Computer-Science-A-level-Ocr
-
3-3-networks8 主题
-
3-2-databases7 主题
-
3-1-compression-encryption-and-hashing4 主题
-
2-5-object-oriented-languages7 主题
-
2-4-types-of-programming-language4 主题
-
2-3-software-development5 主题
-
2-2-applications-generation6 主题
-
2-1-systems-software8 主题
-
1-3-input-output-and-storage2 主题
-
1-2-types-of-processor3 主题
-
1-1-structure-and-function-of-the-processor1 主题
-
structuring-your-responses3 主题
-
the-exam-papers2 主题
-
8-2-algorithms-for-the-main-data-structures4 主题
-
8-1-algorithms10 主题
-
7-2-computational-methods11 主题
-
7-1-programming-techniques14 主题
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
entity-relationship-diagrams
-
data-normalisation
-
relational-databases
-
hashing
-
symmetric-vs-asymmetric-encryption
-
run-length-encoding-and-dictionary-coding
-
lossy-and-lossless-compression
-
polymorphism-oop
-
encapsulation-oop
-
inheritance-oop
-
attributes-oop
-
methods-oop
-
objects-oop
-
capturing-selecting-managing-and-exchanging-data
-
6-5-thinking-concurrently2 主题
-
6-4-thinking-logically2 主题
-
6-3-thinking-procedurally3 主题
-
6-2-thinking-ahead1 主题
-
6-1-thinking-abstractly3 主题
-
5-2-moral-and-ethical-issues9 主题
-
5-1-computing-related-legislation4 主题
-
4-3-boolean-algebra5 主题
-
4-2-data-structures10 主题
-
4-1-data-types9 主题
-
3-4-web-technologies16 主题
-
environmental-effects
-
automated-decision-making
-
computers-in-the-workforce
-
layout-colour-paradigms-and-character-sets
-
piracy-and-offensive-communications
-
analysing-personal-information
-
monitoring-behaviour
-
censorship-and-the-internet
-
artificial-intelligence
-
the-regulation-of-investigatory-powers-act-2000
-
the-copyright-design-and-patents-act-1988
-
the-computer-misuse-act-1990
-
the-data-protection-act-1998
-
adder-circuits
-
flip-flop-circuits
-
simplifying-boolean-algebra
-
environmental-effects
linear-search
Searching Algorithms
What is a searching algorithm?
-
A searching algorithm is a method to find a specific value or element within a data structure.
-
The two most common are:
-
Binary search
-
Linear search
-
Linear search
What is a linear search?
-
The linear search is a standard algorithm used to find elements in an unordered list. The list is searched sequentially and systematically from the start to the end one element at a time, comparing each element to the value being searched for
-
If the value is found the algorithm outputs where it was found in the list
-
If the value is not found it outputs a message stating it is not in the list
-
-
An example of using a linear search would be looking for a specific student name in a list or searching for a supermarket item in a shopping list
Performing the linear search
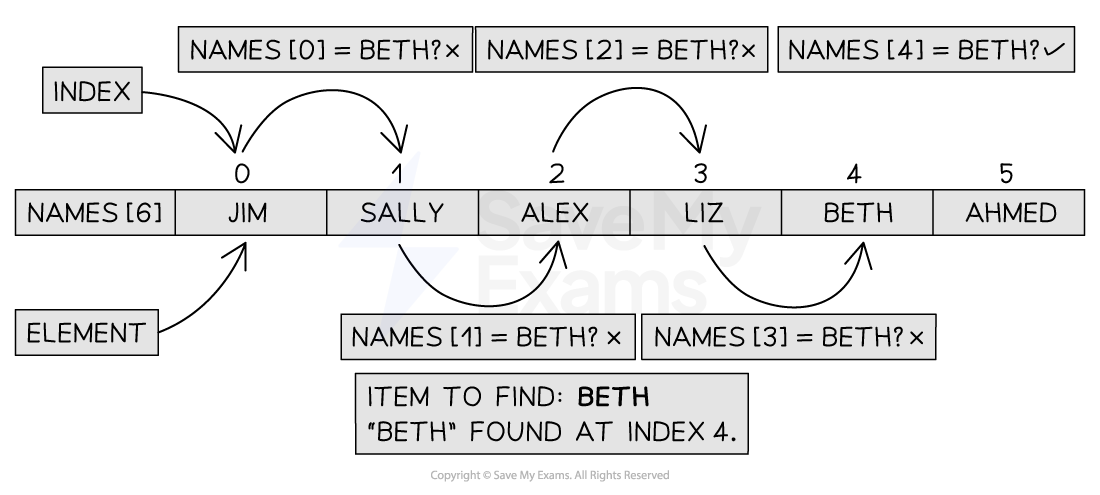
Figure 1: Performing the Linear Search
Time complexity of a linear search
-
To determine the algorithm’s execution time as measured by the number of instructions or steps carried out, Big-O notation must be used
-
The loop is executed n times, once for each item. There are two instructions within the loop, the if statement and an assignment, hence the Big-O for the loop is O(2n)
-
There are three initial statements which are O(1)
-
The overall Big-O notation is therefore 2n + 3, which when coefficients are factored out, becomes O(n) as linear time dominates constant time. The constant term and coefficients contribute significantly less as the input size n grows larger
-
It is important to remember here that O(n) is the worst case scenario. The best case scenario O(1) would find the item the first time, while the average case would be O(n/2) which when we remove coefficients still becomes O(n)
Space complexity of a linear search
-
Linear search has a space complexity of O(1) because it does not require any additional memory that grows with the size of the input
-
It only uses a constant amount of extra space, such as a loop counter or a variable to store the target value
Tracing a linear search
-
Given the following list [5, 4, 7, 1, 3, 8, 9, 2], a trace table for the linear search is shown below
Trace Table of the Linear Search
|
item |
index |
i |
list[i] |
found |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8 |
-1 |
0 |
5 |
False |
|
|
|
1 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
3 |
|
|
8 |
5 |
5 |
8 |
True |
Implementing a Linear Search
Pseudocode
function linearSearch(list, item) index = -1 i = 0 found = False while i < len(list) and found = False if list[i] = item then index = i found = True endif i = i + 1 endwhile return index
endfunction-
In the above algorithm, a list of n ordered items is passed to the function and three variables are initialised
-
index = -1is a default value to indicate “not found”,i = 0is a counter to ensure the loop starts at the beginning of the list andfound = Falsesets a flag to track when/if the value you are searching for is found -
The loop continues as long as the counter hasn’t reached the end of the list and if
list[i] = itemthe current index is stored as the location of the item -
The flag found is set to True to signal the search can be stopped
-
i = i + 1increments the counter to move to the next element in the list if the value is not found -
After the loop completes the function returns the final value of index
Python
def linear_search(list, item): index = -1 for i in range(len(list)): if list[i] == item: index = i break # Stop the loop once the item is found return index
Java
public class LinearSearch { public static int linearSearch(int[] list, int item) { int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if (list[i] == item) { index = i; break; // Stop the loop once the item is found } } return index; }

Responses