Computer Science AS CIE
-
data-representation as5 主题
-
multimedia as3 主题
-
compression as2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet as11 主题
-
computers-and-components as5 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits as2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture as6 主题
-
assembly-language- as4 主题
-
bit-manipulation as1 主题
-
operating-systems as3 主题
-
language-translators as2 主题
-
data-security as3 主题
-
data-integrity as1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership as3 主题
-
database-concepts as3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms- as1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml as1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills as1 主题
-
algorithms as4 主题
-
data-types-and-records as2 主题
-
arrays as2 主题
-
files as1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt as1 主题
-
programming-basics as1 主题
-
constructs as2 主题
-
structured-programming as1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle as1 主题
-
program-design- as2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance as3 主题
state-transition-diagrams as
Exam code:9618
State-Transition Diagrams
What are state-transition diagrams?
-
A state-transition diagram shows how a system moves between different states based on inputs
-
Each state represents a condition or situation of the system
-
Transitions are arrows that show movement between states when certain inputs occur
-
Transitions may also produce outputs, shown as labels on the arrows
-
These diagrams model finite-state machines (FSMs), which are widely used in computing
Key elements
|
Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
State |
Circle labelled with a name (e.g. S1, S2) showing a situation the system can be in |
|
Initial state |
Starting point, sometimes marked with an arrow pointing to it |
|
Transition |
Arrow from one state to another, labelled with input and output |
|
Input |
Event or data that causes a transition (e.g. Button-Y pressed) |
|
Output |
Action or signal produced by a transition (e.g. Output-A) |
|
Next state |
The state the system moves into after the transition |
How to read labels on transitions
-
Labels are often written as Input | Output
-
If no output is produced, “none” may be written
-
Example:
Button-Y | Output-Bmeans pressing Button-Y in the current state produces Output-B and causes a transition to the next state -
The diagram below shows the key features of a state-transition diagram:
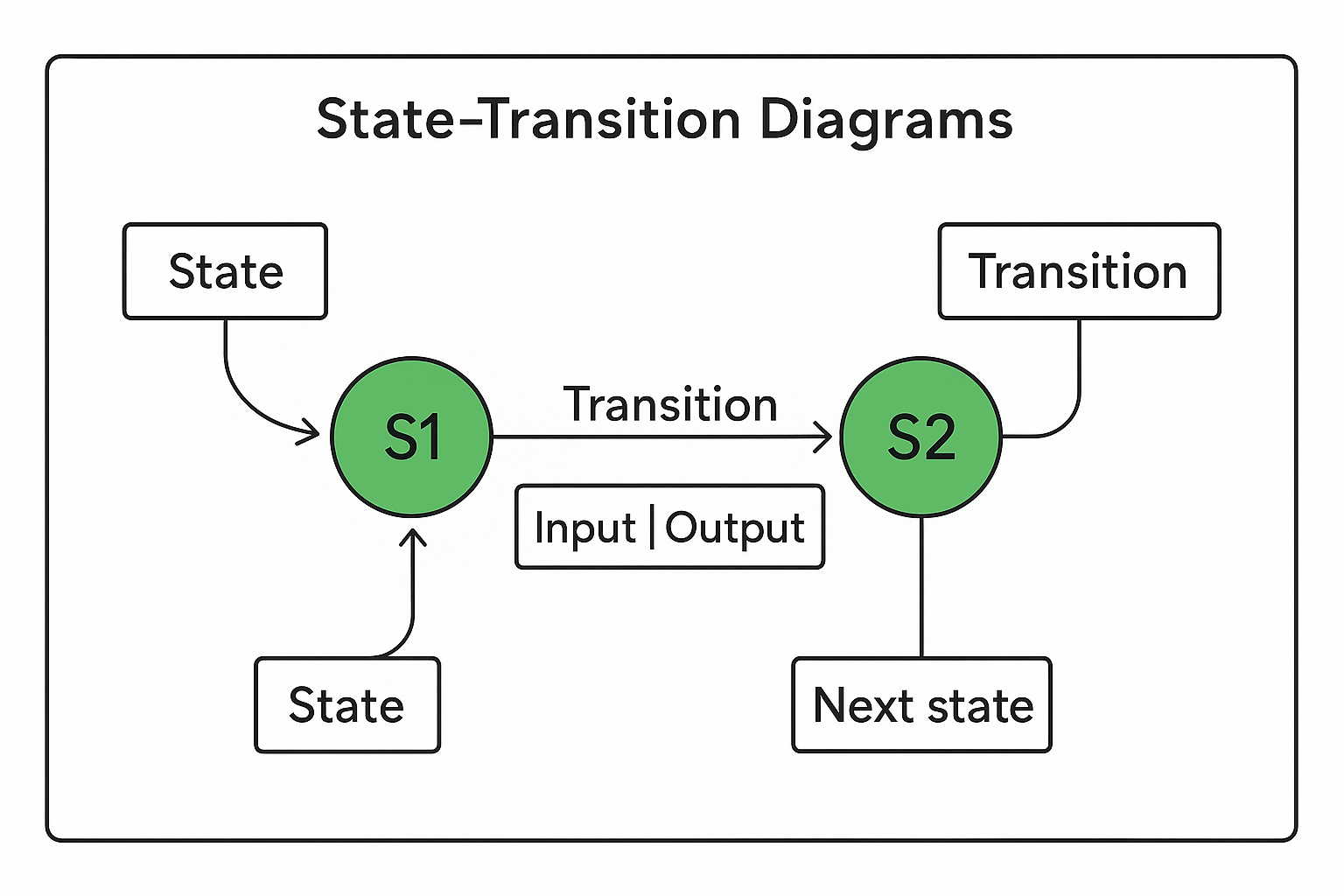
-
States are circles labelled S1, S2, etc
-
Transitions are arrows between states, labelled with Input | Output
-
The initial state is marked with an incoming arrow
Completing transition tables
-
Exam questions often ask you to convert a diagram into a table
-
The table normally has columns for Current state, Input, Output, Next state
-
Work through the diagram row by row, following the arrows for each possible input
Example table structure:
|
Current state |
Input |
Output |
Next state |
|---|---|---|---|
|
S1 |
Button-Y |
Output-A |
S2 |
|
S1 |
Button-Z |
Output-B |
S3 |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
Always identify the initial state before tracing
-
Highlight or mark inputs and outputs on your diagram to avoid missing one
-
For tables, keep the order consistent: Input → Output → Next state
-
Use arrows systematically, avoid guessing paths
-
Remember: more than one sequence can sometimes reach the same state, but exams often ask for the minimum changes
Worked Example
Part of a program is represented by the following state‑transition diagram
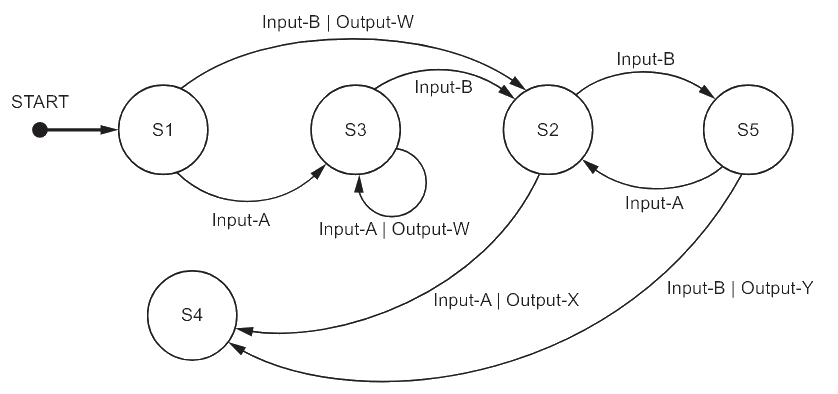
A. Complete the table to show the inputs, outputs and next states.
Assume that the current state for each row is given by the ‘Next state’ on the previous row. For example, the first Input‑A is made when in state S1.
If there is no output for a given transition, then the output cell should contain ‘none’.
The first two rows have been completed.
|
Input |
Output |
Next state |
|---|---|---|
|
S1 |
||
|
Input-A |
none |
S3 |
|
Output-W |
||
|
none |
||
|
Input-B |
||
|
Input-A |
||
|
S4 |
[5]
B. Identify the input sequence that will cause the minimum number of state changes in the transition from S1 to S4
[1]
Answers
A.
|
Input |
Output |
Next state |
|---|---|---|
|
S1 |
||
|
Input-A |
none |
S3 |
|
Input-A |
Output-W |
S3 |
|
Input-B |
none |
S2 |
|
Input-B |
none |
S5 |
|
Input-A |
none |
S2 |
|
Input-A |
Output-X |
S4 |
-
One mark per row 3 to 7 [5 marks]
B. Input-B, Input-A [1 mark]

Responses