Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
programming-classes-objects-methods-and-attributes
Programming Classes
-
To program classes, you should already have a solid understanding of what classes in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
How do you Define a Class?
In this example we will:
-
Define a class for a car sales program where the following is required:
-
Name of Manufacturer
-
Model of Car
-
Price
-
Mileage
-
Whether the car is preowned
-
-
Instantiate two objects for the car sales program ensuring that they have appropriate identifiers
-
List two methods that would be useful for a car object
Pseudocode

Pseudocode for creating classes, a constructor, and functions
Java
//creating a class called cars
public class Cars {
//creating class attributes for a car
private String Manufacturer;
private String Model;
private int Price;
private int Mileage;
private boolean PreOwned;
//Constructor - This is used to create the objects. More on this in the object chapter)
public Cars(String manufacturer, String model, int price, int mileage, boolean preOwned) {
this.Manufacturer = manufacturer;
this.Model = model;
this.Price = price;
this.Mileage = mileage;
this.PreOwned = preOwned;
}
//method to make the car go faster.
public void Accelerate(){
//code to be executed which will make the car go faster
}
//Method to honk horn
public void honkHorn(){
// code to be executed which will honk the car horn
}
}
Python
#creating a class called cars
class Cars:
# constructor - This is used to create the objects. More on this in the object chapter)
def __init__(self, manufacturer, model, price, mileage, preOwned):
self.Manufacturer = manufacturer
self.Model = model
self.Price = price
self.Mileage = mileage
self.PreOwned = preOwned
#method to make the car go faster.
def Accelerate(self):
# code to be executed which will make the car go faster
# method to honk horn
def honkHorn(self):
# code to be executed which will honk the car horn
Programming Objects
-
To program objects, you should already have a solid understanding of what objects in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
Defining an Object
Pseudocode
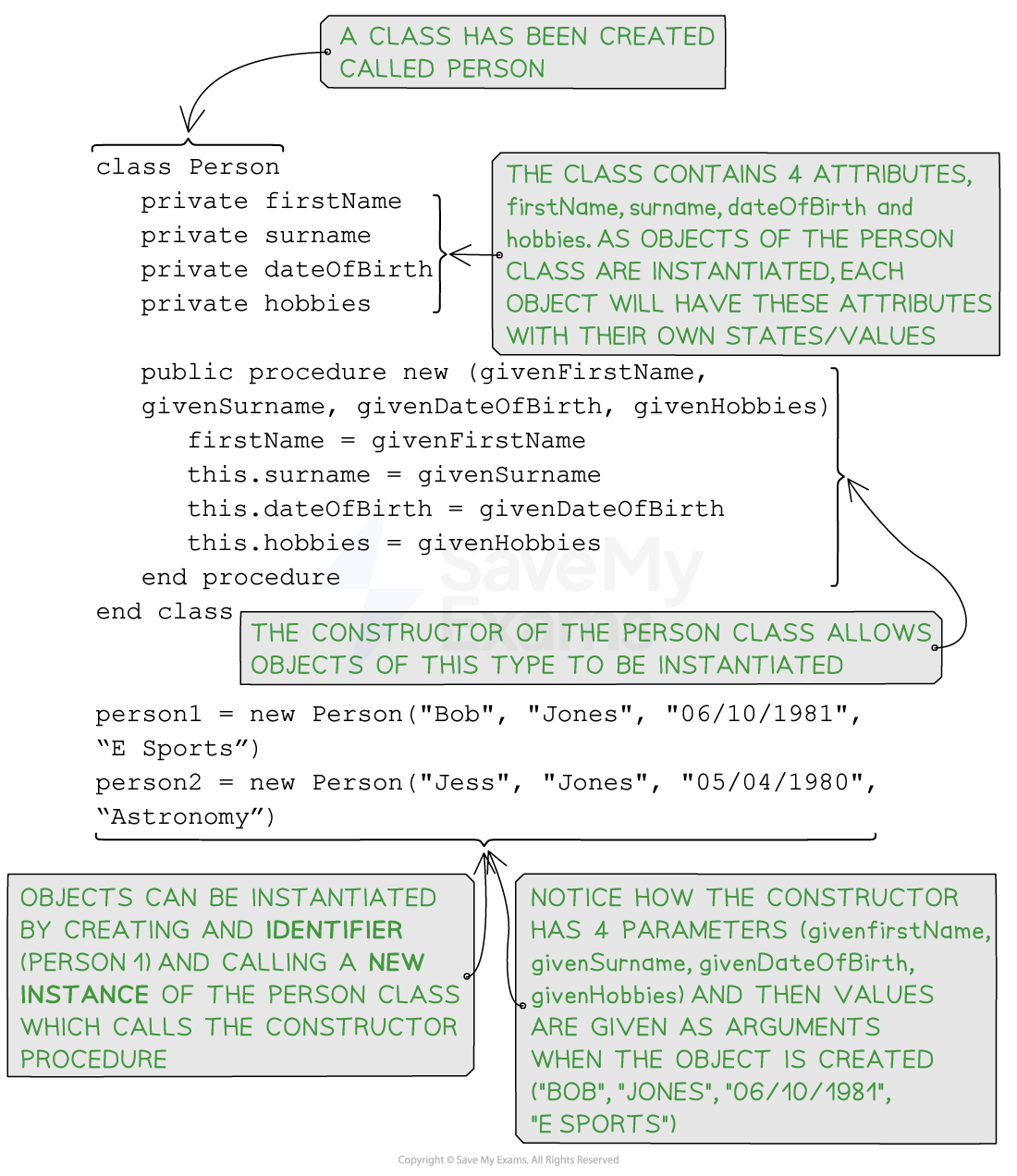
Pseudocode for the class ‘person’ and instantiating two objects
Java
//creating the person class
public class Person {
// creating 4 attributes for the person class
private String firstName;
private String surname;
private String dateOfBirth;
private String hobbies;
// Constructor -This creates objects of the person class
public Person(String firstName, String surname, String dateOfBirth, String hobbies) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.surname = surname;
this.dateOfBirth = dateOfBirth;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
//Creating Objects (Instances) of the person class
Person person1 = new Person("Bob", "Jones", "06/10/1981", “E Sports”);
Person person2 = new Person("Jess", "Jones", "05/04/1980", “Astronomy”);
Python
#creating the person class
class Person:
#Constructor -This creates objects of the person class
def __init__(self, firstName, surname, dateOfBirth, hobbies):
self.firstName = firstName
self.surname = surname
self.dateOfBirth = dateOfBirth
self.hobbies = hobbies
#Creating Objects (Instances) of the person class
person1 = Person("Bob", "Jones", "06/10/1981", "E Sports")
person2 = Person("Jess", "Jones", "05/04/1980", "Astronomy")
Programming Methods
-
To program methods, you should already have a solid understanding of what methods in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
Defining Methods
Pseudocode
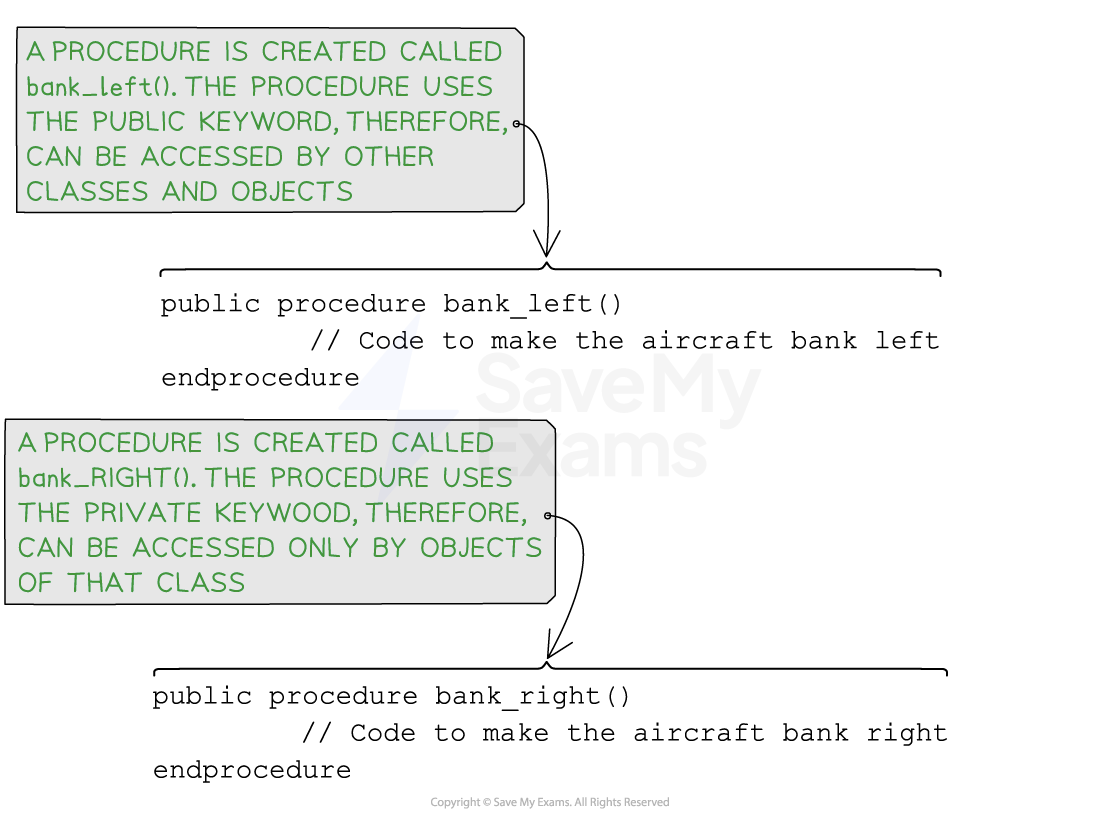
Pseudocode for creating methods
Java
//Creating a public method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}
//Creating a private Method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}
Python
#Creating a public method called BankLeft
def bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank left
#Creating a private method called BankLeft
-
In Python, there is no explicit access modifier for methods like “private” in Java.
-
By convention, methods with a single leading underscore _ are considered private and should not be accessed directly from outside the class.
_def _bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank left
-
It’s important to note that even though the method is marked as private, it can still be accessed and invoked from outside the class. However, as a rule, other developers should treat it as private and avoid accessing it directly.
Programming Attributes
Pseudocode
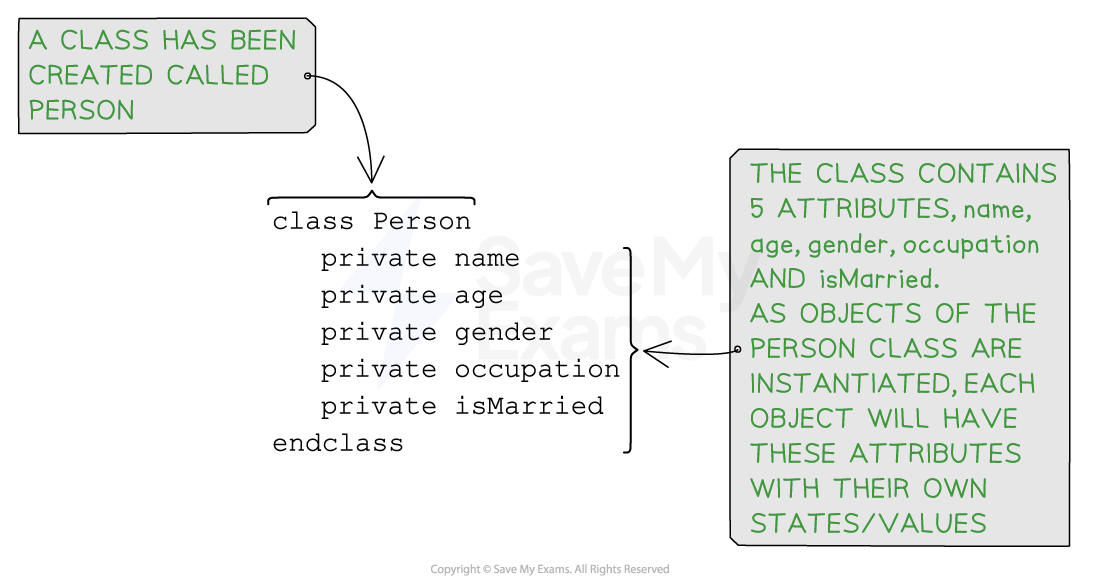
Example of a created class, “Person”, containing several attributes
Java
public class Person {
// Attributes for the person class
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
private String occupation;
private boolean isMarried;
}
Python
In Python attributes are defined using the self keyword followed by the attribute name and its initial value.
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, attribute1, attribute2):
# Define attributes
self.attribute1 = attribute1
self.attribute2 = attribute2
Worked Example
Below is a sample of code for the class “Lizard”.
class Lizard private speed private mass private size public procedure new(givenSpeed, givenMass, givenSize) speed=givenSpeed mass=givenMass size=givenSize endprocedure public function breakBlock(brick) if speed*mass>=brick.getStrength() then speed=((speed*mass)-brick.getStrength())/mass; return true else return false endif endfunction
.........endclass
Identify an attribute in the Lizard class.
1 marks
How to answer this question to get full marks:
-
There are 3 attributes in the Lizard class which are speed, mass and size
Answer:
Speed

Responses