Computer Science AS CIE
-
data-representation as5 主题
-
multimedia as3 主题
-
compression as2 主题
-
networks-and-the-internet as11 主题
-
computers-and-components as5 主题
-
logic-gates-and-logic-circuits as2 主题
-
central-processing-unit-cpu-architecture as6 主题
-
assembly-language- as4 主题
-
bit-manipulation as1 主题
-
operating-systems as3 主题
-
language-translators as2 主题
-
data-security as3 主题
-
data-integrity as1 主题
-
ethics-and-ownership as3 主题
-
database-concepts as3 主题
-
database-management-systems-dbms- as1 主题
-
data-definition-language-ddl-and-data-manipulation-language-dml as1 主题
-
computational-thinking-skills as1 主题
-
algorithms as4 主题
-
data-types-and-records as2 主题
-
arrays as2 主题
-
files as1 主题
-
introduction-to-abstract-data-types-adt as1 主题
-
programming-basics as1 主题
-
constructs as2 主题
-
structured-programming as1 主题
-
program-development-life-cycle as1 主题
-
program-design- as2 主题
-
program-testing-and-maintenance as3 主题
array-basics as
Exam code:9618
Arrays
What is an array?
-
An array is an ordered, static set of elements
-
Can only store 1 data type
-
The position of each element in an array is identified using the array’s index
-
The array’s first element is the lower bound (LB)
-
The array’s last element is the upper bound (UB)
-
The lower bound of an array is typically 0 or 1 depending on the language being used
-
An array can be one-dimensional or multi-dimensional
One-dimensional (1D) arrays
-
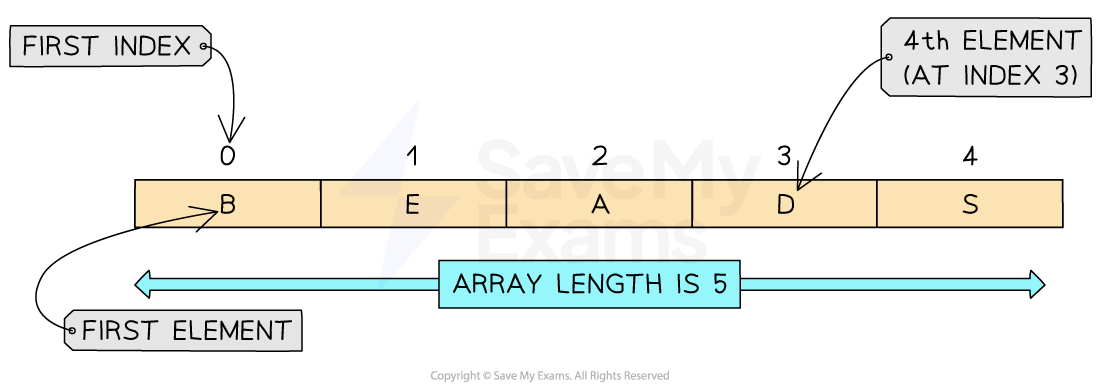
A 1D array is a linear array
-
To declare a 1D array in pseudocode you must include the lower bound, upper bound and data types:
DECLARE <identifier> : ARRAY[LB:UB] OF <data type>-
In this example a 1D array of five elements each containing single character can be declared as:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:4] OF CHAR-
An example complete program could be:
// Declare the array
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:4] OF CHAR // Assign values to each index
Letters[0] ← 'B'
Letters[1] ← 'E'
Letters[2] ← 'A'
Letters[3] ← 'D'
Letters[4] ← 'S' // Output the full array
FOR Index ← 0 TO 4 OUTPUT Letters[Index]
NEXT Index-
The array is declared with indices from
0to4 -
Each element stores a single character using the
CHARdata type -
The loop outputs each letter in order
Two-dimensional (2D) arrays
-
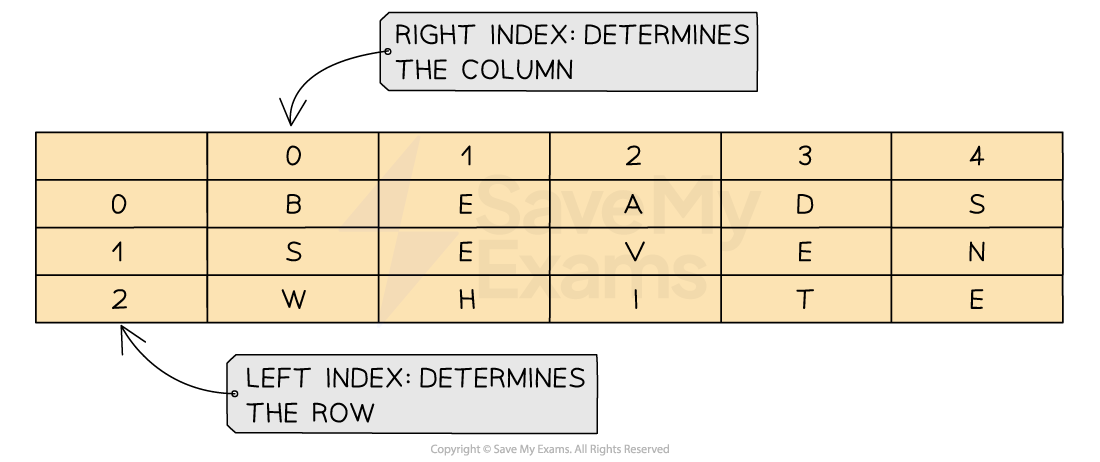
A 2D array can be visualised as a table
-
When navigating through a 2D array you first have to go down the rows and then across the columns to find a position within the array
-
In 2D arrays the following must be declared:
-
Lower bound for rows (LBR) & upper bound for rows (UBR)
-
Lower bound for columns (LBC) & upper bound for columns (UBC)
-
DECLARE <identifier> : ARRAY[LBR:UBR, LBC:UBC] OF <data type>-
In this example a 2D array can be declared as:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:2, 0:4] OF CHAR-
An example complete program could be:
DECLARE Letters : ARRAY[0:2, 0:4] OF CHAR // Row 0
Grid[0,0] ← 'B'
Grid[0,1] ← 'E'
Grid[0,2] ← 'A'
Grid[0,3] ← 'D'
Grid[0,4] ← 'S' // Row 1
Grid[1,0] ← 'S'
Grid[1,1] ← 'E'
Grid[1,2] ← 'V'
Grid[1,3] ← 'E'
Grid[1,4] ← 'N' // Row 2
Grid[2,0] ← 'W'
Grid[2,1] ← 'H'
Grid[2,2] ← 'I'
Grid[2,3] ← 'T'
Grid[2,4] ← 'E'-
ARRAY[0:2, 0:4]creates 3 rows and 5 columns -
First index is the row, second is the column:
Letters[row, column] -
All elements are of type
CHAR
Worked Example
A program reads data from a file and searches for specific data.
The main program needs to read 25 integer data items from the text file Data.txt into a local 1D array, DataArray
Write program code to declare the local array DataArray [1]
Answer
-
1D array with name
DataArray(with 25 elements of type Integer) [1 mark]
Java
public static Integer[] DataArray = new Integer[25];
VB.NET
Dim DataArray(24) As Integer
Python
DataArray = [] #25 elements Integer

Responses