Exam code:J277
Denary to Hexadecimal Conversion
What is hexadecimal?
-
Hexadecimal is a number system that is made up of 16 digits, 10 numbers (0-9) and 6 letters (A-F)
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
-
Hexadecimal is referred to as a Base-16 number system
-
Each digit has a weight factor of 16 raised to a power, the rightmost digit is 1s (16^0), the next digit to the left 16s (16^1)
-
In GCSE you are required to work with up to and including 2 digit hexadecimal values
|
16s |
1s |
|
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
3 |
|
|
1 x16 |
3 x 1 |
= 19 |
-
A quick comparison table demonstrates a relationship between hexadecimal and a binary nibble
-
One hexadecimal digit can represent four bits of binary data

Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common exam mistake is mixing up which letter matches with what number, write out the 16 hexadecimal digits at the start of the exam!
Why is hexadecimal used?
-
In Computer Science hexadecimal is often preferred when working with large values
-
It takes fewer digits to represent a given value in hexadecimal than in binary
-
It is beneficial to use hexadecimal over binary because:
-
The more bits there are in a binary number, the harder it is to read
-
Numbers with more bits are more prone to errors when being copied
-
-
Examples of where hexadecimal can be seen:
-
MAC addresses
-
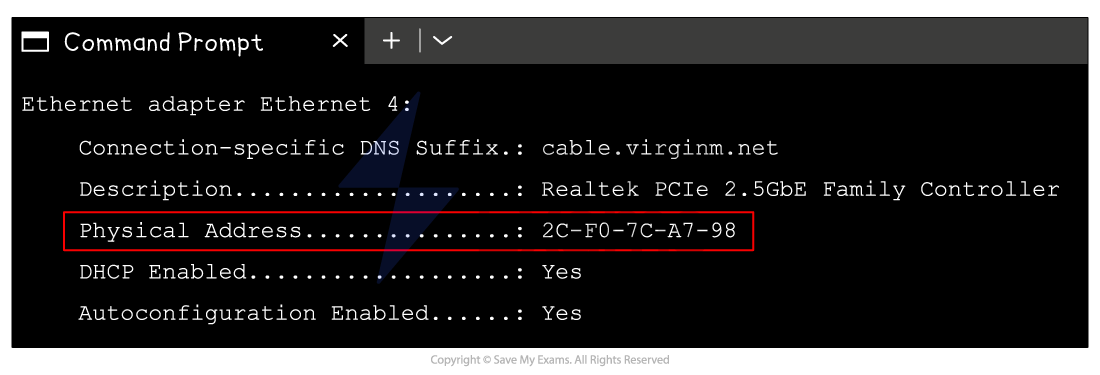
-
Colour values
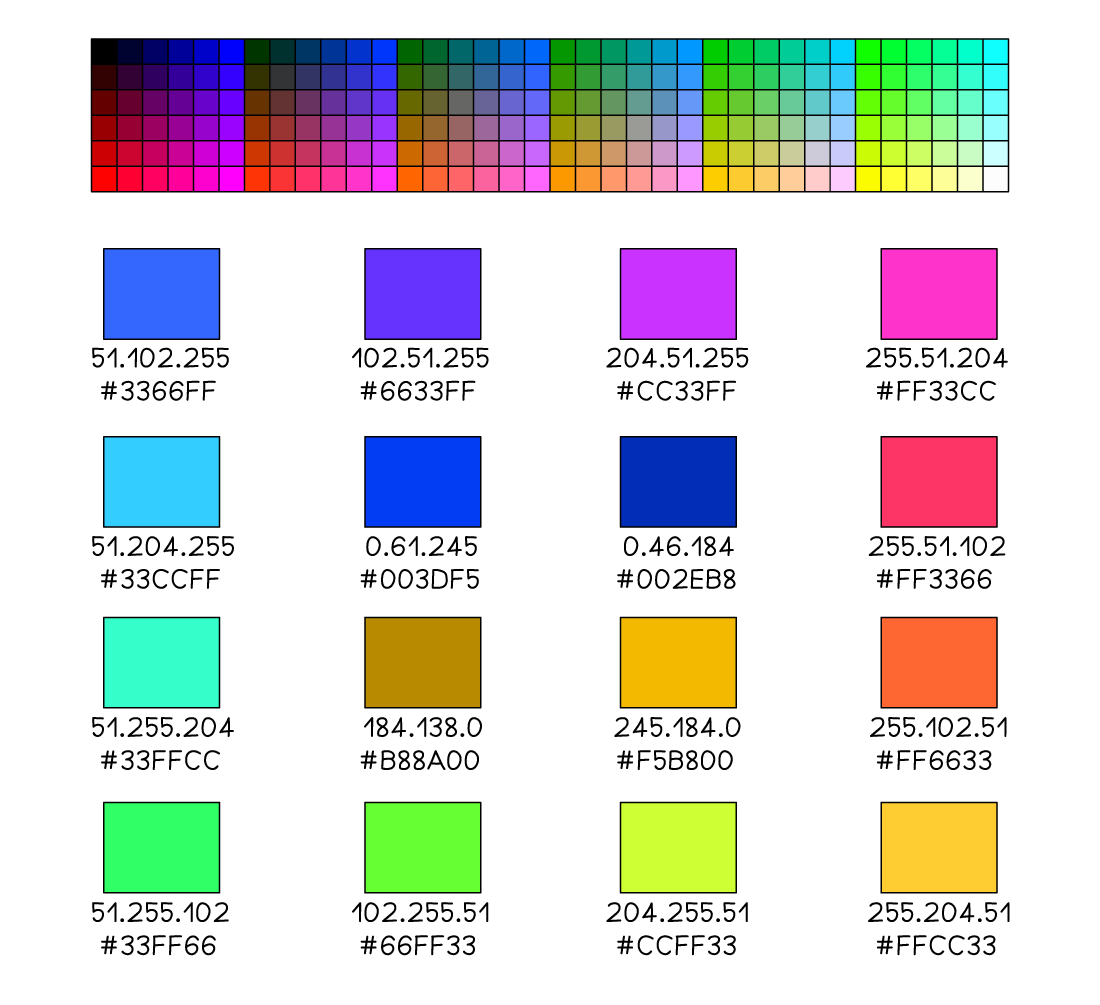
How do you convert denary to hexadecimal?
Method 1 (denary to binary to hexadecimal)
-
To convert the denary number 28 to hexadecimal, start by converting the denary number to binary
|
128 |
64 |
32 |
16 |
8 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
-
Split the 8 bit binary number into two nibbles as shown below

-
Convert each nibble to its denary value
-
0001 = 1 and 1100 = 12
-
Using the comparison table, the denary value 1 is also 1 in hexadecimal whereas denary value 12 is represented in hexadecimal as C
-
Denary 28 is 1C in hexadecimal
Method 2 (divide by 16)
-
To convert the denary number 163 to hexadecimal, start by dividing the denary value by 16 and recording the whole times the number goes in and the remainder
-
163 <img alt=”divided by” data-mathml=”<math ><semantics><mo>÷</mo><annotation encoding=”application/vnd.wiris.mtweb-params+json”>{“fontFamily”:”Times New Roman”,”fontSize”:”18″,”autoformat”:true,”toolbar”:”<toolbar ref=’general’><tab ref=’general’><removeItem ref=’setColor’/><removeItem ref=’bold’/><removeItem ref=’italic’/><removeItem ref=’autoItalic’/><removeItem ref=’setUnicode’/><removeItem ref=’mtext’ /><removeItem ref=’rtl’/><removeItem ref=’forceLigature’/><removeItem ref=’setFontFamily’ /><removeItem ref=’setFontSize’/></tab></toolbar>”}</annotation></semantics></math>” height=”19″ role=”math” src=”data:image/svg+xml;charset=utf8,%3Csvg%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F2000%2Fsvg%22%20xmlns%3Awrs%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.wiris.com%2Fxml%2Fmathml-extension%22%20height%3D%2219%22%20width%3D%2219%22%20wrs%3Abaseline%3D%2216%22%3E%3C!–MathML%3A%20%3Cmath%20xmlns%3D%22http%3A%2F%2Fwww.w3.org%2F1998%2FMath%2FMathML%22%3E%3Cmo%3E%26%23xF7%3B%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E–%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A’math13cec07e9ba5f5bb252d13f5f43’%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAm2hlYWQQC2qxAAACKAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAmAAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKEAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACjAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAApgAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAAK4AAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEWAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABHgAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAAPf%2F%2FwAAAPf%2F%2F%2F8KAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAADAIAAgAMAAoAAAwAHAAsAQRgBsAQQsQAD9LEEB%2FSwCDyxBRH0sAo8sQEH9LEMA%2BYAsQMMENWxAAX1sAMQsQgF9bELEfWwABCxBwX1sQQR9TAxEyEVIQEzFSMRMxUjgAKA%2FYABAICAgIABq1YBK4D%2FAIAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVA4AAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAmwABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADg

Responses