The purpose of sales forecasts
-
Sales forecasts predict future revenues based on past sales figures
-
They commonly focus on what will happen in the future to:
-
The volume and value of sales
-
The size of the market
-
Sales as a result of promotional activity
-
Sales as a result of cyclical factors
-
-
Sales forecasts are an important tool to support planning and can improve the validity of cash flow forecasts
-
Businesses use sales forecasts to determine resource requirements in a variety of ways, including:
-
How many staff will be needed?
-
How much stock will be required?
-
Does capacity need to be expanded (or reduced)?
-
Does the equipment need to be upgraded, replaced or increased (or reduced)?
-
How much and what type of finance will be required?
-
Is promotional activity (e.g. advertising) required — and when?
-
Factors affecting sales forecasts
-
Developing accurate sales forecasts is a skill that requires an understanding of several factors that can influence the reliability of the forecast
Consumer trends
-
Seasonal variations
-
Demand for certain goods is seasonal
-
Events such as major religious festivals, holiday periods and annual events impact demand for a wide range of products
-
For example, sales of basic homewares increase when students start university each September
-
-
-
Fashion
-
Fashion is often led by celebrities, and their influence can have a short-term impact on sales
-
For example, when Hollywood legend Megan Fox appeared in September 2021 at a star-studded event in a Boohoo dress, the company’s sales unexpectedly soared by more than 400% during that month
-
-
-
Long-term trends
-
Consumer behaviour, attitudes and spending habits change over time
-
In recent years, environmentally conscious consumers have led many businesses to amend sales forecasts to reflect increased demand for green products
-
For example, in late 2022, vehicle manufacturer Ford increased its sales forecasts for electric vehicles by almost 70%
-
-
Economic variables
-
Economic growth
-
During periods of economic growth, increased consumer incomes will lead to higher-than-forecast sales
-
The opposite will occur during periods of economic slowdown, and sales may be lower than forecast
-
-
Inflation
-
The general increase in prices over time reduces consumers’ spending power
-
Firms may revise their sales forecasts downwards during periods of rising inflation
-
Firms may revise their sales forecasts upwards during periods of falling inflation
-
-
-
Unemployment
-
Increased levels of unemployment are often experienced during periods of recession and tend to be a key cause of reduced spending in the economy
-
Sales forecasts for lifestyle and luxury goods may reduce as consumers focus their spending on essentials
-
-
-
Interest rates
-
When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive for consumers
-
Businesses that sell products that consumers frequently buy on credit may therefore adjust their sales forecasts downwards
-
For example, property sales are set to drop to 1.01bn in 2023 from 1.27bn in 2022, causing many estate agencies to adjust their sales forecasts downwards
-
-
-
Exchange rates
-
When the value of the UK pound sterling falls against other global currencies, overseas consumers will find that British exports become relatively cheaper
-
Businesses that sell products overseas or that cater to tourists visiting the UK may adjust their sales forecasts upwards to reflect the expected increase in demand from a cheaper sterling
-
For example, Visit Britain expects the number of tourists entering Britain in 2023 to be 14% higher than in 2022
-
-
Actions of competitors
-
Sales forecasts should consider the short-term actions of competitors, such as sales promotions, as well as longer-term strategies, such as changes to product ranges and expansion plans
-
Competitor actions are difficult to predict, so the usefulness of past data to predict future sales may be limited
-
For example, Marks & Spencer announced plans to open 20 new high street stores in 2023, partly in response to the closure of several key competitors, including Debenhams
-
Difficulties of sales forecasting
-
Sales forecasting usually involves the use of past data to predict the future
-
In the short term, sales forecasts are likely to reflect the recent past
-
Longer-term sales forecasting is often more problematic, as several factors affect its reliability
The main difficulties of sales forecasting
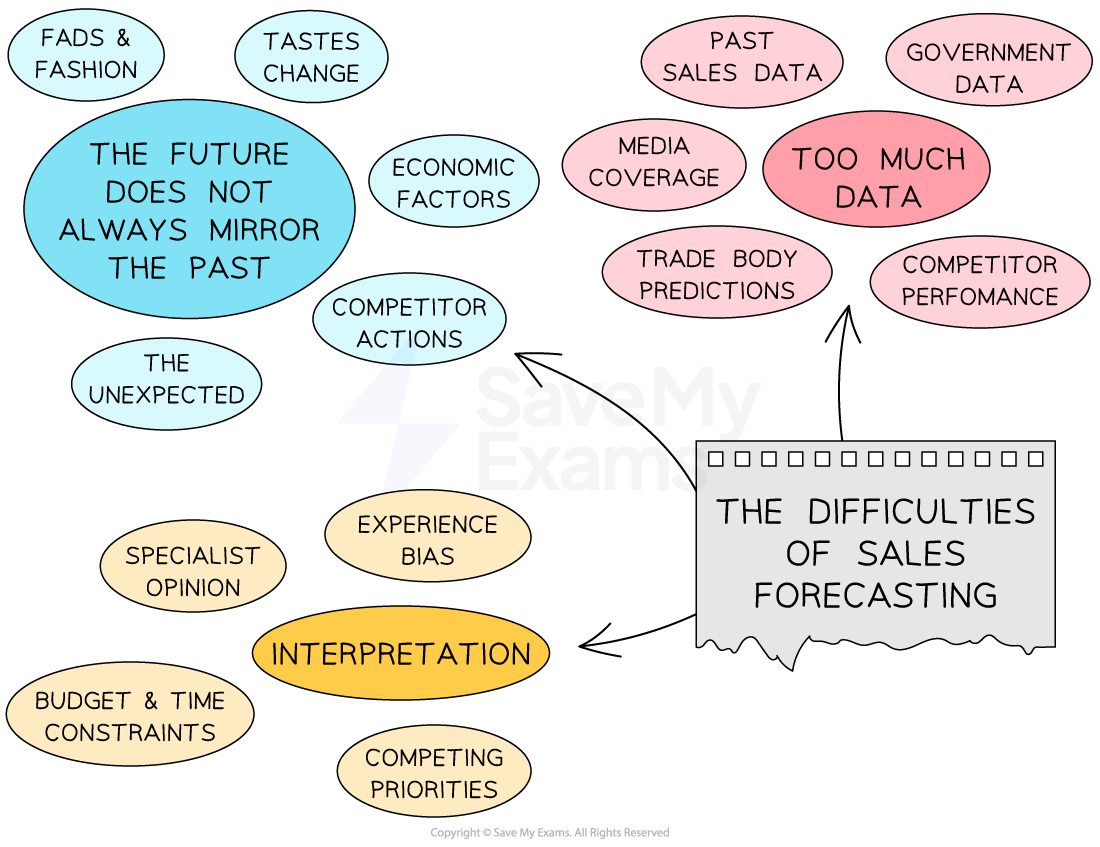
-
Effective sales forecasting requires skill, time and the accurate use of timely data
-
Smaller businesses in particular may lack the experience or specialised personnel to construct, analyse and interpret sales forecasts
-
It is difficult to avoid experience bias (e.g. opinions of the future based on experiences in the past)
-
Businesses may face problems in constructing sales forecasts that ignore the priorities of key stakeholders
-
-
-
The future seldom repeats the occurrences of the past
-
Sales forecasts will rarely reflect the full range of external influences that can affect future inflows, such as fashions, trends and the actions of competitors
-
-
There is a significant amount of data available for businesses to consider when constructing sales forecasts
-
Internal data, such as previous sales figures, will be a key source of information when constructing forecasts
-
Selecting the most appropriate external data to support sales forecasts is extremely challenging and requires careful evaluation
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
While sales forecasting as a planning tool has several potential uses for a business, you should carefully consider how a sales forecast is constructed when evaluating its usefulness.
-
Who is responsible for the sales forecast?
-
Which data is used in its construction?
-
How reliable or accurate are the data sources underpinning the forecast?
You may even conclude that no sales forecasting is better than a poorly constructed, biased attempt!

Responses