Understanding PESTLE analysis
-
PESTLE analysis examines the external factors that are likely to impact the activities and outcomes of a business
-
PESTLE is an acronym for:
-
Political
-
Economic
-
Social
-
Technological
-
Legal
-
Environmental
-
-
PESTLE analysis can support effective decision-making by senior managers who will better understand the complex context within which the business operates
-
Managers can use the information gathered to understand the potential threats to the business’s performance and identify future difficulties so that action can be taken to help avoid and eliminate their effects
PESTLE factors
|
External factor |
Explanation |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Political |
|
|
|
Economic |
|
|
|
Social |
|
|
|
Technological |
|
|
|
Legal |
|
|
|
Environmental |
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When using PESTLE analysis, you must focus on each factor’s impact on business activity rather than its origin. The cause is not so important, but the impact of the factor is what needs to be considered.
The changing competitive environment
-
The structure of the market in which a business operates is likely to change over time
-
Businesses have to respond to this changing competitive environment
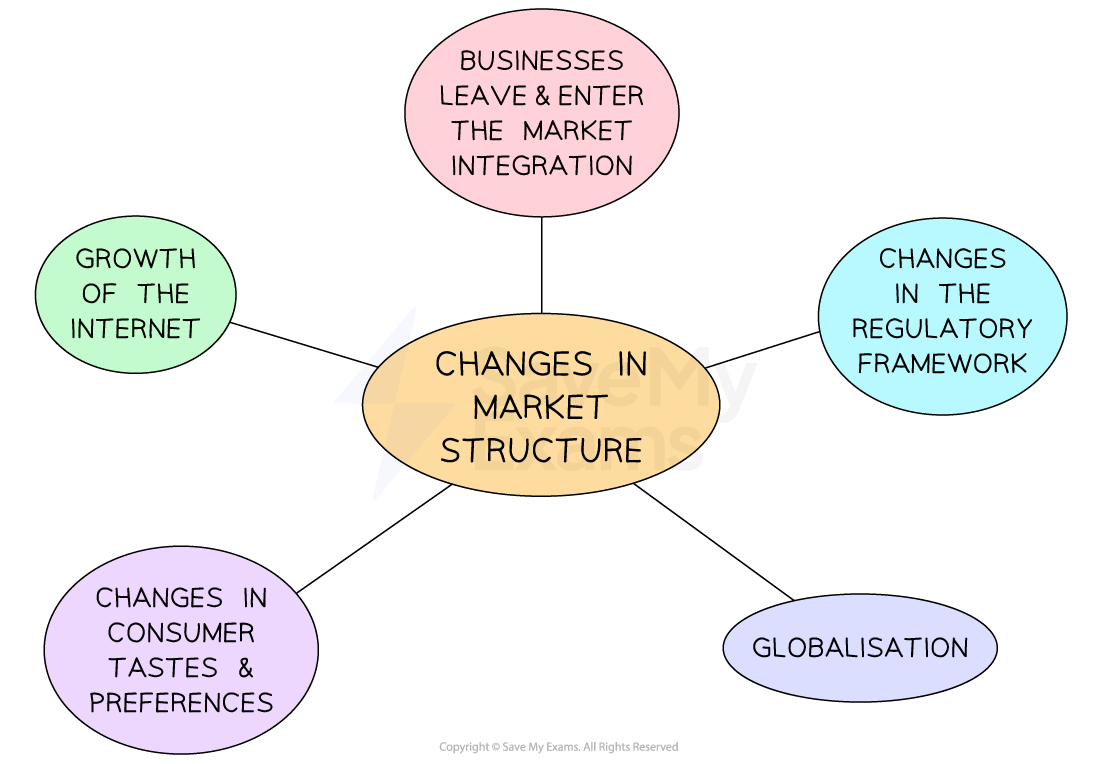
Reasons for changes in market structure
-
New businesses may enter the market, and existing businesses may leave or integrate with others
-
For example, until the early 2000s, UK supermarkets were dominated by a small number of giants, including Tesco, Sainsbury’s and Asda
-
The entry of businesses such as Aldi and Lidl has made the market more competitive, while takeovers involving leading brands, such as that of Somerfield by Morrisons in 2004, have had the opposite effect
-
-
The legislation (laws) may change, likely leading to fewer barriers to entry for new businesses
-
For example, until the 1980s, only local councils were permitted to operate local bus services in the UK, and following deregulation, any business with the financial resources to enter the market could run a bus service
-
-
The growth of the internet has increased the number of competitors businesses face in the majority of markets
-
For example, UK booksellers have faced severe price competition largely from the online giant Amazon
-
Many smaller independent retailers have closed down, as they have been unable to compete
-
Remaining retailers such as Waterstones have needed to change their operations significantly to survive
-
-
-
Consumer tastes and preferences are changing more rapidly, leading to short product life cycles and a requirement for businesses to innovate to compete
-
For example, the growth in fast fashion has meant that many clothing retailers must now constantly update their product ranges rather than rely on seasonally focused product selections
-
Businesses such as Primark and Zara have been particularly successful in meeting customer demand for fast fashion, giving customers the chance to buy the latest fashions in as little as 13 days
-
-
Globalisation has increased competition with rivals from around the world
-
For example, between 1970 and 2010, trade barriers around the world were reduced, and customers were able to buy an increasing number of motor vehicle brands
-
By 2015, more than half of all cars sold in the UK were manufactured by Japanese companies
-
-
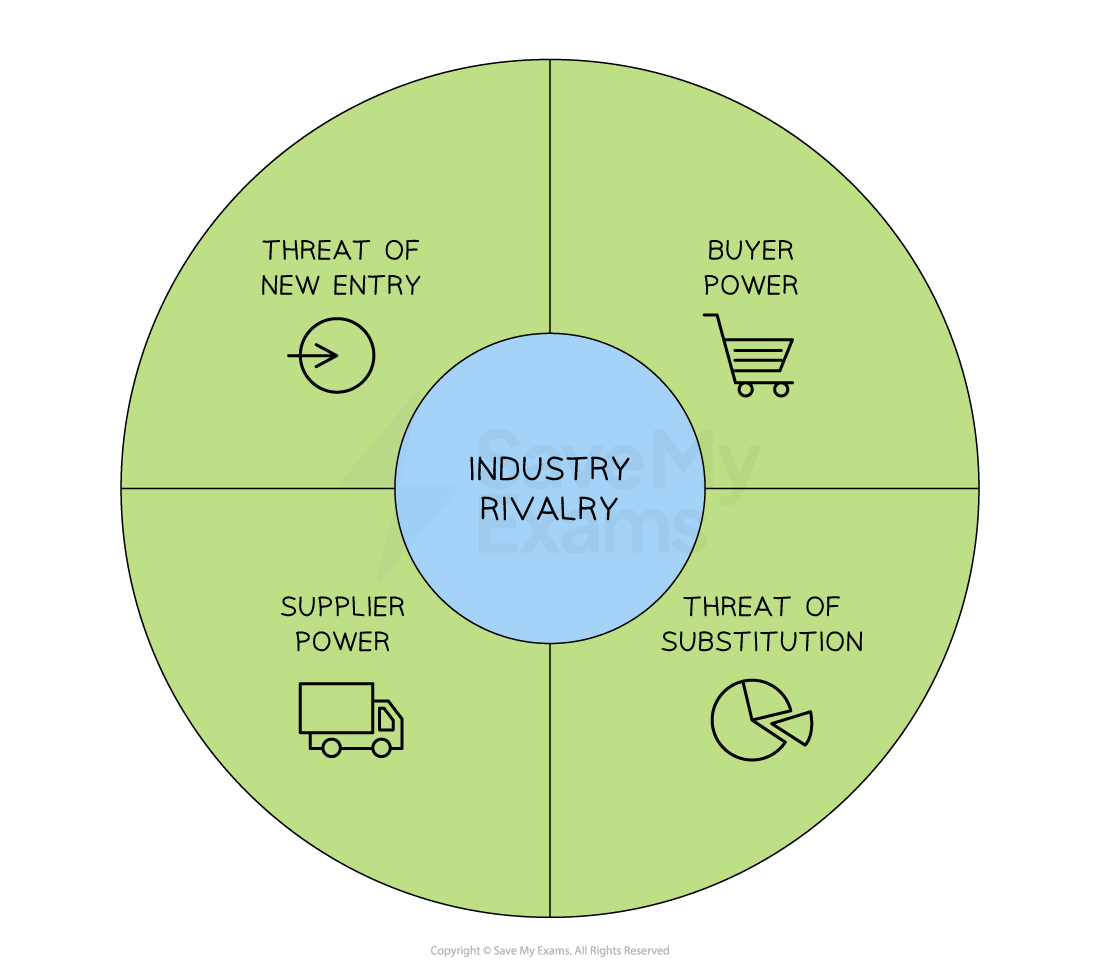
Porter’s Five Forces
-
Porter’s Five Forces identify the key pressures on an industry that impact the ability of a business to compete with rivals
The Five Forces model
-
Porter argued that once a business fully understands these pressures in context, it can take strategic decisions to achieve and sustain a competitive advantage
-
This will then increase the business’s chances of success
Explanation of Porter’s Five Forces model
|
Force |
Explanation |
E |
|---|

Responses