Impact of multinational companies on the local economy
-
A multinational company (MNC) is a business that is registered in one country but has manufacturing operations/outlets in different countries
-
E.g. Starbucks’s headquarters is in Washington, USA, but the company has 32,000 stores in 80 countries
-
-
Factors such as globalisation and deregulation have contributed to the growth of MNCs
-
MNCs will choose locations based on factors such as cost advantages and access to markets
-
Nike originates from the USA, but 50% of its manufacturing takes place in China, Vietnam and Indonesia due to the lower production costs in those countries
-
-
MNCs offer both advantages and disadvantages with regard to:
-
Employment, wages and working conditions
-
The impact on local businesses
-
The impact on the local community and environment
-
Advantages and disadvantages of MNCs on employment, wages and working conditions
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of MNCs for local businesses
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Advantages and disadvantages of MNCs for local communities and the environment
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Impact of MNCs on the national economy
-
Many governments are in favour of MNCs establishing operations in their countries, as there are benefits to the wider economy
The impact of MNCs on national economies
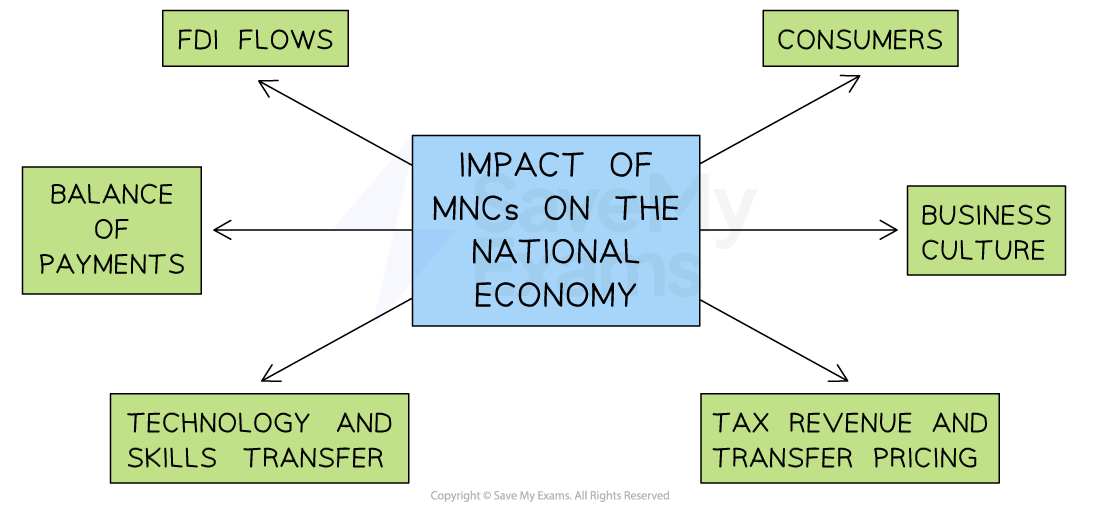
Foreign direct investment flows
-
There will be an inflow of money into a country if an MNC decides to invest through foreign direct investment (FDI)
Advantages and disadvantages of FDI flows from MNCs
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Balance of payments
-
The balance of payments is a statement showing all of the financial transactions between a country and the rest of the world
-
MNCs can help to improve a country’s balance of payments, as the FDI flows into the country will help improve its balance of payments
-
Any goods and services exported for sale by the MNC will generate further inflows to the country’s balance of payments
-
This is especially beneficial to a country when the MNC is exporting a rare and valuable raw material, e.g. cobalt
-
-
MNCs can also have a negative impact on the balance of payments
-
If the MNC buys raw materials or equipment abroad (imports), there is a flow of money out of the country
-
If the MNC sends profits back to its home country, this is also a flow of money out of the country
-
Technology and skills transfer
-
MNCs can bring new technologies and skills to local businesses
-
This will help improve efficiency and productivity, helping domestic businesses to become more competitive in the national and international markets
-
Consumers
-
Customers in countries that host MNCs benefit from:
-
A wider choice of goods and services
-
Lower prices if MNCs pass their cost advantages on in the form of lower prices
-
Better quality goods and services
-
Improved living standards, as people may have higher incomes due to the job creation and the resulting reduction in unemployment
-
-
However, in the long run, MNCs can push domestic businesses out of the market, leaving customers with less choice
-
This may lead to MNCs exploiting customers with higher prices and low-quality products, as customers have limited choice
-
Business culture
Advantages and disadvantages of MNCs on business culture
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Tax revenue and transfer pricing
-
There is the potential for the host country to gain significant tax revenue
-
Governments can use tax revenue paid by MNCs to invest in improving public services and infrastructure
-
However, MNCs seek to maximise profits and will try to reduce their tax liabilities
-
Transfer pricing is a method used by MNCs to shift profits from the countries in which they are generated to countries with lower tax rates
-
This is a method of tax avoidance and means that the businesses will pay less tax in the host country
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In Papers 1 and 3, when assessing the impact of MNCs on the local and national economies, consider the scale of the multinational in comparison to the country in which it is looking to establish itself. For example, if the MNC makes more profit than the GDP of the country in a year, it is likely to have a strong influence on the country.

Responses