Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
hexadecimal-numbers
Representing Hexadecimal Numbers
What is hexadecimal?
-
Hexadecimal serves as a more human-friendly representation of binary-coded values
-
Hexadecimal is a base-16 number system that consists of:
-
10 numbers (0-9)
-
6 letters (A-F)
-
Why use hexadecimal instead of binary?
-
It is more concise as four binary bits (e.g. 1010) can be represented with one hexadecimal character (e.g. A)
-
It is easier for humans to read and write
-
it is less prone to error as it is more likely to be communicated correctly
Potential uses of hexadecimal
-
It is commonly used for debugging, configuring hardware devices, and in cryptographic algorithms
-
It also also commonly used to define colours. As there are millions of colours in the visual spectrum that require very large binary numbers to represent them, they can be replaced with shorter hexadecimal values
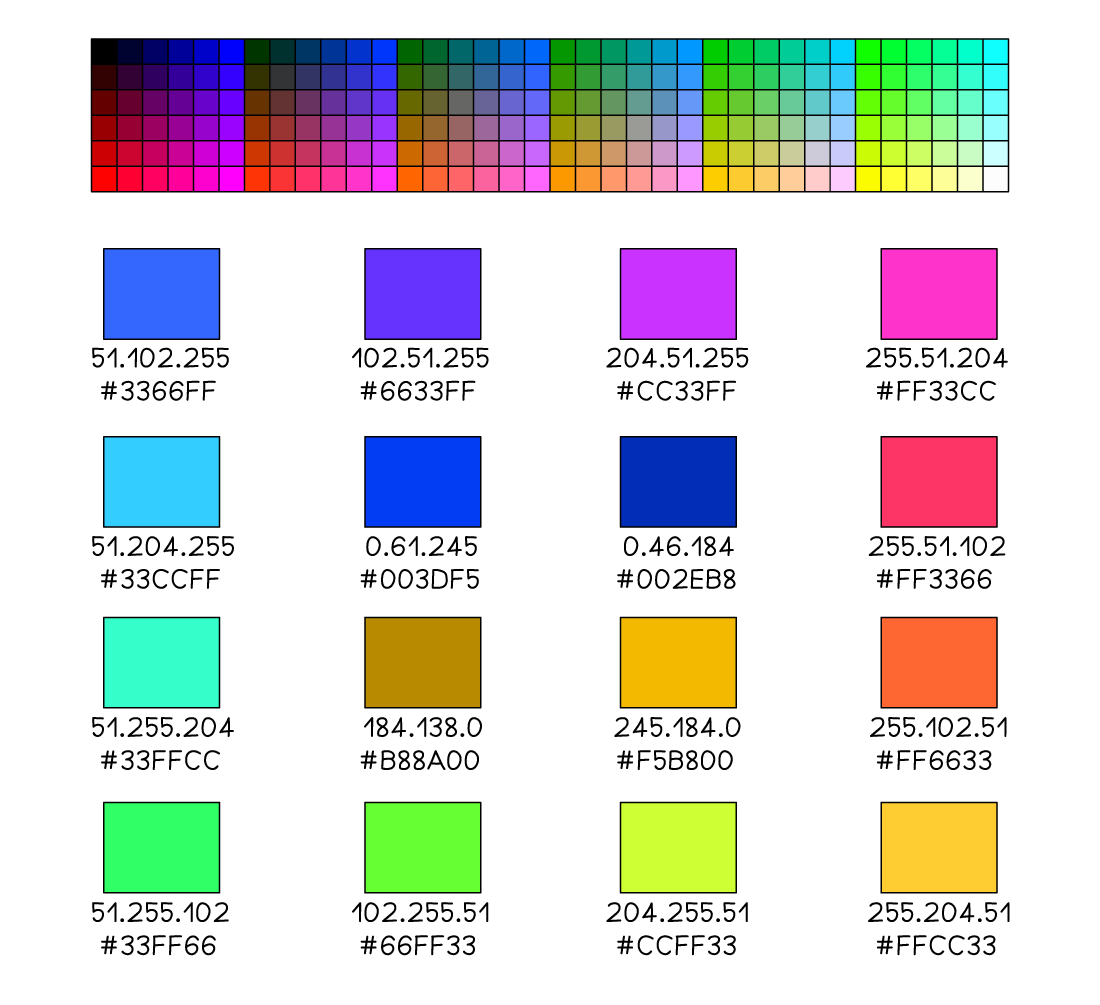
Sample hexcolours
Hexadecimal Lookup Table
-
The hexadecimal lookup table serves as a quick reference for converting numbers between denary, binary and hexadecimal values
-
The hexadecimal scale is identical to the denary scale until the tens column is introduced
-
When the denary scale reaches 10, this is when the hexadecimal scale switches to letters, starting with A
|
Denary |
Binary |
Hexadecimal |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
0000 |
0 |
|
1 |
0001 |
1 |
|
2 |
0010 |
2 |
|
3 |
0011 |
3 |
|
4 |
0100 |
4 |
|
5 |
0101 |
5 |
|
6 |
0110 |
6 |
|
7 |
0111 |
7 |
|
8 |
1000 |
8 |
|
9 |
1001 |
9 |
|
10 |
1010 |
A |
|
11 |
1011 |
B |
|
12 |
1100 |
C |
|
13 |
1101 |
D |
|
14 |
1110 |
E |
|
15 |
1111 |
F |
Using subscript in number representation
-
The subscript in number representation denotes the base of a number
-
It helps in differentiating between number systems
-
Common uses:
-
indicates the number is in binary (base 2), and its value is ’10’ in binary
-
indicates the number is in denary (base 10), and its value is ’10’ in denary
-
indicates the number is in hexadecimal (base 16), and its value is ’10’ in hex, equivalent to ’16’ in denary
-
-
It provides clarity, especially in contexts where multiple numbering systems are discussed
Denary to Hexadecimal
Convert the denary number 241 to hexadecimal.
Step 1: Convert the number to binary

Step 2: Split the binary number into nibbles

Step 3: Convert each nibble into its hexadecimal value

Step 4: Final result
The denary number 241 is F1 in hexadecimal.
Hexadecimal to Denary
Convert the hexadecimal value 1A to denary.
Step 1: Convert each hexadecimal character into binary

Responses