Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
flip-flop-circuits
D Type Flip Flops
What is a D type flip flop?
-
In A Level Computer Science, a D type flip flop is a fundamental component in digital circuits and computer memory
-
Can be referred to as Positive Edge Triggered
Key features
-
Contains two stable states, making it a type of bistable circuit
-
Used to store the state of 1 bit of data
-
Changes state on the edge of the clock pulse
Components
-
Data input (D)
-
Clock input (CLK)
-
Two outputs: Q and NOT(Q)

D Type Flip Flip Components
Operation
-
On the rising edge of the clock pulse:
-
If D is high (1), Q goes high and NOT(Q) goes low
-
If D is low (0), Q goes low and NOT(Q) goes high
-
-
The state of Q holds or “remembers” its value until the next rising clock edge
Use cases
-
Forms the basis of most types of flip flops and latches
-
Used in shift registers, counters, and memory units
-
Helpful in edge-triggered devices, synchronous circuits, and data storage
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will not be asked to recall the logic gates that make up a D-type flip flop and they can be made from various different gates
They are often built using NAND gates which are AND gates that have their output inverted:

D Type Flip Flip Logic Gates
Worked Example
-
Draw the output of the Flip Flop on the diagram below

D Type Flip Flop Question
-
For a question like this remember that the output line Q that you are asked to draw wants to be the same as the input D BUT it can only change when the clock signal changes from low to high (i.e. at the dotted lines)
-
At the start assume Q starts the same as D (low in this case)
-
Then draw it along from left to right until you get to a vertical dotted line (in an exam you would draw these lines on to help you if they weren’t there
-
At each dotted line, Q has the chance to change to whatever D is

D Type Flip Flop Working 1
-
So at the first line, D is low so Q stays low
-
At the second dotted line D has changed to high so now Q can become high

D Type Flip Flop Working 2
-
Q now stays high until the next rising edge of the clock (the next dotted line) where it gets another chance to change, but here D is still high so Q stays high

D Type Flip Flop Working 3
-
And you continue to do this until you reach the right hand side of the diagram
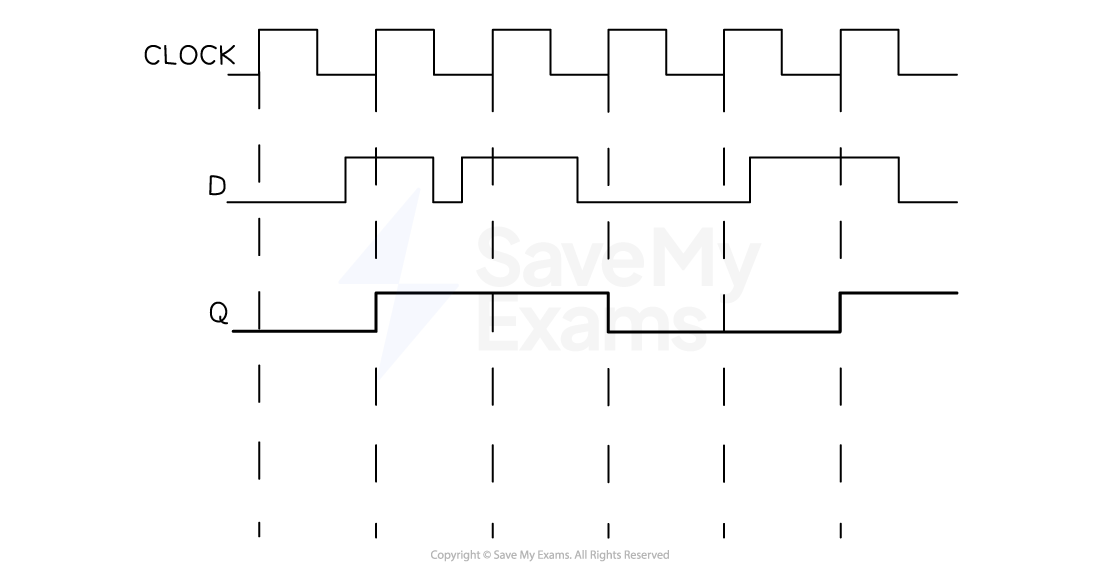
D Type Flip Flop Working 4

Responses