Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
arrays
1D Arrays
What is an array?
-
An array is an ordered, static set of elements
-
Can only store 1 data type
-
A 1D array is a linear array
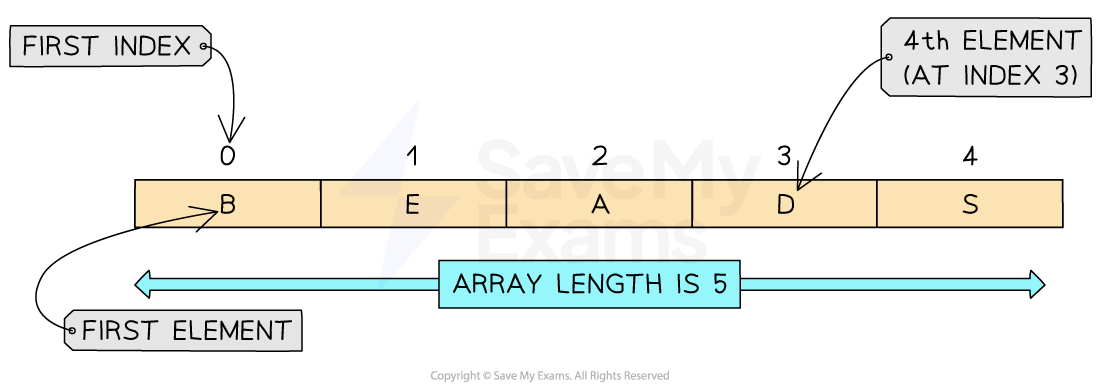
Structure of a 1D array
Example in pseudocode
-
In this example we will be creating a one-dimensional array called ‘array’ which contains 5 integers.
-
To create the array we can use the following syntax:
array[0] = 1array[1] = 2array[2] = 3array[3] = 4array[4] = 5 -
We can access the individual elements of the array by using the following syntax:
array[index] -
We can also modify the individual elements by assigning new values to specific indices using the following syntax:
array[index] = newValue -
We can also use the len function to determine the length of the array by using the following syntax:
len(array)
-
-
In the example we have iterated through the array to output each element within the array. We have used a For Loop for this.
// Creating a one-dimensional arrayarray array[5]array[0] = 1array[1] = 2array[2] = 3array[3] = 4array[4] = 5
// Accessing elements of the arrayprint(array[0])print(array[2])
// Modifying elements of the arrayarray[1] = 10print(array)
// Iterating over the arrayfor element in array print(element)
// Length of arraylength = len(array)print(length)
Example in Python
-
Creating a one-dimensional array called ‘array’ which contains 5 integers.
-
Create the array with the following syntax:
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] -
Access the individual elements of the array by using the following syntax:
array[index] -
Modify the individual elements by assigning new values to specific indices using the following syntax:
array[index] = newValue -
Use the len function to determine the length of the array by using the following syntax:
len(array)
-
-
In the example the array has been iterated through to output each element within the array. A for loop has been used for this
# Creating a one-dimensional arrayarray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Accessing elements of the arrayprint(array[0]) # Output: 1print(array[2]) # Output: 3
# Modifying elements of the arrayarray[1] = 10print(array) # Output: [1, 10, 3, 4, 5]
# Iterating over the arrayfor element in array: print(element)
# Output:# 1# 10# 3# 4# 5
# Length of the arraylength = len(array)print(length) # Output: 5
Example in Java
-
Creating a one-dimensional array called ‘array’ which contains 5 integers.
-
To create the array, use the following syntax:
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; -
Access the individual elements of the array by using the following syntax:
array[index] -
Modify the individual elements by assigning new values to specific indices using the following syntax:
array[index] = newValue; -
Use the following syntax to print the array as a string:
arrays.toString(array) -
Use the length function to determine the length of the array by using the following syntax:
array.length;
-
-
In the example, the array has been iterated through to output each element within the array. A for loop has been used for this
public class OneDimensionalArrayExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a one-dimensional array int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// Accessing elements of the array System.out.println(array[0]); // Output: 1 System.out.println(array[2]); // Output: 3
// Modifying elements of the array array[1] = 10; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); // Output: [1, 10, 3, 4, 5]
// Iterating over the array for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { System.out.println(array[i]); }
// Output: // 1 // 10 // 3 // 4 // 5
// Length of the array int length = array.length; System.out.println(length); // Output: 5 }}
2D Arrays
-
A 2D array can be visualised as a table
-
When navigating through a 2D array you first have to go down the rows and then across the columns to find a position within the array
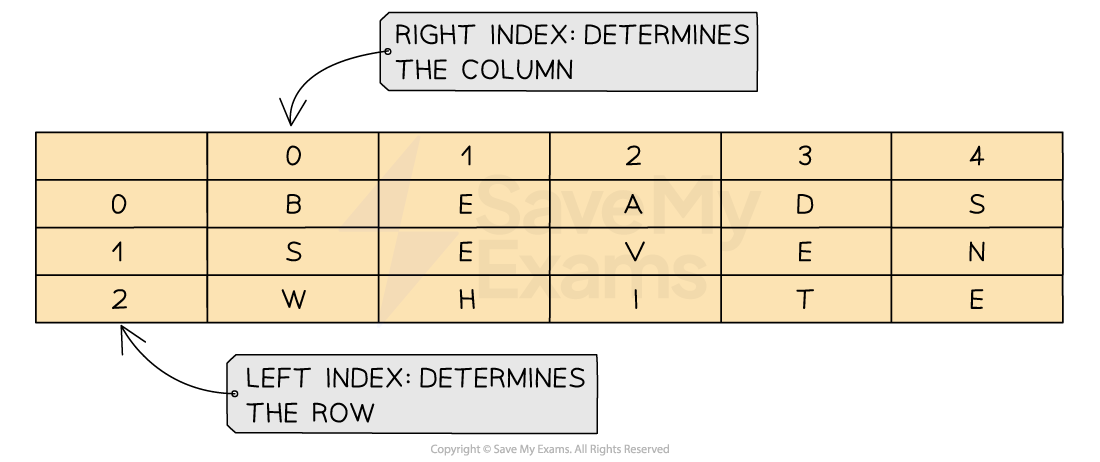
Structure of a 2D array
Example in Pseudocode
// Define the dimensions of the 2D arrayROWS = 3COLS = 4
// Create a 2D array with the specified dimensionsarray_2d = new Array[ROWS][COLS]
// Initialize the 2D array with values (optional)for row = 0 to ROWS-1: for col = 0 to COLS-1: array_2d[row][col] = initial_value
// Accessing elements in the 2D arrayvalue = array_2d[row_index][col_index]
Example in Python
# Method 1: Initialising an empty 2D arrayrows = 3cols = 4array_2d = [[0 for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)]# The above code creates a 2D array with 3 rows and 4 columns, filled with zeros.
# Method 2: Initialising a 2D array with valuesarray_2d = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]# The above code creates a 2D array with 3 rows and 3 columns, with the specified values.
# Accessing elements in the 2D arrayprint(array_2d[0][0]) # Output: 1print(array_2d[1][2]) # Output: 6
Example in Java
// Method 1: Initialising an empty 2D arrayint rows = 3;int cols = 4;int[][] array2D = new int[rows][cols];// The above code creates a 2D array with 3 rows and 4 columns, filled with zeros.
// Method 2: Initialising a 2D array with valuesint[][] array2D = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} };// The above code creates a 2D array with 3 rows and 3 columns, with the specified values.
// Accessing elements in the 2D arraySystem.out.println(array2D[0][0]); // Output: 1System.out.println(array2D[1][2]); // Output: 6
3D Arrays
-
A 3D array can be visualised as a multi-page spreadsheet and can also be thought of as multiple 2D arrays
-
Selecting an element within a 3D array requires the following syntax to be used:
3DArrayName[z, y, x] -
This is where z is the array index, y is the row index and x is the column index
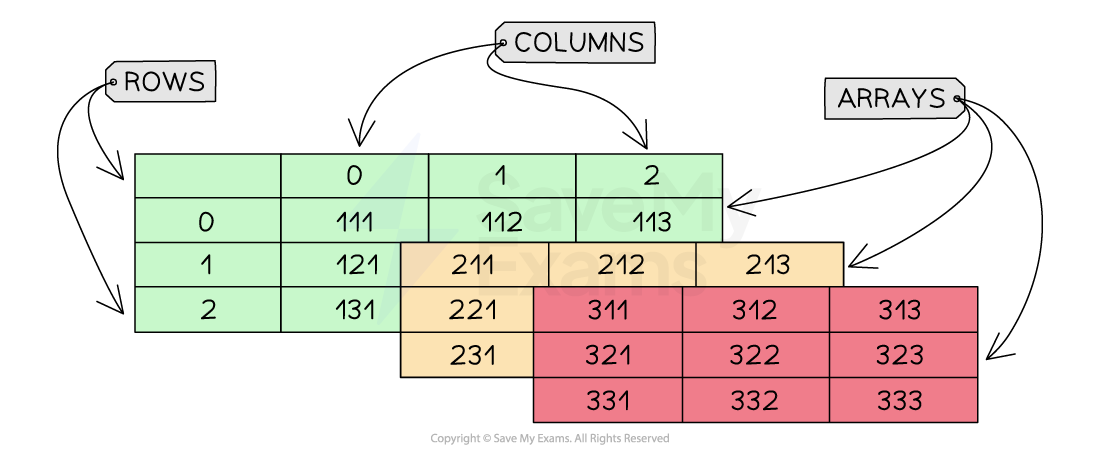
Structure of a 3D array
Example in Pseudocode
// Define the dimensions of the 3D arrayROWS = 3COLS = 4DEPTH = 2
// Create a 3D array with the specified dimensionsarray_3d = new Array[ROWS][COLS][DEPTH]
// Initialize the 3D array with values (optional)for row = 0 to ROWS-1: for col = 0 to COLS-1: for depth = 0 to DEPTH-1: array_3d[row][col][depth] = initial_value
// Accessing elements in the 3D arrayvalue = array_3d[row_index][col_index][depth_index]
Example in Python
# Method 1: Initialising an empty 3D arrayrows = 3cols = 4depth = 2array_3d = [[[0 for _ in range(depth)] for _ in range(cols)] for _ in range(rows)]# The above code creates a 3D array with 3 rows, 4 columns, and 2 depths, filled with zeros.
# Method 2: Initialising a 3D array with valuesarray_3d = [[[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]], [[9, 10], [11, 12], [13, 14], [15, 16]], [[17, 18], [19, 20], [21, 22], [23, 24]]]# The above code creates a 3D array with the specified values.
# Accessing elements in the 3D arrayprint(array_3d[0][0][0]) # Output: 1print(array_3d[1][2][1]) # Output: 14
Example in Java
// Method 1: Initialising an empty 3D arrayint rows = 3;int cols = 4;int depth = 2;int[][][] array3D = new int[rows][cols][depth];// The above code creates a 3D array with 3 rows, 4 columns, and 2 depths, filled with zeros.
// Method 2: Initialising a 3D array with valuesint[][][] array3D = { { {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}, {7, 8} }, { {9, 10}, {11, 12}, {13, 14}, {15, 16} }, { {17, 18}, {19, 20}, {21, 22}, {23, 24} } };// The above code creates a 3D array with the specified values.
// Accessing elements in the 3D arraySystem.out.println(array3D[0][0][0]); // Output: 1System.out.println(array3D[1][2][1]); // Output: 14

Responses