Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm
Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm
-
In Computer Science, an optimisation problem involves finding the most efficient solution to a given problem
-
This could mean minimising cost, time, or resource usage, or maximising output, efficiency, or value
-
Examples of optimisation problems include:
-
Finding the shortest route between two locations (e.g. Google Maps)
-
Minimising resource usage in manufacturing or video games
-
Creating efficient timetables (e.g. for schools or offices)
-
Scheduling tasks and staff shifts to avoid conflicts or downtime
-
-
One of the most common real-world examples is finding the shortest path from A to B, which is exactly what Dijkstra’s algorithm solves
What is Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm?
-
In A Level Computer Science, Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm is a classic optimisation algorithm
-
It calculates the shortest path from a starting node to all other nodes in a weighted graph
-
It is often compared to breadth-first search, but Dijkstra’s includes edge weights and ensures the lowest total cost to reach each destination node
How It works:
-
The graph is made up of nodes (vertices) and edges (arcs)
-
Each edge has a weight, which can represent:
-
Time
-
Distance
-
Cost
-
-
The algorithm explores all possible routes, keeping track of the shortest known distance to each node
-
It guarantees the optimal path from the start node to every other node in the graph
-
For revision on graphs, see section 18 – AI & Graphs
-
An illustrated example of Dijkstra’s algorithm is shown below:
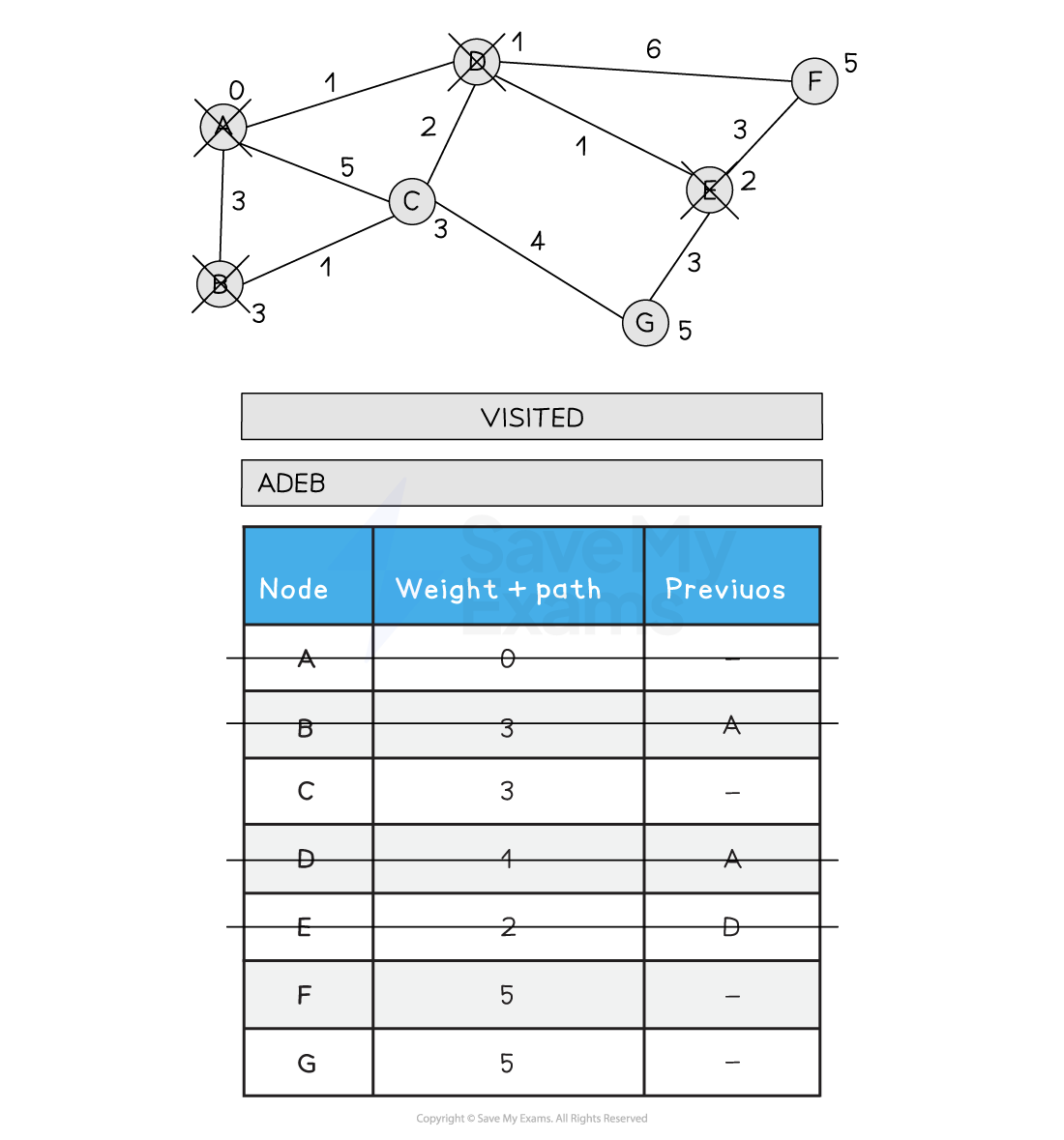
Performing Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm
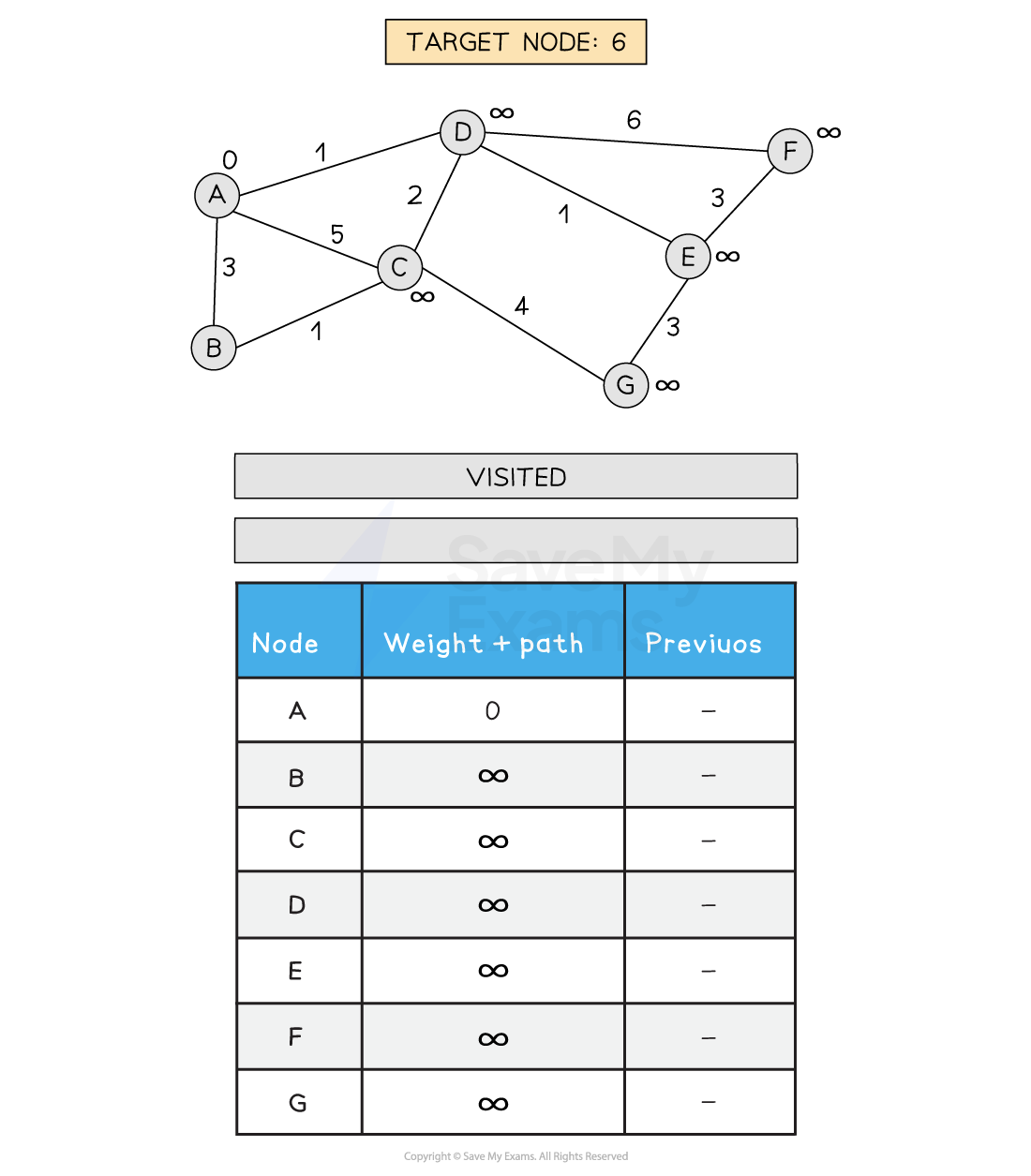
-
Set A path to 0 and all other path weights to infinity
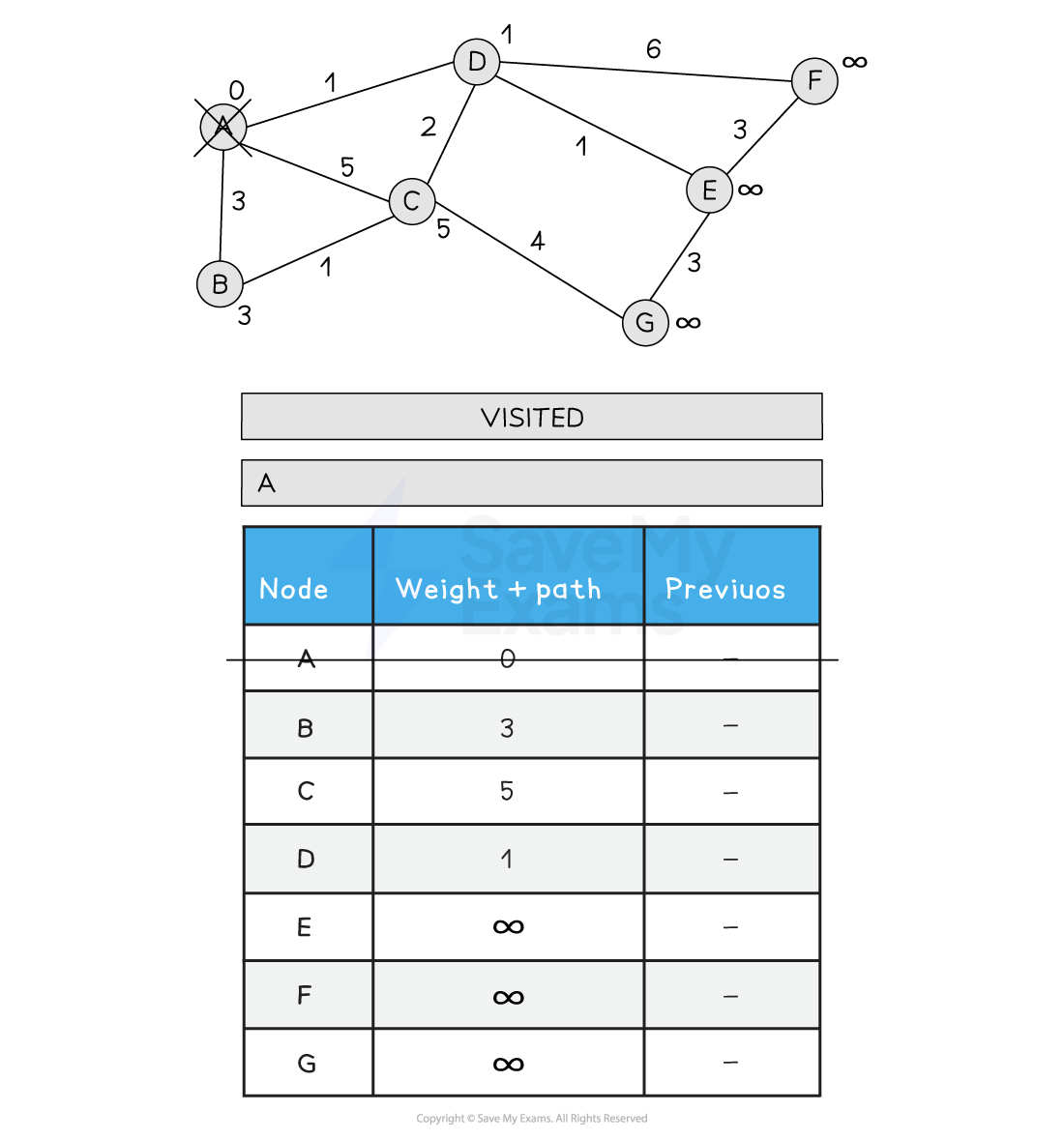
-
Visit A. Update all neighbouring nodes path weights to the distance from A + A’s path weight (0)
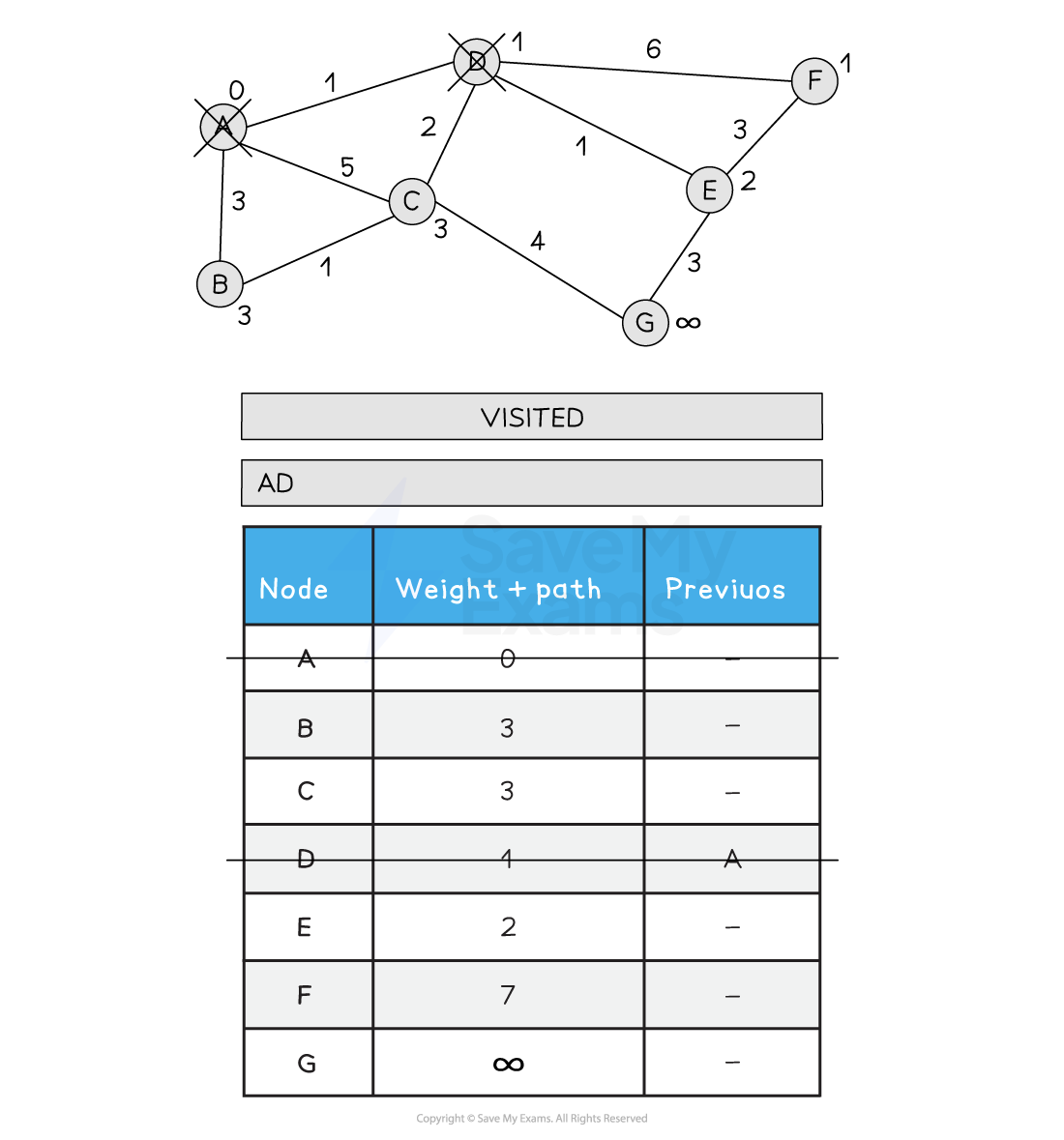
-
Choose the next node to visit that has the lowest path weight (D)
-
Visit D
-
Update all neighbouring, non-visited nodes with a new path weight if the old path weight is bigger than the new path weight
-
C is updated from 5 to 3 as the new path is shorted (A > D > C)
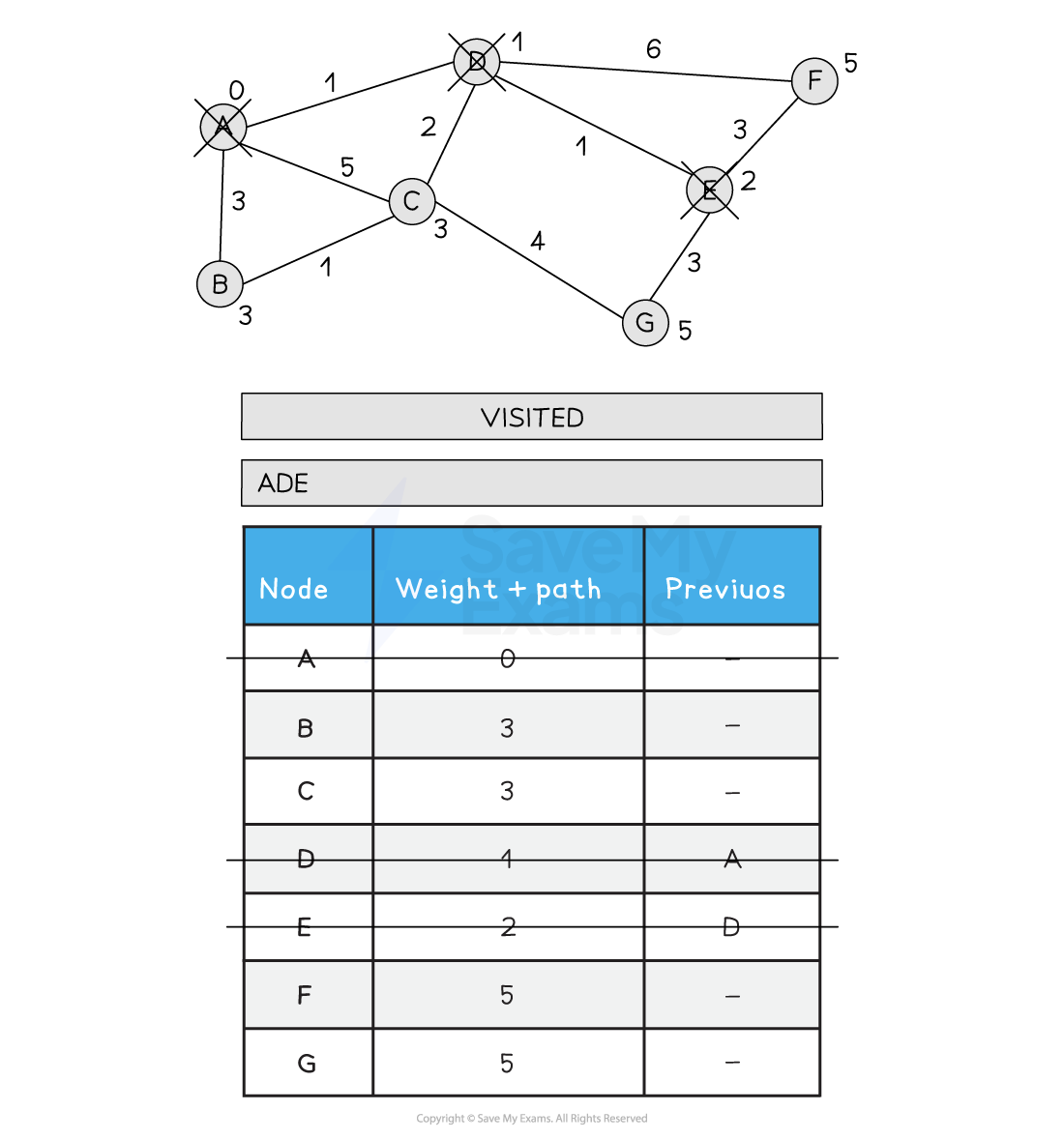
-
Choose the next node to visit that has the lowest path weight (E)
-
Visit E
-
Update all neighbouring, non-visited nodes from E with a new path weight
-
F is updated from 7 to 5 as the new path is shorter (A > D > E > F)
-
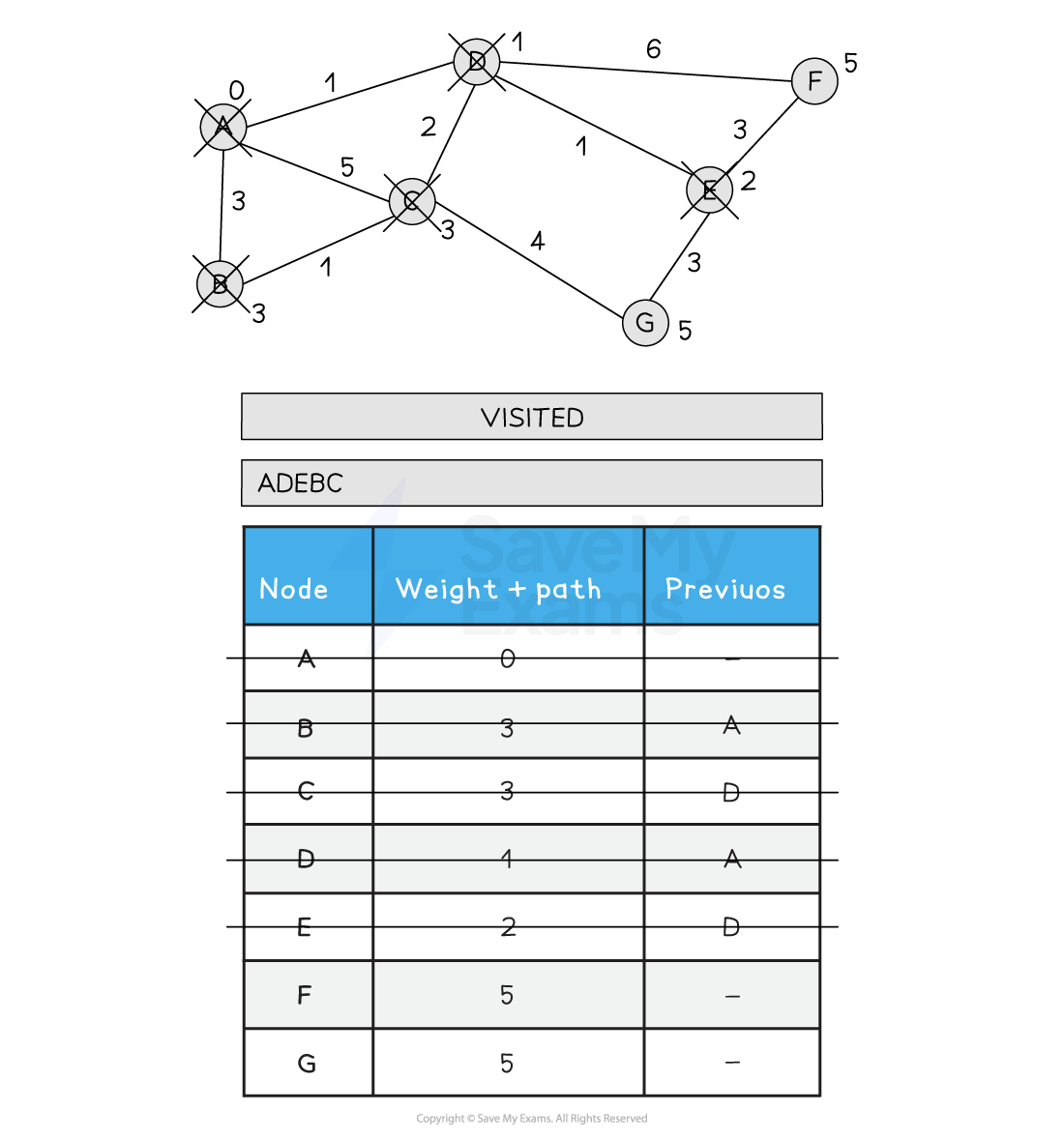
Choose the next node to visit, alphabetically (B)
-
Visit B
-
Update all neighbouring non-visited nodes from B with a new weight if the path is less than the current path
-
C is not updated as A > B > C is 4
-
Choose the next lowest node and visit (C)
-
Update C’s neighbours if the new path is shorter than the old path
-
A > D > C > G is 8, so G is not updated

Responses