Exam code:J277
Vectors & Bitmaps
-
Computers represent all data in binary, including images that are seen on a screen, TV or other output device
-
Images can be stored in binary as Bitmap or Vector
What is a bitmap?
-
A bitmap image is made up of squares called pixels
-
A pixel is the smallest element of a bitmap image
-
Each pixel is stored as a binary code
-
Binary codes are unique to the colour in each pixel
-
A typical example of a bitmap image is a photograph
-
The more colours and more detail in the image, the higher the quality of the image and the more binary that needs to be stored
What is a vector?
-
A vector image is created from mathematical equations and points
-
Only the mathematics used to create the image are stored
-
For example, to create a circle the data stored would be:
-
Centre point (x, y coordinates)
-
Radius
-
-
Typical examples of vector images are logos and clipart
-
Vector images are infinitely scalable
-
Ideal for situations where the same image will be made bigger and smaller and a loss of quality is unacceptable. For example, the same logo used on both a pencil and a billboard
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the exam, the focus will be on bitmap images. You need to know the basics of a vector but after that all questions will relate to bitmaps only!
Resolution & Colour Depth
What is resolution?
-
Resolution is the total amount of pixels that make up a bitmap image
-
The resolution is calculated by multiplying the height and width of the image (in pixels)
-
In general, the higher the resolution the more detail in the image (higher quality)
-
Resolution can also refer to the total amount of pixels horizontally in a display, such as:
-
Computer monitors – 1440p means 1440 pixels horizontally compared to 4K which is 3840 pixels (roughly 4 thousand)
-
TVs – HD (high definition) channels have a resolution of 1080p, 1080 pixels horizontally compared to newer UHD (ultra high definition) channels with 3840 pixels (4K)
-
YouTube – The quality button allows a user to change the video playback resolution from 144p (144 pixels horizontally) up to 4K
-
What is colour depth?
-
Colour depth is the number of bits stored per pixel in a bitmap image
-
The colour depth is dependent on the number of colours needed in the image
-
In general, the higher the colour depth the more detail in the image (higher quality)
-
In a black & white image the colour depth would be 1, meaning 1 bit is enough to create a unique binary code for each colour in the image (1=white, 0=black)

-
In an image with a colour depth of 2, you would have 00, 01, 10 & 11 available binary codes, so 4 colours
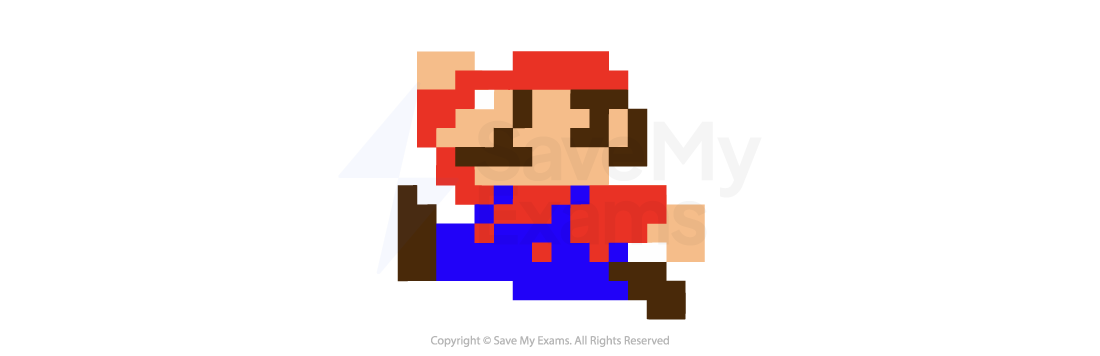
-
As colour depth increases, so does the amount of colours available in an image
-
The amount of colours can be calculated as 2n (n = colour depth)
|
Colour Depth |
Amount of Colours |
|---|---|
|
1 bit |
2 (B&W) |
|
2 bit |
4 |
|
4 bit |
16 |
|
8 bit |
256 |
|
24 bit |
16,777,216 (True Colour) |
What is the impact of resolution and colour depth?
-
As the resolution and/or colour depth increases, the bigger the size of the file becomes on secondary storage
-
The higher the resolution, the more pixels are in the image, the more bits are stored
-
The higher the colour depth, the more bits per pixel are stored
-
Striking a balance between quality and file size is always a consideration
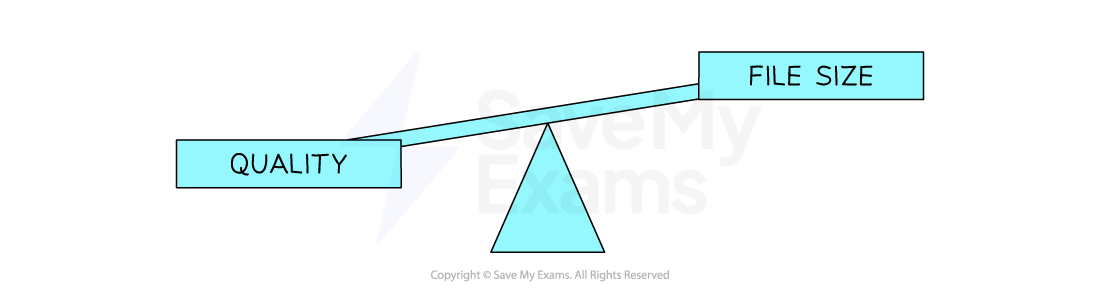
Worked Example
1. Define the term Pixel [1]
2. If an image has a colour depth of 2 bits, how many colours can the image represent? [1]
3. Describe the impact of changing an images resolution from 500×500 to 1000×1000 [2]
Answers
-
The smallest element of a bitmap image (1 square)
-
4
-
The image quality would be higher [1] the file size would be larger [1]
Metadata
What is metadata?
-
Metadata is data about data
-
Metadata is additional information stored with the image, although not required to display the image it provides context and information
-
Examples of metadata that can be stored are:
-
Author – Who created the image?
-
Date/Time – When and what time was the image created/taken?
-
Location – Where was the image taken?
-
Width & height of the image (resolution)
-
Colour depth
-
Worked Example
A parent takes a photograph of their family whilst on holiday. The image file includes metadata.
Identify three pieces of metadata that is often stored with an image [3]
Answer
-
Location
-
Author
-
Resolution

Responses