Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
linear-search
Linear search
What is a linear search?
-
The linear search is a standard algorithm used to find elements in an unordered list
-
The list is searched sequentially and systematically from the start to the end one element at a time
-
Comparing each element to the value being searched for
-
If the value is found the algorithm outputs where it was found in the list
-
If the value is not found it outputs a message stating it is not in the list
-
-
An example of using a linear search would be looking for a specific student name in a list or searching for a supermarket item in a shopping list
Performing the linear search
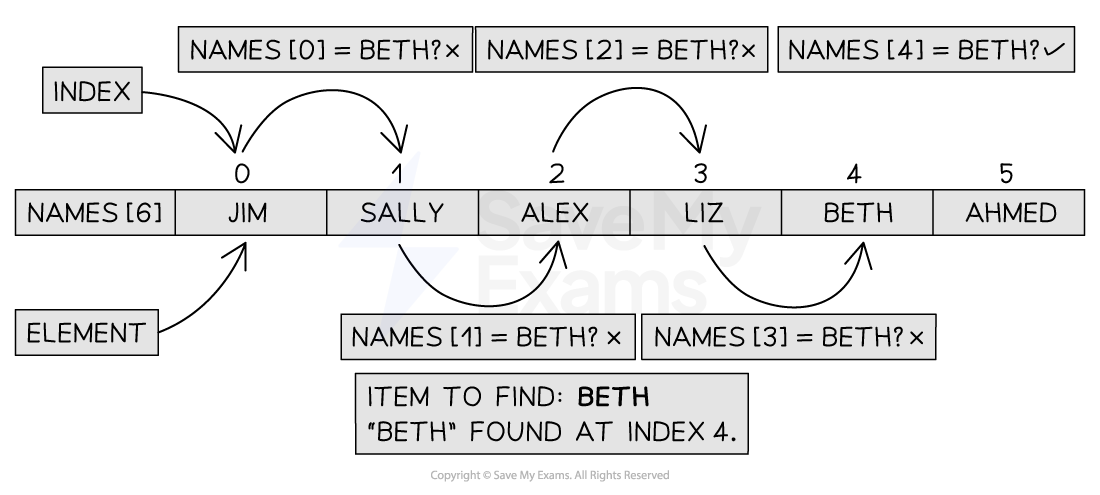
Figure 1: Performing the Linear Search
Time complexity of a linear search
-
To determine the algorithm’s execution time as measured by the number of instructions or steps carried out, Big-O notation must be used
-
The loop is executed n times, once for each item. There are two instructions within the loop, the if statement and an assignment, hence the Big-O for the loop is O(2n)
-
There are three initial statements which are O(1)
-
The overall Big-O notation is therefore 2n + 3, which when coefficients are factored out, becomes O(n) as linear time dominates constant time. The constant term and coefficients contribute significantly less as the input size n grows larger
-
It is important to remember here that O(n) is the worst case scenario. The best case scenario O(1) would find the item the first time, while the average case would be O(n/2) which when we remove coefficients still becomes O(n)
Space complexity of a linear search
-
As the linear search requires no additional space, it is space complexity O(n) where n is the number of items in the list
Tracing a linear search
-
Given the following list [5, 4, 7, 1, 3, 8, 9, 2], a trace table for the linear search is shown below
Trace Table of the Linear Search
|
item |
index |
i |
list[i] |
found |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8 |
-1 |
0 |
5 |
False |
|
|
|
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
3 |
|
|
8 |
5 |
5 |
8 |
True |
Implementing a linear search
Pseudocode
FUNCTION linearSearch(list : ARRAY OF STRING, item : STRING) RETURNS INTEGER DECLARE index : INTEGER DECLARE i : INTEGER DECLARE found : BOOLEAN index ← -1 i ← 0 found ← FALSE WHILE i < LENGTH(list) AND found = FALSE IF list[i] = item THEN index ← i found ← TRUE ENDIF i ← i + 1 ENDWHILE RETURN index
ENDFUNCTION-
Function definition:
FUNCTION linearSearch(list : ARRAY OF STRING, item : STRING) RETURNS INTEGER-
The function takes a list and a target item.
-
It returns the index of the item if found, or -1 if not.
-
-
Variable declarations:
index,i, andfoundare declared:-
indexstores the result (default is -1 if not found). -
iis the loop counter. -
foundis a boolean used to stop the search once the item is found.
-
-
Initialisation:
-
index ← -1→ start with “not found” -
i ← 0→ start from the first index of the list -
found ← FALSE→ the item hasn’t been found yet
-
-
Loop condition:
WHILE i < LENGTH(list) AND found = FALSE-
Continue looping while there are items left to check and the item hasn’t been found.
-
-
Comparison inside loop:
IF list[i] = item THEN-
Check if the current element equals the search item.
-
-
If a match is found:
-
index ← i→ save the current index -
found ← TRUE→ stop searching
-
-
Increment:
-
i ← i + 1→ move to the next item
-
-
End of loop:
-
Once the loop finishes (either item is found or end of list is reached), return the result.
-
-
Return value:
RETURN index-
Returns the index where the item was found.
-
If it wasn’t found, it returns
-1.
-
Python
def linear_search(list, item): index = -1 for i in range(len(list)): if list[i] == item: index = i break # Stop the loop once the item is found return indexJava
public class LinearSearch { public static int linearSearch(int[] list, int item) { int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (list[i] == item) { index = i; break; // Stop the loop once the item is found } } return index; }
Responses