Computer-science_A-level_Cie
-
computers-and-components6 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture6 主题
-
assembly-language-4 主题
-
bit-manipulation1 主题
-
operating-systems3 主题
-
language-translators2 主题
-
data-security3 主题
-
data-integrity1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership3 主题
-
database-concepts3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms-1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills1 主题
-
algorithms14 主题
-
data-types-and-records2 主题
-
arrays2 主题
-
files1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt1 主题
-
programming-basics1 主题
-
constructs2 主题
-
structured-programming1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle2 主题
-
program-design-2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance3 主题
-
user-defined-data-types1 主题
-
file-organisation-and-access-3 主题
-
floating-point-numbers-representation-and-manipulation3 主题
-
protocols2 主题
-
circuit-switching-packet-switching1 主题
-
processors-parallel-processing-and-virtual-machines5 主题
-
boolean-algebra-and-logic-circuits4 主题
-
purposes-of-an-operating-system-os3 主题
-
translation-software3 主题
-
encryption-encryption-protocols-and-digital-certificates3 主题
-
artificial-intelligence-ai4 主题
-
recursion1 主题
-
programming-paradigms4 主题
-
object-oriented-programming7 主题
-
file-processing-and-exception-handling2 主题
-
data-representation5 主题
-
multimedia3 主题
-
compression2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet11 主题
a-algorithm
A* algorithm
What is the A* algorithm?
-
The A* (A-star) algorithm is a pathfinding algorithm that builds upon Dijkstra’s algorithm
-
It introduces a heuristic function to improve efficiency
-
It is used to find the shortest path from a starting node to a goal node in a graph
-
While Dijkstra’s algorithm considers only the actual cost from the start node:
-
A* enhances this by estimating the remaining distance to the goal
-
This makes it more goal-oriented and often more efficient
-
How A* improves on Dijkstra’s
-
To avoid inefficient detours, A* introduces a heuristic function, called h(x)
-
It estimates the straight-line distance (Euclidean distance) from the current node to the goal
-
A* combines both cost and estimate using the formula:
-
f(x) = g(x) + h(x)
-
g(x) = the actual cost from the start node to the current node
-
h(x) = the heuristic estimate to the goal node
-
f(x) = the total estimated cost of the cheapest solution through node x
-
-
-
By choosing nodes with the lowest f(x) value, A* aims to explore paths that are both cheap and move closer to the goal
Heuristics in A*
-
The heuristic function h(x) should never overestimate the true cost to the goal
-
This ensures A* remains optimally efficient
-
The closer h(x) is to the true cost, the fewer nodes A* needs to explore
-
If h(x) increases, it may indicate the algorithm is moving away from the goal, helping it backtrack or choose a better path
-
Below is an illustration of the A* search:
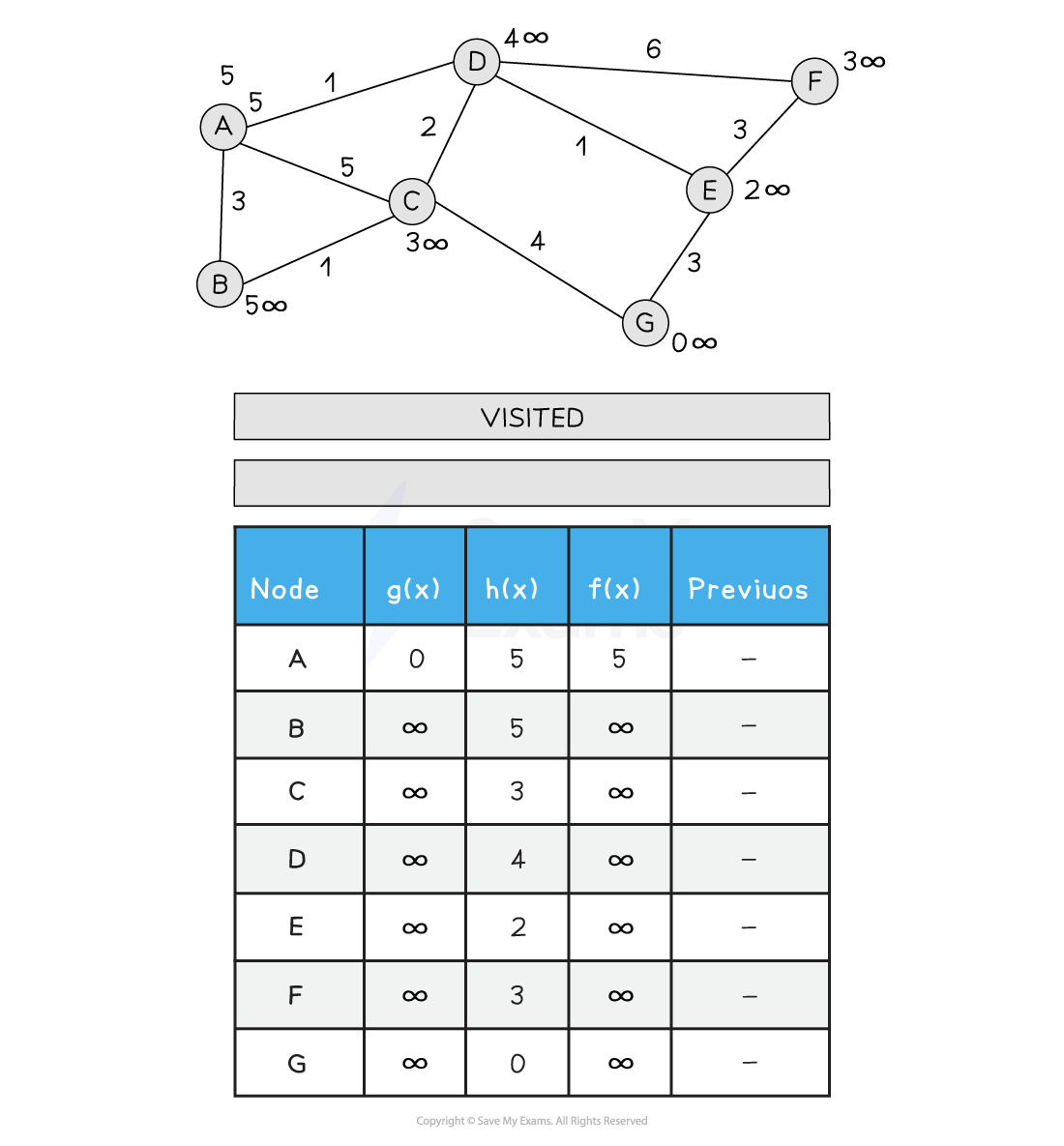
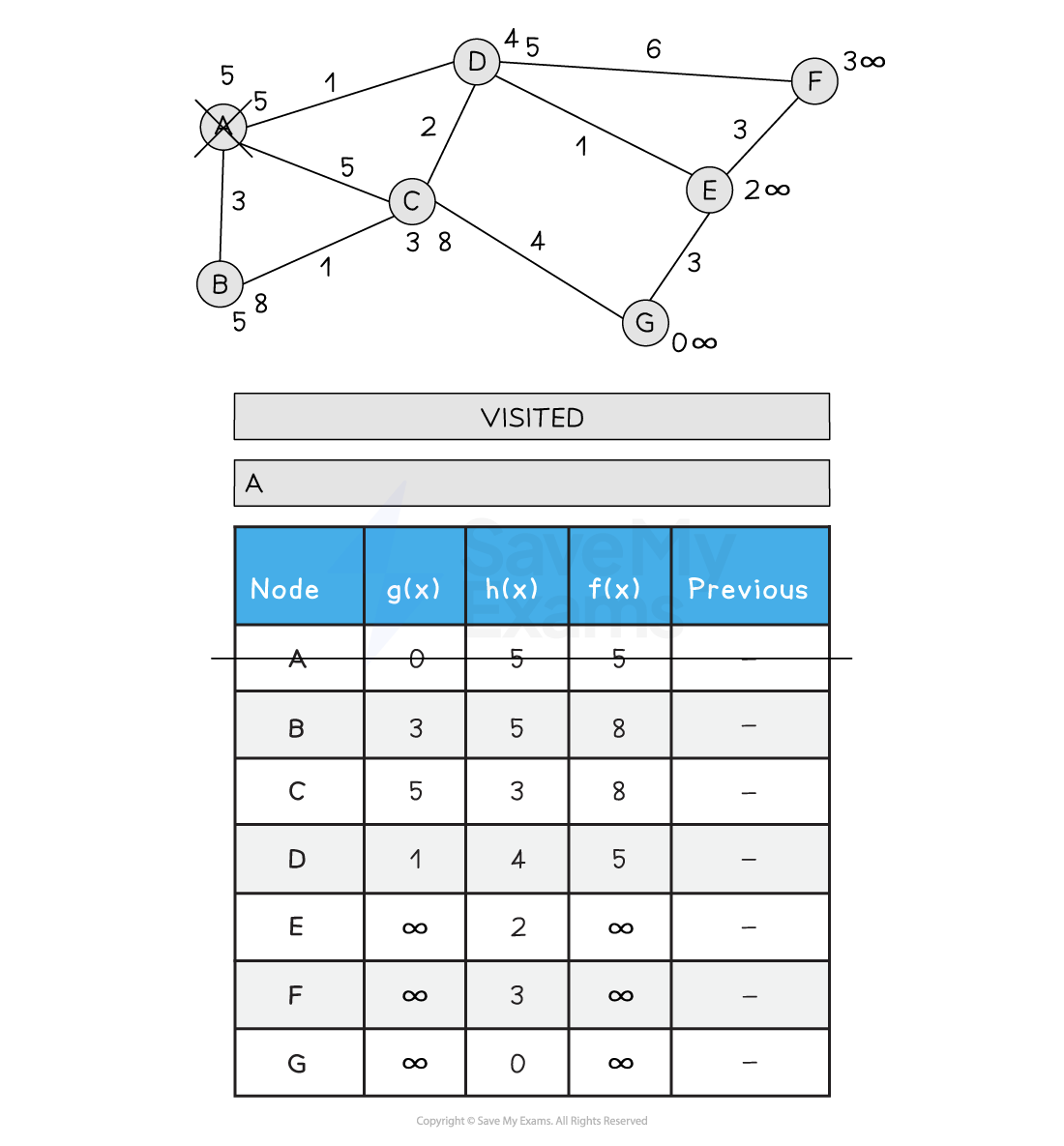
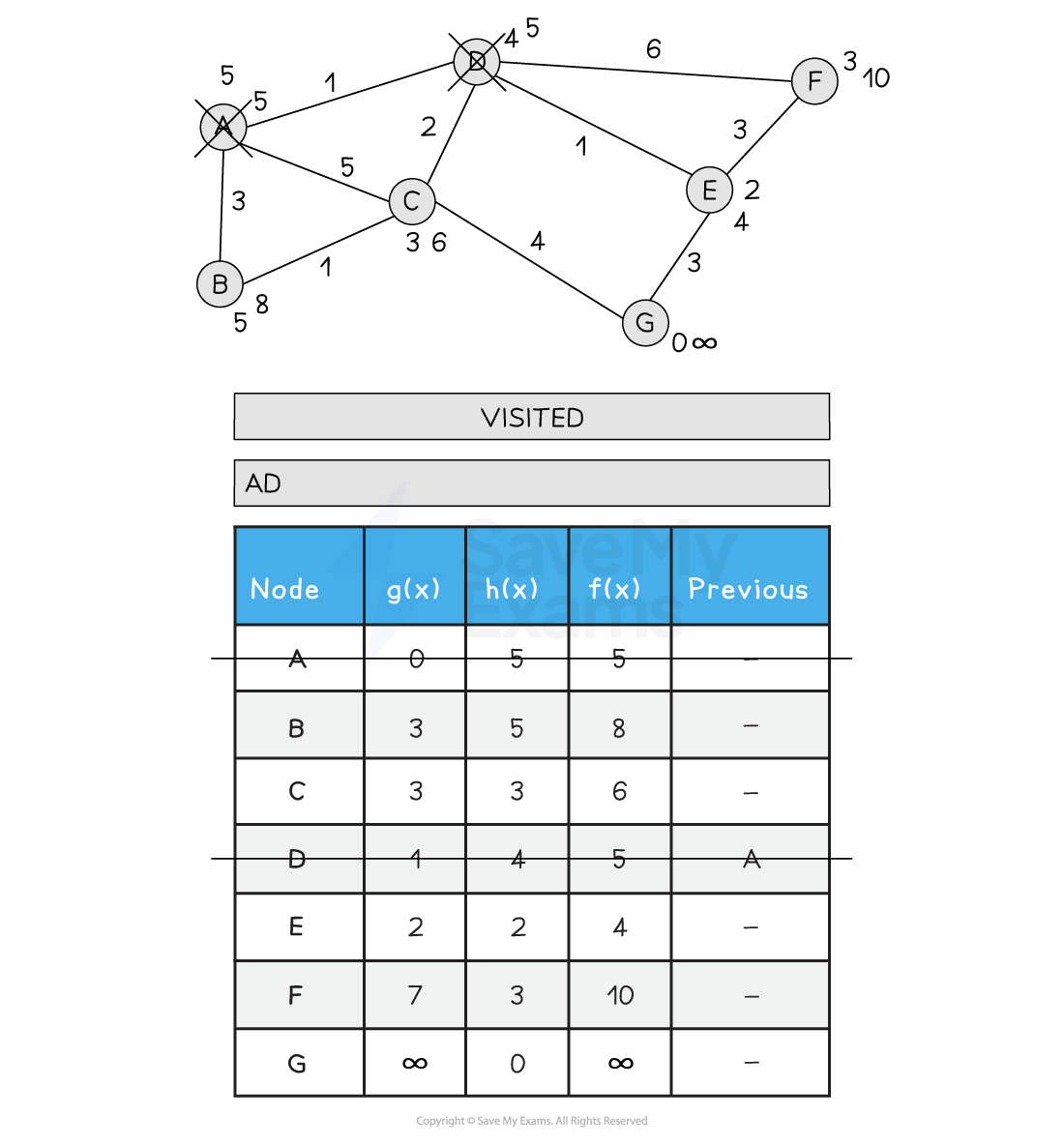
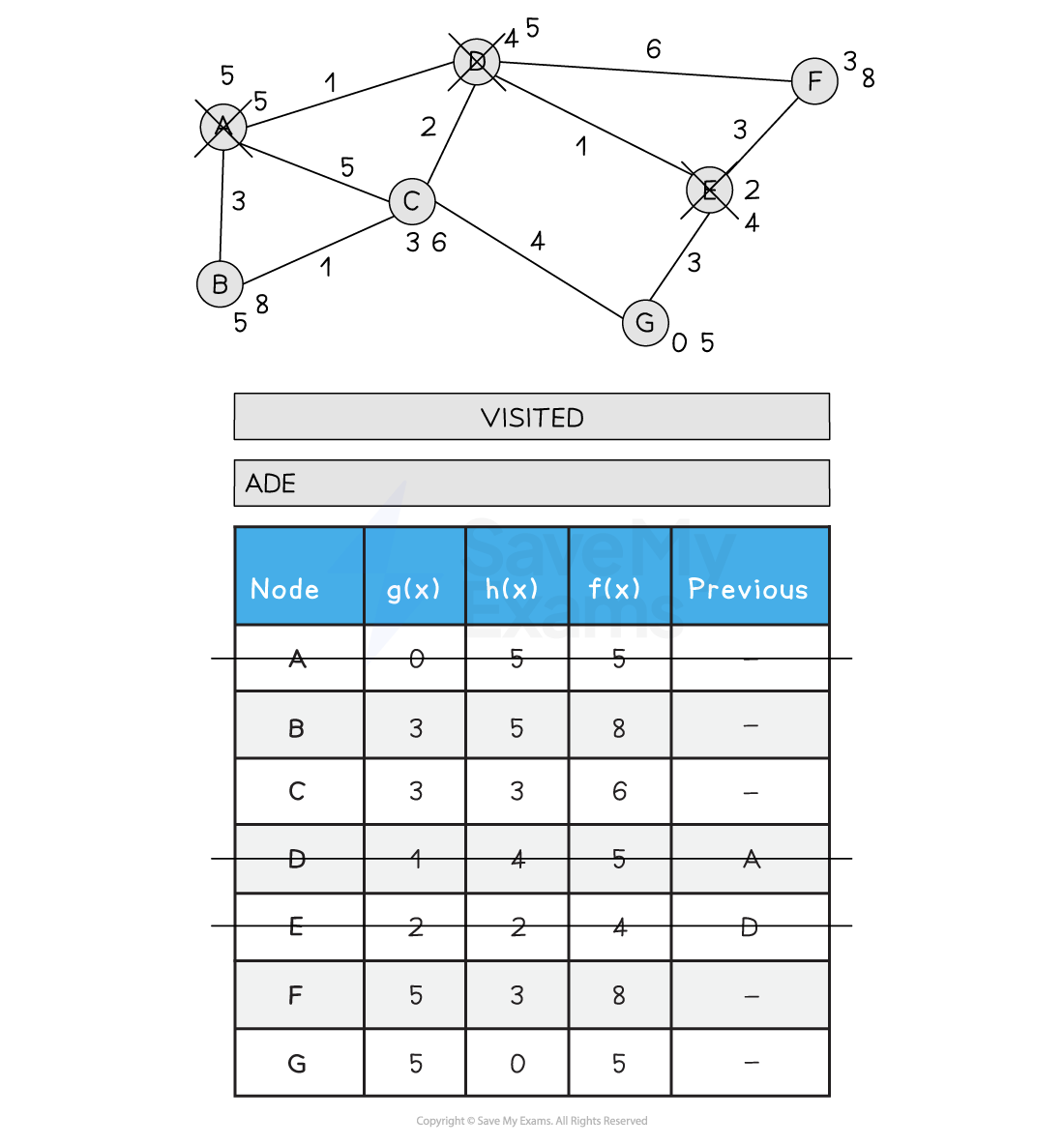
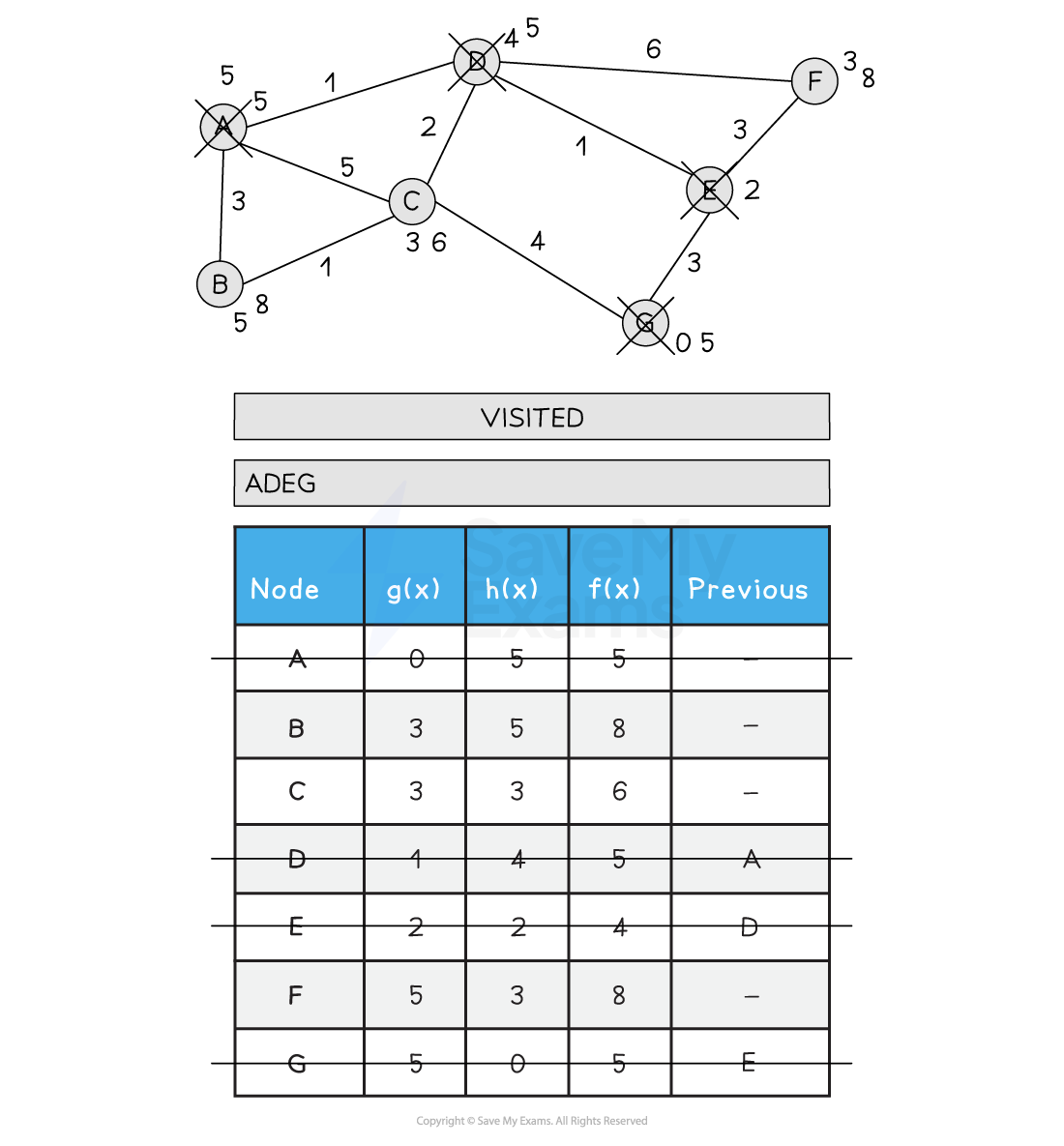
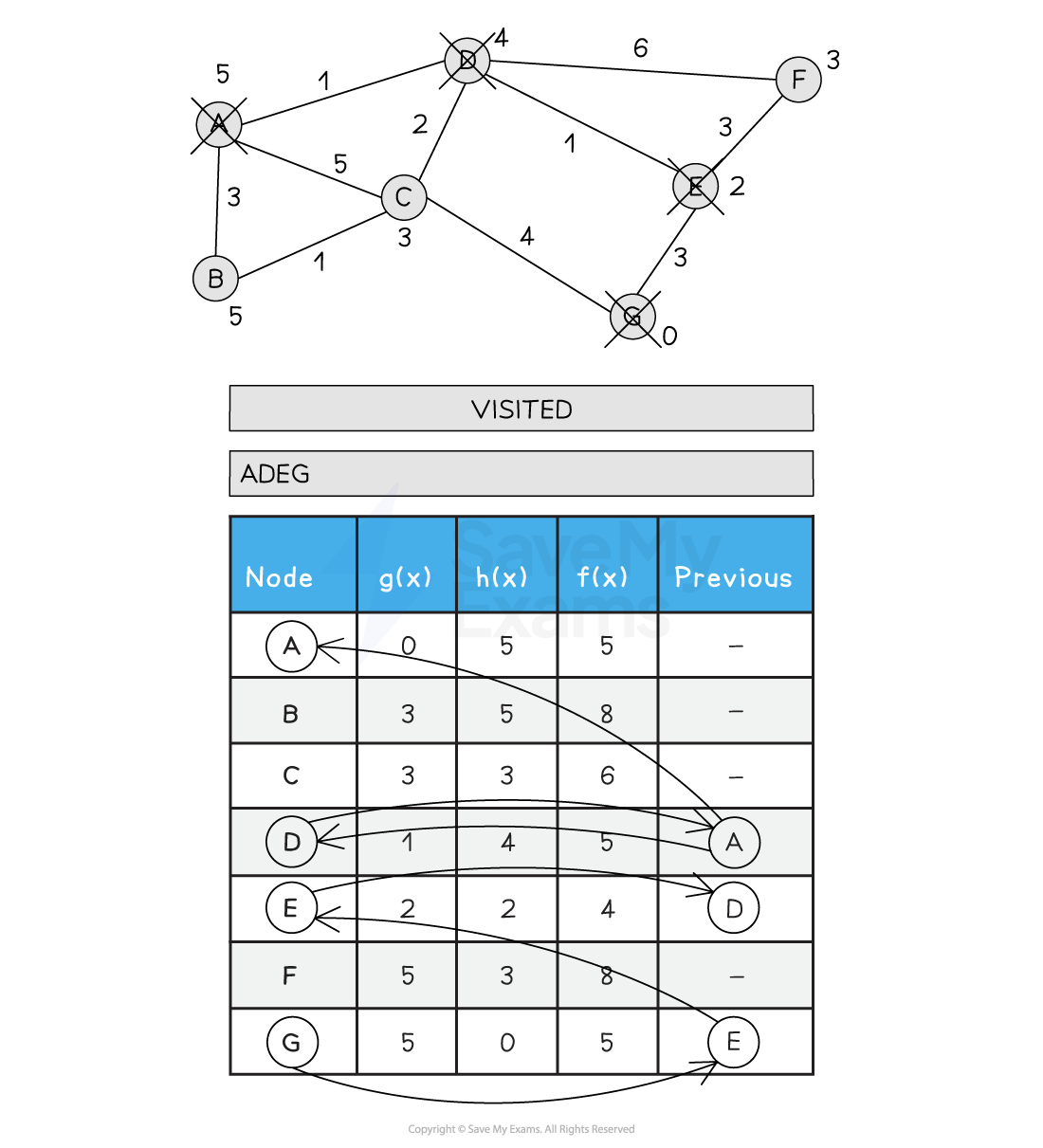
Figure 2: Performing the A* Search
A* vs Dijkstra’s
|
Feature |
Dijkstra’s |
A* Search |
|---|---|---|
|
Goal-aware? |
No |
Yes |
|
Cost function |
|
|
|
Speed |
Slower (explores more) |
Faster (more direct toward goal) |
|
Use of heuristic |
None |
Yes, estimates distance to goal |
|
Best for… |
Full shortest path map |
Fastest route to a specific destination |
Programming A* algorithm
How do you write an A* algorithm?
Pseudocode
FUNCTION AStarSearch(graph, start, goal) // Initialise distances and f-scores FOR EACH node FROM graph SET g[node] TO infinity SET f[node] TO infinity NEXT node SET g[start] TO 0 SET f[start] TO h[start] DECLARE openSet AS LIST ADD start TO openSet WHILE openSet IS NOT EMPTY // Find node in openSet with the lowest f value SET min TO null FOR EACH node FROM openSet IF min = null THEN SET min TO node ELSEIF f[node] < f[min] THEN SET min TO node ENDIF NEXT node IF min = goal THEN EXIT WHILE ENDIF REMOVE min FROM openSet // Check all neighbours of current node FOR EACH neighbour FROM graph[min] SET tentativeG TO g[min] + cost(min, neighbour) IF tentativeG < g[neighbour] THEN SET g[neighbour] TO tentativeG SET f[neighbour] TO g[neighbour] + h[neighbour] SET previousNode[neighbour] TO min IF neighbour NOT IN openSet THEN ADD neighbour TO-
graph[min]assumes you’re storing adjacency lists -
h[node]is your heuristic table -
g[]andf[]are maps (dictionaries) for real cost and estimated total cost -
cost(min, neighbour)should be defined or assumed available
Python
def a_star_search(graph, start, goal, h): open_set = [start] g = {node: float('inf') for node in graph} f = {node: float('inf') for node in graph} came_from = {} g[start] = 0 f[start] = h[start] while open_set: # Get node with lowest f value current = min(open_set, key=lambda node: f[node]) if current == goal: break open_set.remove(current) for neighbour, cost in graph[current]: tentative_g = g[current] + cost if tentative_g < g[neighbour]: g[neighbour] = tentative_g f[neighbour] = g[neighbour] + h[neighbour] came_from[neighbour] = current if neighbour not in open_set: open_set.append(neighbour) # Reconstruct path path = [] node = goal while node != start: path.append(node) node = came_from[node] path.append(start) path.reverse() return pathExample usage:
graph = { 'A': [('B', 2), ('C', 5)], 'B': [('D', 4)], 'C': [('D', 1)], 'D': [('E', 3)], 'E': []
} h = { 'A': 7, 'B': 6, 'C': 4, 'D': 2, 'E': 0
} print(a_star_search(graph, 'A', 'E', h))Output:
-
A possible shortest path from
'A'to'E', guided by the heuristic values

Responses