The recruitment and selection process
-
Recruitment is the process of attracting and identifying potential job candidates who are suitable for a particular role
-
Recruitment activities include job advertising, job fairs, social media outreach and referrals from current employees
-
The goal of recruitment is to create a pool of qualified candidates who can be considered for the role
-
-
Selection is the process of choosing the best candidate
-
Selection activities often involve reviewing curricula vitae (CVs) and conducting interviews or assessment tasks
-
The goal of selection is to hire the most suitable candidate for the job
-
The recruitment and selection process
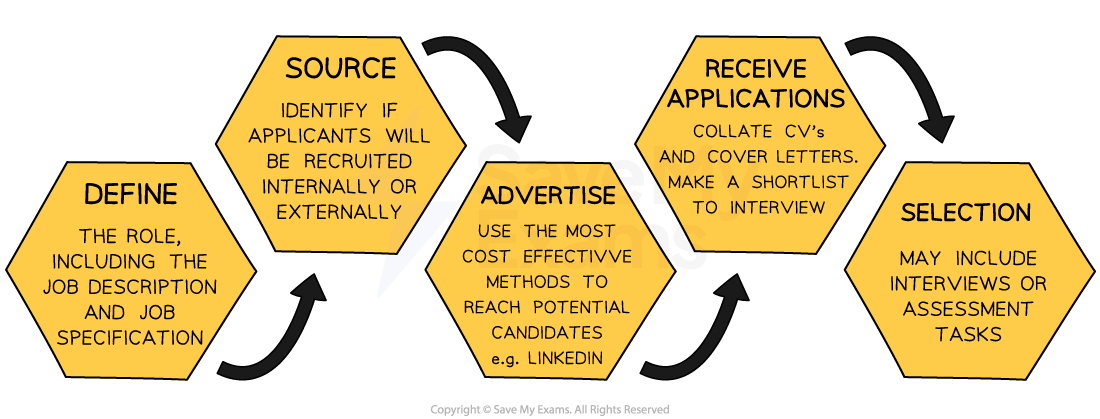
1. Define the role
-
Businesses should determine exactly what is required, and part of that is developing a job description and a person/job specification
-
A job specification outlines the qualifications, skills, experience and personal qualities required from a candidate for a specific job; e.g. problem solver, good communicator, able to code in Java
-
A job description outlines the duties, responsibilities and requirements of a particular job
-
2. Determine the best source of candidates
-
The business can advertise the role internally, externally, or a combination of both
-
Internal recruitment is the process of hiring employees from within the organisation
-
It can involve the promotion or redeployment of staff to fill a vacant post
-
Vacancies are advertised internally on staff notice boards, in newsletters or via in-house electronic communications
-
-
Evaluation of internal recruitment
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
External recruitment is the process of hiring employees from outside the organisation
-
External recruitment can bring fresh ideas, experiences and perspectives to the organisation
-
It overcomes some of the disadvantages of internal recruitment
-
However, it is often more expensive than internal recruitment
-
There is also a greater degree of uncertainty, as external candidates are unknown to the business
-
Comparison of external recruitment methods
|
Method |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Referrals / personal recommendations |
|
|
Online advertising |
|
|
Newspaper advertising |
|
|
Specialist trade publications |
|
|
Employment agencies |
|
|
Headhunting |
|
|
Job centres |
|
|
Career fairs |
|
3. Advertise
-
Businesses with a strong social media presence can use these platforms to advertise cost-effectively, e.g. Facebook, LinkedIn, TikTok
-
Depending on the nature of the business, there may be specialist recruitment portals through which they can advertise; these tend to cost more, e.g. The TES is one of the main publications used to recruit teaching staff
4. Receive applications
-
The application stage involves collecting information from potential candidates
-
A business may have its own application form, which should gather information such as personal details, qualifications and work experience
-
Applicants may also be asked to submit their CV and a cover letter explaining why they believe they are the right person for the role
-
Someone within the business must be nominated to manage the application process
-
This person (possibly together with others) will draw up a shortlist of candidates from the many applications received
-
The shortlist usually includes three to five candidates who are invited to interview
-
5. The selection process
-
This process varies significantly between organisations
-
Businesses must decide on the most appropriate method that will help them identify the best candidate
-
The most commonly used methods include interviews and assessment tasks
Interviews and assessment tasks
|
Interviews |
Assessment tasks |
|---|---|
|
|
Costs of recruitment, selection and training
-
Recruitment, training and selection are essential processes for any business to attract, develop and retain a skilled workforce
-
These processes involve significant costs for businesses, which can impact their overall profitability and competitiveness
Costs of recruitment, selection and training
|
Recruitment costs |
Training costs |
Selection costs |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
-
By reducing labour turnover rates and improving the effectiveness of their training programmes, businesses can minimise these costs and improve their overall profitability and competitiveness
Types of training provided by businesses
-
Different types of training have their advantages and disadvantages for the business
Training types
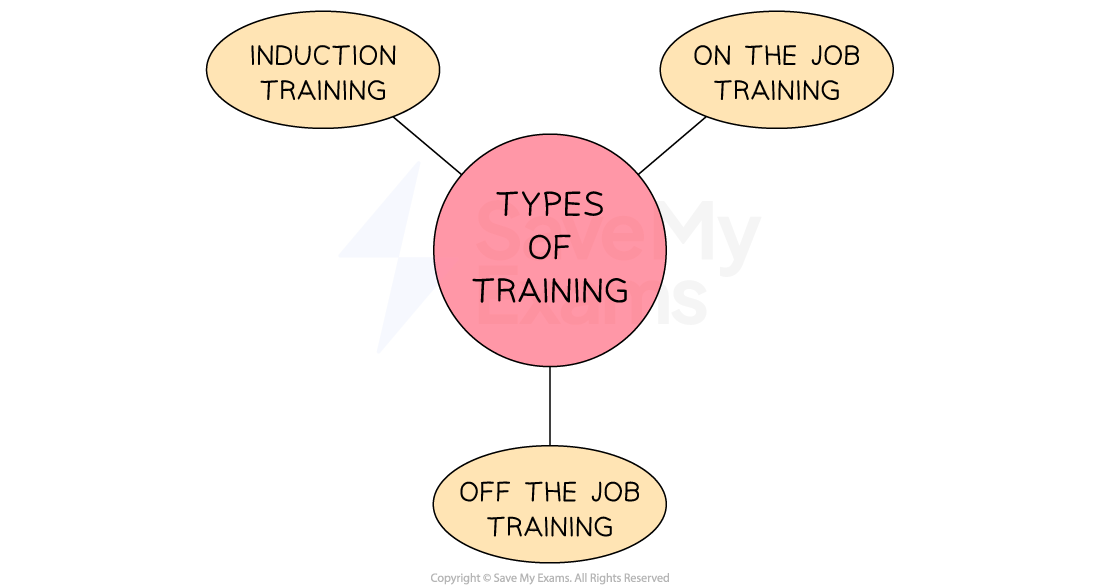
Induction training
-
Induction training is a type of training that new employees receive when they start working for a company
-
It introduces them to the company, its culture, policies and procedures, and their job roles and responsibilities
-
E.g. when a new employee joins Marks & Spencer, they receive induction training that covers customer service, product knowledge, store policies and safety procedures
-
-
Evaluation of induction training
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|

Responses