The importance of employee motivation
-
Motivation refers to the inner desire or willingness that propels a person to take action and achieve a specific goal or outcome
-
Motivation can be intrinsic, coming from within a person (values, beliefs, etc.)
-
Motivation can be extrinsic, coming from external factors (rewards or punishments)
-
-
Motivation plays a critical role in a business’s success and can have a significant impact on productivity, reliability and loyalty of its workers and labour turnover rates
Motivation and productivity
-
Motivated employees are more productive and efficient, as they are more likely to be engaged in their work and take the initiative to meet or exceed their goals
-
They will generate higher levels of output and quality
-
Increased productivity results in higher profits for the business
Motivation and the reliability of workers
-
Motivated employees are more likely to be reliable and dependable
-
They take pride in their job, show up on time, meet deadlines and take fewer sick days
-
This leads to increased trust between the business and its employees as well as higher productivity
Motivation and staff turnover
-
Motivated employees are more likely to stay with the company long-term, which reduces the turnover rate
-
Lower turnover rates reduce the need for costly recruitment and training
Motivation theories: Taylor’s Scientific Management
-
Developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the early 20th century
-
It focuses on breaking down complex tasks into simpler ones, standardising work processes and providing workers with clear instructions and training to achieve maximum efficiency
-
Many manufacturing businesses use Taylor’s principles to structure their staff benefits, e.g. piece-rate pay
-
Production lines involving human labour are often set up based on these principles
-
Taylor’s approach to staff motivation
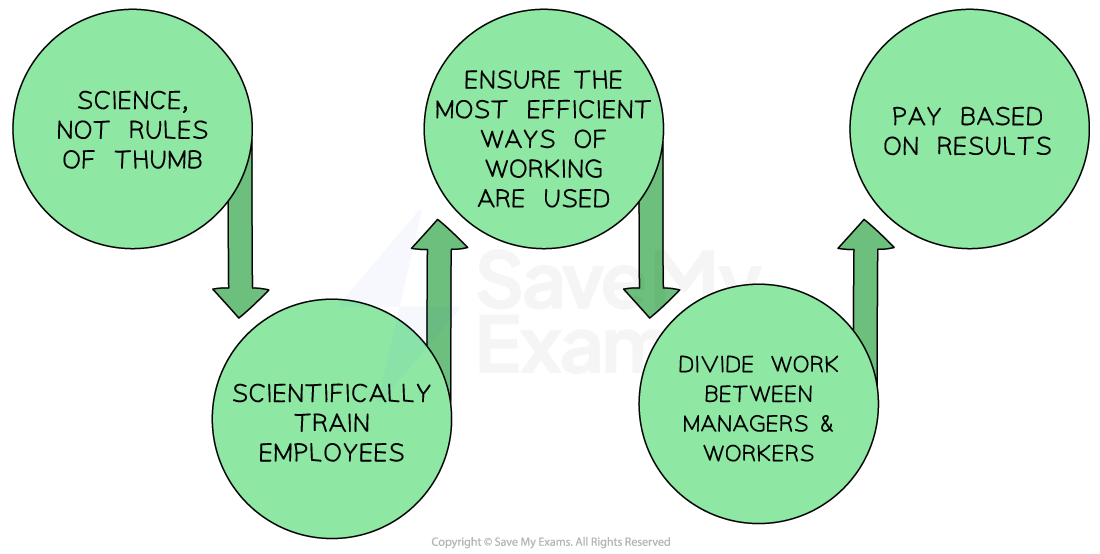
Explanation
1. Study and analyse the work process
-
Carefully analyse each step of the work process
-
Break down complex tasks into simpler ones, and identify the most efficient and effective way to perform each task
2. Standardise the work process
-
This involves creating detailed procedures and instructions for each task so that workers can follow these procedures consistently
3. Select and train the workers
-
Workers should be carefully selected based on their skills and abilities
-
Train workers to perform their tasks efficiently and effectively
-
This training includes both technical skills and the proper attitudes and behaviours required to be successful (e.g. patience in a repetitive task)
-
4. Provide incentives for performance
-
Scientific management emphasises the use of incentives to motivate workers
-
This may include bonuses or piece-rate pay
-
How businesses use Taylor’s Scientific Management
|
How businesses use Taylor’s approach |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Motivation theories: Mayo’s Human Relations Theory
-
Mayo’s Human Relations Theory was developed by Elton Mayo in the 1930s
-
It focuses on the importance of social factors in the workplace
-
These include factors such as communication, motivation and job satisfaction
-
-
Mayo suggests that the key to improving productivity and job satisfaction lies in understanding and improving the relationships between workers, supervisors and management
How businesses use Mayo’s Human Relations Theory
|
How businesses use Mayo’s approach |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Motivation theories: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
-
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a theory of human motivation that outlines five tiers of human needs that must be met for individuals to reach their full potential
Maslow’s hierarchy
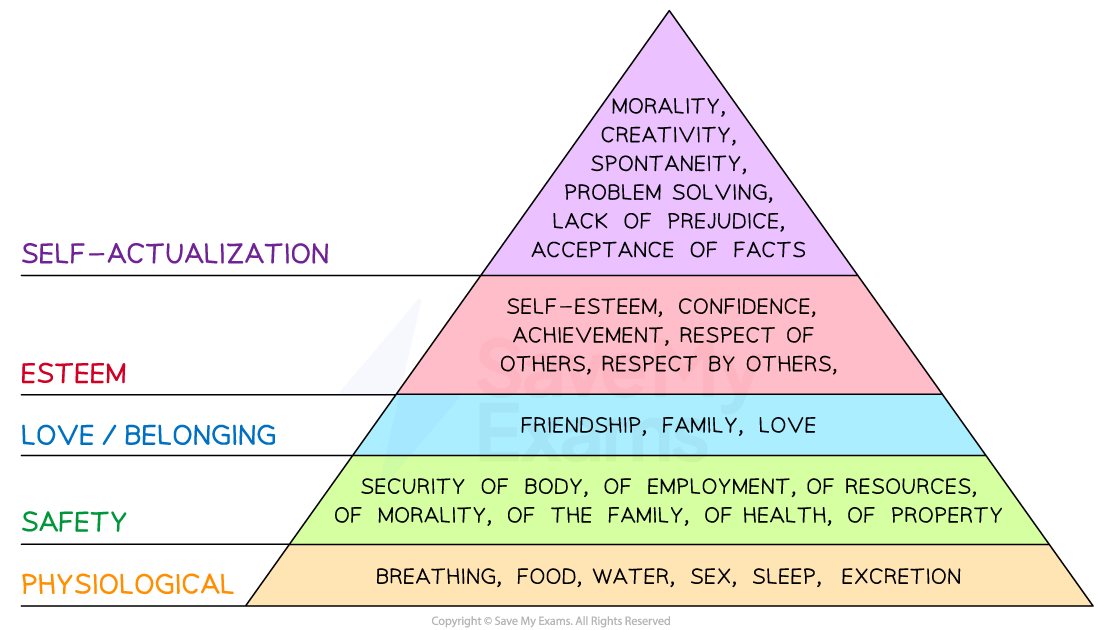
Application of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
-
Physiological needs
-
Businesses can provide necessities for their employees
-
E.g. comfortable work environment, access to clean water and food and adequate rest breaks
-
-
Safety needs
-
Businesses can provide job security, fair pay, benefits and safe working conditions for their employees
-
-
Love and belonging (social) needs
-
Businesses can encourage teamwork and generate a sense of community within the workplace
-
-
Esteem needs
-
Businesses can provide recognition for employees’ accomplishments and provide a positive work culture that values individual contributions
-
-
Self-actualisation needs
-
Businesses can help employees achieve this need by offering opportunities for employees to pursue their passions and interests
-
E.g. Barclays was known for supporting elite sportspeople by allowing them time off work during the day to continue their training (the focus was on getting the job done, not having to be in at a certain time)
-
Evaluation of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Motivation theories: Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
-
Herzberg’s theory suggests that there are two types of factors that affect employee motivation and job satisfaction
-
Hygiene factors are elements that do not necessarily lead to job satisfaction, but their absence can cause dissatisfaction, which decreases motivation, e.g. poor teamwork in the workplace
-
Motivators are elements that lead to job satisfaction and motivation, e.g. increased responsibility
-

Responses