Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
selection-in-javascript
Selection in JavaScript
-
Programming code is made up of constructs which control the flow of a program
-
Constructs tell the computer the order in which to carry out the statements/lines of code
-
There are 3 programming constructs:
-
Sequence
-
Selection
-
Iteration
-
-
Selection is selecting a line/lines of code to run depending on whether a condition is true or false
-
There are two ways to write selection statements:
-
Ifstatements -
Switch casestatements
-
-
When writing a condition there will need to be a comparison operator. They are listed below:
|
Operator |
Description |
Example (where x=5) |
Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
|
== |
equal to |
x == 8 |
false |
|
x == 5 |
true |
||
|
x == “5” |
true |
||
|
=== |
equal value and equal type |
x === 5 |
true |
|
x === “5” |
false |
||
|
!= |
not equal |
x != 8 |
true |
|
!== |
not equal value or not equal type |
x !== 5 |
false |
|
x !== “5” |
true |
||
|
x !== 8 |
true |
||
|
> |
greater than |
x > 8 |
false |
|
< |
less than |
x < 8 |
true |
|
>= |
greater than or equal to |
x >= 8 |
false |
|
<= |
less than or equal to |
x <= 8 |
true |
IF Statements in JavaScript
-
An
if thestatement will let you choose a line/lines of code to run if a condition is true or false -
Below are three examples of
ifstatements:
-
if -
if else -
if else if else
Syntax of an if statement
The syntax of an if the statement consists of the if keyword, followed by a condition enclosed in brackets, and a code block that is executed if the condition evaluates to true:
if (condition) { // Code to be executed if the condition is true}
Pseudocode example of an if statement

Example in JavaScript: checking if a number is positive
const number = 5;
if (number > 0) { console.log('The number is positive.');}
-
In this example, the
ifstatement checks if the value of the variablenumberis greater than0. If the condition is true, the message'The number is positive.'is output to the browser
Syntax of an if-else statement
The if the statement can be extended with an else clause to specify an alternative block of code that is executed when the condition evaluates to false:
if (condition) { // Code to be executed if the condition is true} else {
// Code to be executed if the condition is false
}
Pseudocode example of an if-else statement
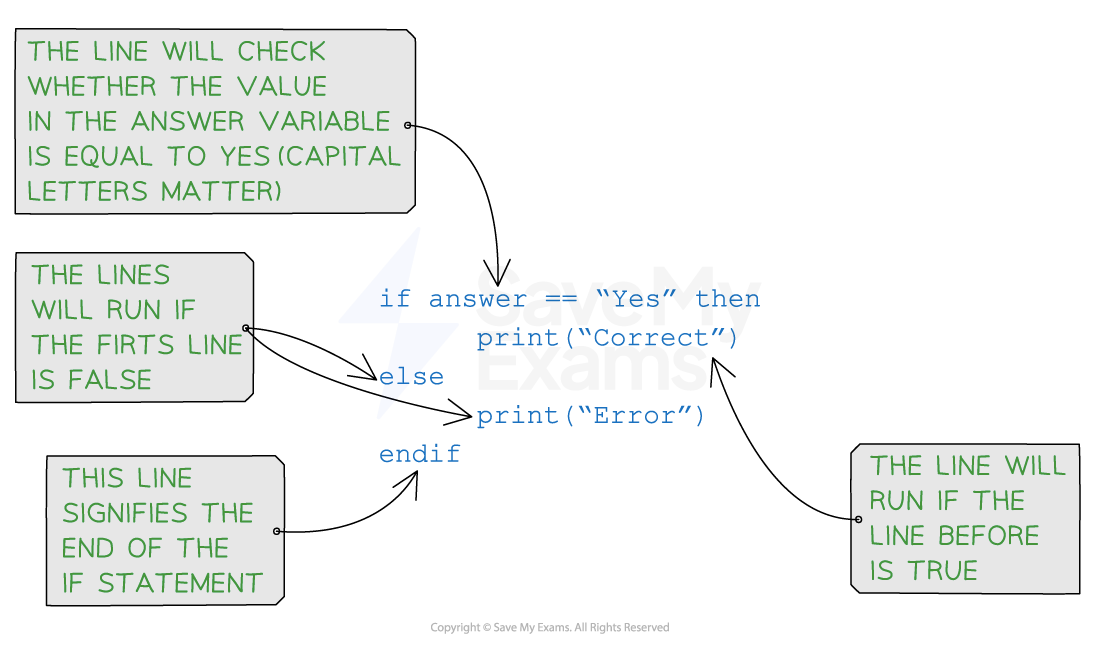
Example in JavaScript: Checking if a number is positive or negative
const number = -3;
if (number > 0) { console.log('The number is positive.');} else { console.log('The number is not positive.');}
-
In this example, if the value of
numberis greater than0, the message'The number is positive.'is output. Otherwise, the message'The number is not positive.'is output
Syntax of an If Else-If Else statement
The else if the clause specifies additional conditions to check if the initial if condition is false. This allows the handling of multiple scenarios in a more complex decision-making process:
if (condition) { // Code to be executed if the condition is true} else if (condition) {
// Code to be executed if the condition is true} else {
// Code to be executed if the condition is false
}
Pseudocode example of an If Else-If Else statement
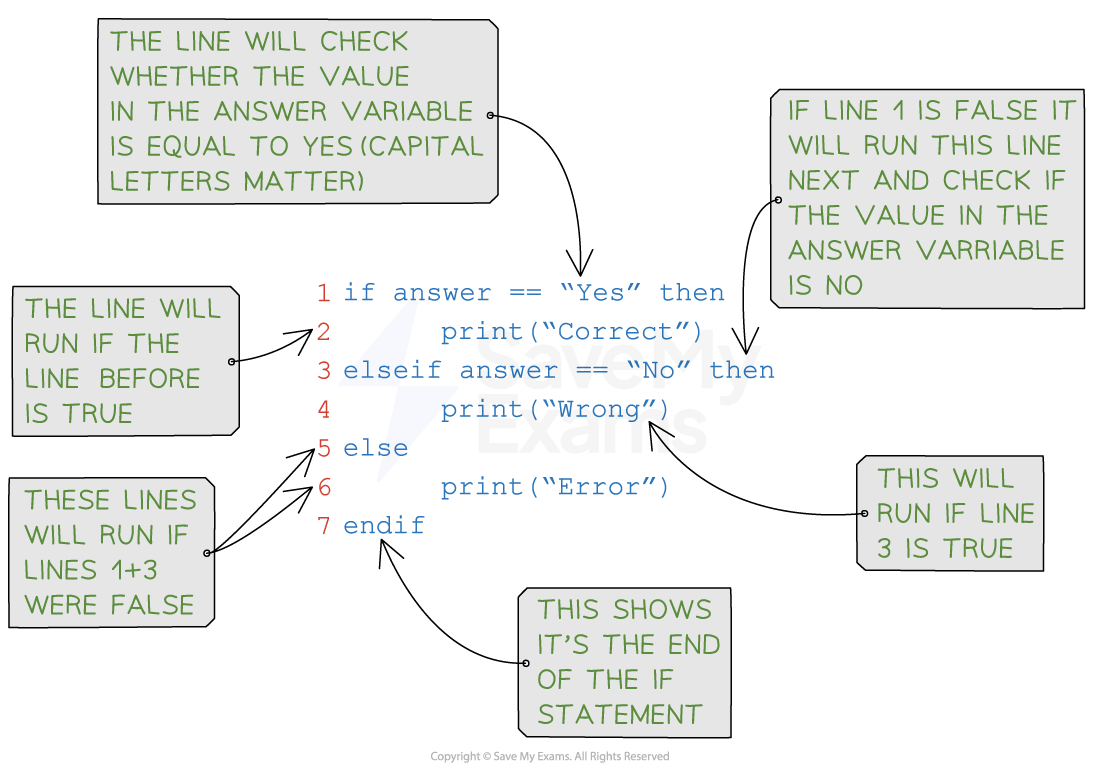
Example in JavaScript: Grading a score
const score = 85;
if (score >= 90) { console.log('Excellent!');} else if (score >= 80) { console.log('Good.');} else if (score >= 70) { console.log('Fair.');} else { console.log('Needs improvement.');}
-
In this example, the
if-else if-elsestatement evaluates the value ofscoreto determine the corresponding message based on the score range
Examiner Tips and Tricks
-
You can use as many
else ifs as you want to within yourifstatement but it might be clearer to use aswitch casestatement -
You can have an
if else-ifstatement without an end as the catch-all condition at the end
How do I write my condition?
-
Think of it like writing a yes/no question
-
E.g.
-
Is the number bigger than 10?
-
Is the number between 50 and 100?
-
Is the answer Paris?
-
-
If the question can’t be answered with yes/no then it needs to be rewritten in this way
Is it possible to use more than one operator?
-
Yes! Using one operator is most common but sometimes 2 are needed. More than 2 could be used but it gets more complicated. This involves using boolean operators
-
Imagine a program where the user has to enter a number based on the role of a dice. The number needs to be between 1 and 6
-
The yes/no question could be is the number between 1 and 6 – but it would be structured slightly differently in the code
-
IF number >=1 AND number <=6 then -
The first check is if the number is greater than or equal to 1
-
The second check is if the number is less than or equal to 6
-
The final check is if both sides are True

Responses