Computer Science GCES AQA
-
Representing Algorithms Aqa4 主题
-
Efficiency Of Algorithms Aqa1 主题
-
Searching Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Sorting Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Data Types Aqa1 主题
-
Programming Concepts Aqa5 主题
-
Arithmetic Relational And Boolean Operations Aqa1 主题
-
Data Structures Aqa3 主题
-
String Manipulation Aqa1 主题
-
Random Number Generation Aqa1 主题
-
Structured Programming Aqa2 主题
-
Robust And Secure Programming Aqa4 主题
-
Number Bases Aqa2 主题
-
Converting Between Number Bases Aqa3 主题
-
Units Of Information Aqa9 主题
-
Hardware And Software Aqa4 主题
-
Boolean Logic Aqa3 主题
-
Programming Languages And Translators Aqa2 主题
-
Cpu Architecture Performance And Embedded Systems Aqa4 主题
-
Memory Aqa2 主题
-
Secondary Storage Aqa3 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Computer Networks Aqa8 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Cyber Security Aqa1 主题
-
Methods Of Preventing Cyber Security Threats Aqa1 主题
-
Relational Databases Aqa2 主题
-
Ethical Legal And Environmental Impacts Aqa2 主题
Representing Images Aqa
Exam code:8525
Pixels
What is a bitmap?
-
A bitmap image is made up of squares called pixels, meaning picture elements
-
A pixel is a single point in a image
-
Each pixel is stored as a binary code
-
Binary codes are unique to the colour in each pixel
-
A typical example of a bitmap image is a photograph
-
The more colours and more detail in the image, the higher the quality of the image and the more binary that needs to be stored
Image Size & Colour Depth
What is image size?
-
image size is the total amount of pixels that make up a bitmap image
-
The image size is calculated by multiplying the height and width of the image (in pixels)
-
In general, the higher the image size the more detail in the image (higher quality)
What is colour Depth?
-
Colour depth is the number of bits stored per pixel in a bitmap image
-
The colour depth is dependent on the number of colours needed in the image
-
In general, the higher the colour depth the more detail in the image (higher quality)
-
In a black & white image the colour depth would be 1, meaning 1 bit is enough to create a unique binary code for each colour in the image (1=white, 0=black)

-
In an image with a colour depth of 2, you would have 00, 01, 10 & 11 available binary codes, so 4 colours
-
As colour depth increases, so does the amount of colours available in an image
-
The amount of colours can be calculated as 2n (n = colour depth)
|
Colour Depth |
Amount of Colours |
|
1 bit |
2 (B&W) |
|
2 bit |
4 |
|
4 bit |
16 |
|
8 bit |
256 |
|
24 bit |
16,777,216 (True Colour) |
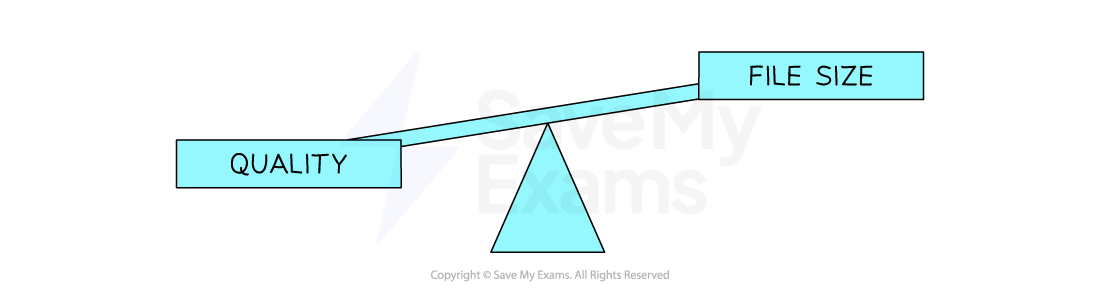
What is the impact of image size and colour depth?
-
As the image size and/or colour depth increases, the bigger the size of the file becomes on secondary storage
-
The higher the image size, the more pixels are in the image, the more bits are stored
-
The higher the colour depth, the more bits per pixel are stored
-
Striking a balance between quality and file size is always a consideration
Calculate Bitmap File Size
How do you calculate the size of a bitmap image?
-
Calculating the size of a bitmap image is carried out with the following formula:
-
Image size x colour depth OR
-
Image width x image height x colour depth
-
Example
|
Image Files |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(Image size) x (Colour Depth) |
||||||||||||
|
OR
|
Image Files |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(Image width) x (Image height) x (Colour Depth) |
|||||||||||||||
|
Converting Between Binary Data & Bitmaps
How do you convert binary data into a bitmap image?
-
To convert binary data into a bitmap image:
-
Image metadata is read
-
Using this information binary data can be mapped to individual pixels
-
A bitmap image is created
-
What is metadata?
-
Metadata is data about data
-
Metadata is additional information stored with the image, it provides context and information
-
Examples of metadata that are stored are:
-
Image size
-
Colour depth
-
Author – Who created the image?
-
Date/Time – When and what time was the image created/taken?
-
Location – Where was the image taken?
-
Example
-
A bitmap image with binary data:
|
Binary data |
|---|
|
111111111110111011100010001100000001100000001110000011111000111111101111111111111 |
-
And metadata of:
-
Width: 9px
-
Height: 9px
-
Colour depth: 1 bit
-
-
1 bit is a monochrome image (B&W), typically 1 = black and 0 = white
-
Every 9 pixels a new line is created
-
The resulting image would be:
|
Binary data |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|||

Responses