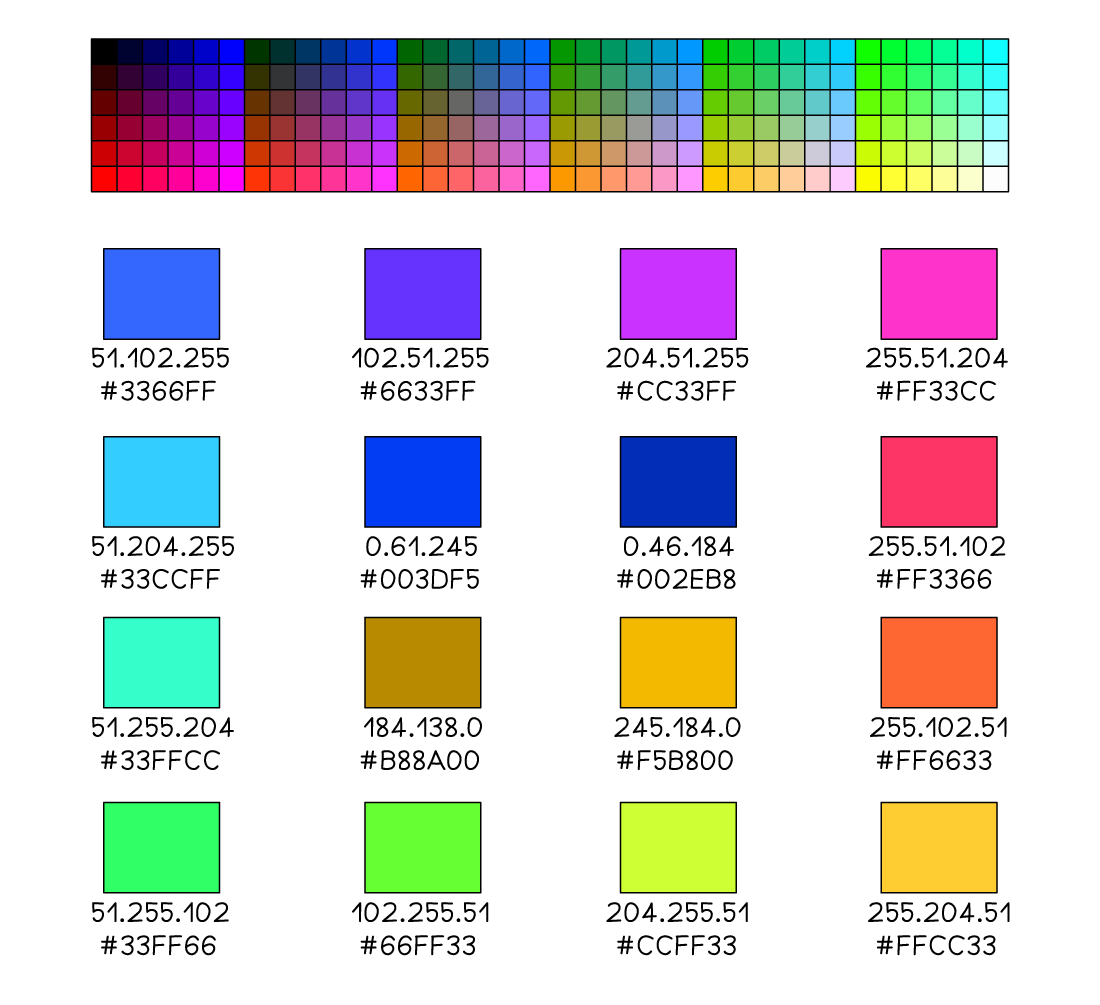
URL’s
-
A URL can only contain standard characters (a-z and A-Z), numbers (0-9) and some special symbols which is enough for basic web browsing
-
If a URL needs to include a character outside of this set, they are converted into a hexadecimal code
-
Hexadecimal codes included in a URL are prefixed with a % sign

Responses