Exam code:J277
What is a Programming Construct?
-
A programming construct determines the order in which lines of code are executed
-
They control logic and behaviour of code
-
There are three core programming constructs:
-
Sequence
-
Selection
-
Iteration
-
Sequence
What is sequence?
-
Sequence refers to lines of code which are run one line at a time
-
The lines of code are run in the order that they written from the first line of code to the last line of code
-
Sequence is crucial to the flow of a program, any instructions out of sequence can lead to unexpected behaviour or errors
Example
-
A simple program to ask a user to input two numbers, number two is subtracted from number one and the result is outputted
|
Line |
OCR reference language/Python |
|---|---|
|
01 |
|
|
02 |
|
|
03 |
|
|
04 |
|
|
05 |
|
|
06 |
|
-
A simple swap of line 01 and line 02 would lead to an unexpected behaviour, the user would be prompted to input information without knowing what they should enter
Selection
What is selection?
-
Selection is when the flow of a program is changed, depending on a set of conditions
-
The outcome of this condition will then determine which lines or block of code is run next
-
Selection is used for validation, calculation and making sense of a user’s choices
-
There are two ways to write selection statements:
-
if… then… else… statements – this is when you test conditions sequentially
-
case select or switch… statements – this is when you test an expression against multiple possible constant values (known as cases)
-
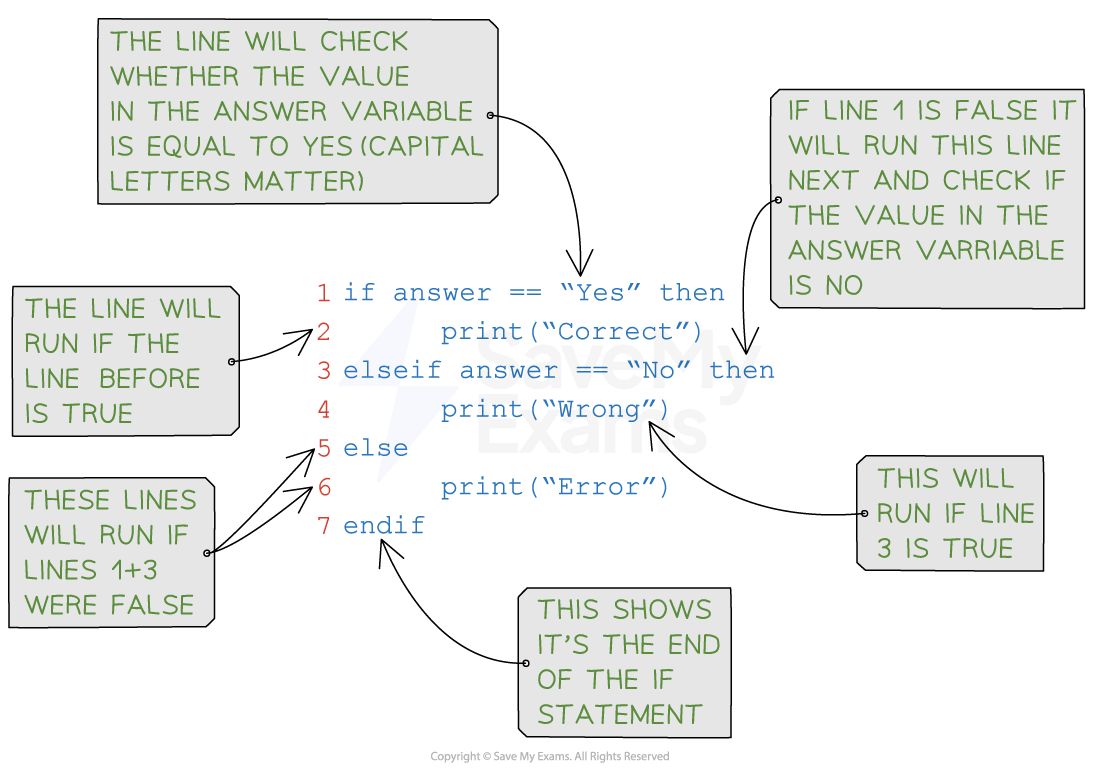
Example
|
Concept |
OCR exam reference |
Python |
|---|---|---|
|
IF-THEN-ELSE |
|
|
|
CASE SELECT or SWITCH |
|
|
If vs select case
-
Select case can mean less code but it only useful when comparing multiple values of the same variable
-
If statements can be more flexible and are generally used more in languages such as Python
Iteration
What is iteration?
-
Iteration is repeating a line or a block of code using a loop
-
Iteration can be:
-
count controlled – this is when the code is repeated a fixed number of times (e.g. using a for loop)
-
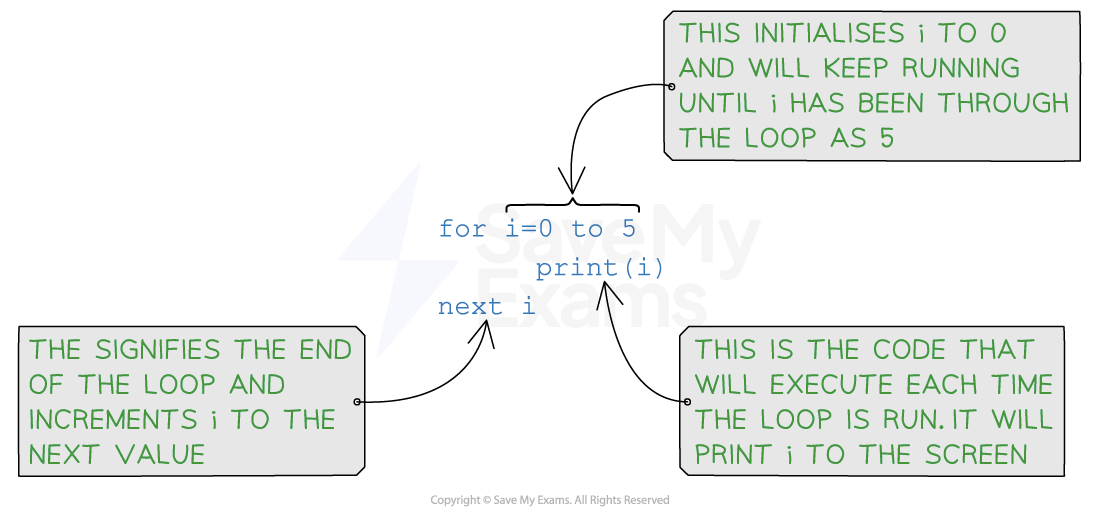
-
condition controlled – this is when the code is repeated until a condition is met (e.g. using a while loop or a do while loop)

Examples
|
Iteration |
OCR exam reference |
Python |
|---|---|---|
|
FOR loop (Count controlled) |
|
|
|
This will print the word “Hello” 10 times (0-9 inclusive) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
This will print the even numbers from 2 to 10 inclusive |
||
|
|
|
|
|
This will print the numbers from 10 to 0 inclusive |
||
|
WHILE loop (Condition controlled) |
|
|
|
|
This will loop until the user inputs the colour “Red”. Check condition is carried out before entering loop |
|
|
DO WHILE loop (Condition controlled) |
|
|
|
|
This will loop until the user inputs the colour “Red”. Loop iterates once before a check is carried out |
|
How to identify programming constructs
-
You can identify which programming constructs are used by looking at certain keywords
-
The keywords if, elseif, else, endif, switch, case indicate that the construct is selection
-
The keywords for, while, do indicate that the construct is iteration
-
If none of these keywords are used, this is a good indication that the construct is sequence
Worked Example
Tick (✓) one box in each row to identify whether each programming construct has or has not been used in the program [3]
total = 0
for i = 1 to 5
num = input("Enter a number")
total = total + num
next i
print(total)

Responses