Computer Science GCES AQA
-
Representing Algorithms Aqa4 主题
-
Efficiency Of Algorithms Aqa1 主题
-
Searching Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Sorting Algorithms Aqa3 主题
-
Data Types Aqa1 主题
-
Programming Concepts Aqa5 主题
-
Arithmetic Relational And Boolean Operations Aqa1 主题
-
Data Structures Aqa3 主题
-
String Manipulation Aqa1 主题
-
Random Number Generation Aqa1 主题
-
Structured Programming Aqa2 主题
-
Robust And Secure Programming Aqa4 主题
-
Number Bases Aqa2 主题
-
Converting Between Number Bases Aqa3 主题
-
Units Of Information Aqa9 主题
-
Hardware And Software Aqa4 主题
-
Boolean Logic Aqa3 主题
-
Programming Languages And Translators Aqa2 主题
-
Cpu Architecture Performance And Embedded Systems Aqa4 主题
-
Memory Aqa2 主题
-
Secondary Storage Aqa3 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Computer Networks Aqa8 主题
-
Fundamentals Of Cyber Security Aqa1 主题
-
Methods Of Preventing Cyber Security Threats Aqa1 主题
-
Relational Databases Aqa2 主题
-
Ethical Legal And Environmental Impacts Aqa2 主题
Basic Programming Concepts Aqa
Exam code:8525
What is a programming concept?
-
A programming concept, also known as a construct, determines the order in which lines of code are executed
-
They control the logic and behaviour of code
-
There are three core programming constructs:
-
Sequence
-
Selection
-
Iteration
-
Sequence
What is sequence?
-
Sequence refers to lines of code which are run one line at a time
-
The lines of code are run in the order that they written from the first line of code to the last line of code
-
Sequence is crucial to the flow of a program, any instructions out of sequence can lead to unexpected behaviour or errors
Example
-
A simple program to ask a user to input two numbers, number two is subtracted from number one and the result is outputted
|
Line |
Python |
|
01 |
|
|
02 |
|
|
03 |
|
|
04 |
|
|
05 |
|
|
06 |
|
-
A simple swap of line 01 and line 02 would lead to an unexpected behaviour, the user would be prompted to input information without knowing what they should enter
Selection
What is selection?
-
Selection is when the flow of a program is changed, depending on a set of conditions
-
The outcome of this condition will then determine which lines or block of code is run next
-
Selection is used for validation, calculation and making sense of a user’s choices
-
if… then… else… statements are used when you test conditions sequentially
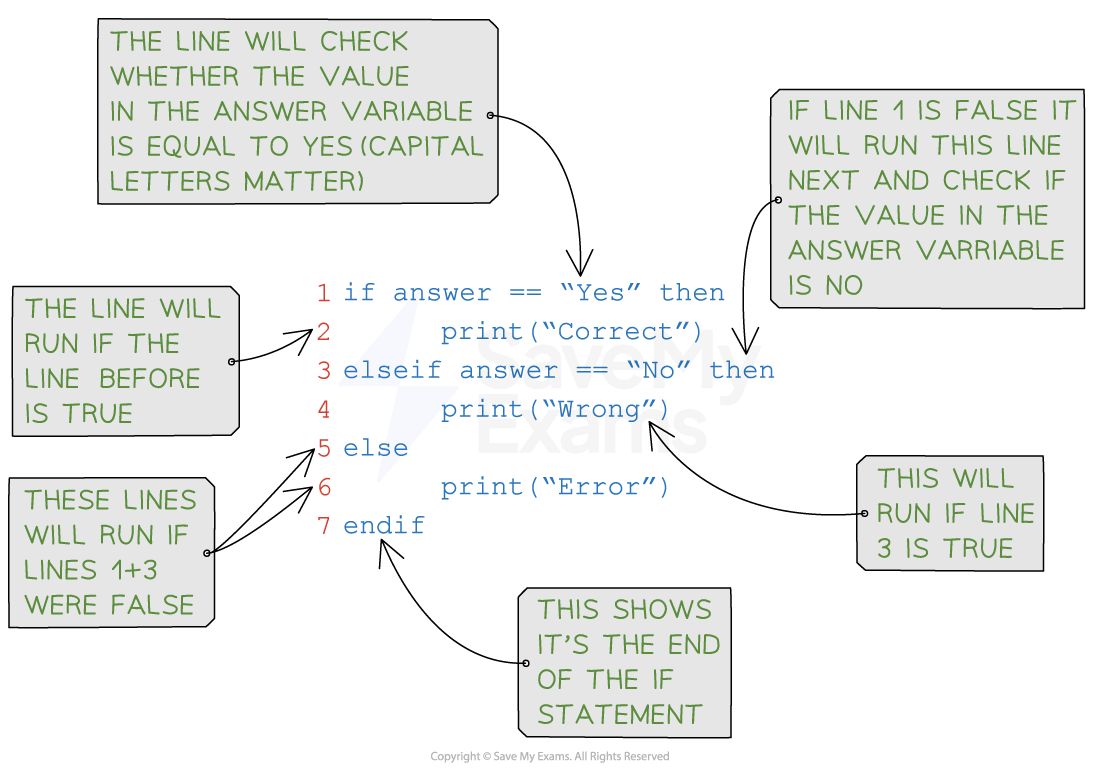
Example
|
Concept |
Pseudocode |
Python |
|---|---|---|
|
IF-THEN-ELSE |
|
|
Nested Selection
What is nested selection?
-
Nested means to be ‘stored inside the other’
-
An example of nested selection is one IF statement inside of another
-
It is worth noting that iteration can be nested as well and this can be seen in the iteration revision note
Examples of nested selection


Responses