Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
methods-of-quality-management
The importance of quality
-
Quality considers the characteristics and features of a product that satisfy the needs of customers
-
Businesses need to maintain a level of quality that attracts and retains customers if they want to remain successful
-
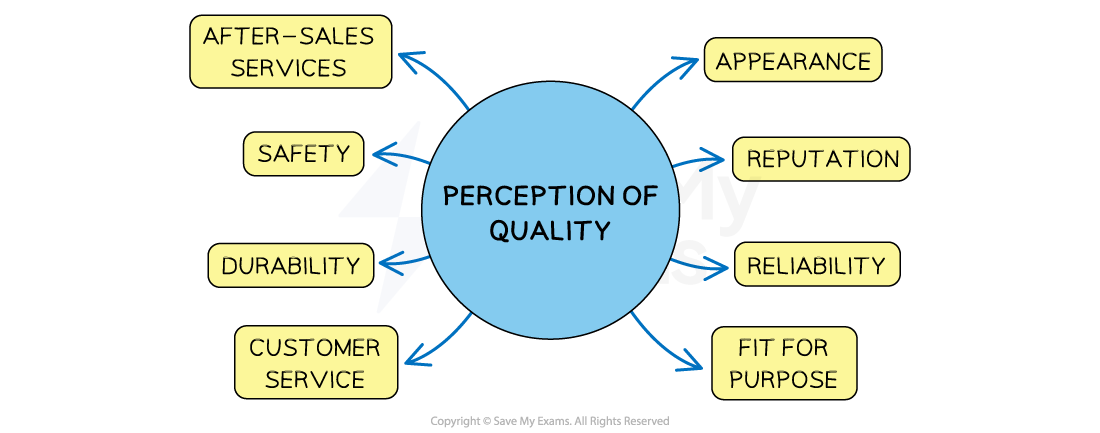
Customer perceptions of quality are related to a range of product or business features
Factors that influence quality perception
-
Customers may consider products or services to be of good quality if they
-
Look good and are sold by a reputable business or brand
-
Are reliable and durable
-
Are safe and fit for purpose
-
Receive good customer service, including after-sales service
-
-
If quality is not maintained, then businesses may be at risk of
-
Losing their competitive advantage and customers to other brands that offer better quality goods or services
-
Experiencing higher costs due to having to replace faulty or defective goods
-
Gaining a poor reputation as customers spread poor reviews about the business to others
-
-
In some countries laws protect consumers so businesses need to ensure that the products they sell are free of faults or defects to avoid harming customers or their reputation
Quality control
-
Quality control is a traditional method of checking quality at the end of the production process by using quality inspectors to find faults
-
It is not possible to achieve perfection in every production process
-
E.g. there will always be some variation in terms of materials used, production skills applied or reliability of the finished product
-
The impact of quality control on business
1. Reduces risk of poor-quality products reaching customers
-
Helps maintain the business’s reputation and avoid customer complaints
2. Wasted output may increase
-
Faulty items are found after production, so time and materials may already be wasted
3. Higher inspection costs
-
Employing inspectors adds to labour costs, especially in large-scale operations
4. Low training costs
-
Limited staff training is needed as inspectors check quality rather than the employees themselves
5. Less responsibility for workers
-
Employees may depend on inspectors instead of taking ownership of quality themselves
6. Inconsistent quality improvements
-
Problems are found but not always prevented, so the same issues may continue to occur
Quality assurance
-
Quality assurance involves inspecting the quality of production throughout the process
-
Workers check their own work and, sometimes, the work of others throughout the various stages of production
-
-
Some business take a whole-business approach to quality assurance, with systems such as quality circles, benchmarking and total quality management
The impact of quality assurance on business
|
Impact |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Fewer errors and waste |
|
|
Improved customer satisfaction |
|
|
Workers take more responsibility |
|
|
Training and systems required |
|
|
Can improve brand reputation |
|
Total Quality Management (TQM)
-
Total Quality Management (TQM) places quality at its core and makes every worker responsible for quality throughout the business
-
Quality is considered from the customer’s perspective
-
Inefficiency and wastage is removed from every business activity or function, including those that are not directly related to production
-
Advantages and disadvantages of TQM
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Case Study
The impact of TQM at Nestlé
-
Nestlé is one of the largest food and beverage companies in the world, with operations in over 180 countries
-
With such a large global footprint, consistent product quality and customer trust are essential to its success

Why Nestlé introduced TQM
-
To maintain consistent quality across its many factories and brands
-
To improve efficiency in production and reduce waste
-
To respond better to customer expectations regarding food safety, nutrition, and quality
What changes were made
-
Nestlé introduced a global quality management system based on TQM principles, including continuous improvement (Kaizen)
-
It developed a company-wide culture of quality with the slogan: “Quality is the foundation of our company”
-
It invested heavily in employee training, so every worker understood their role in maintaining high standards
-
It used customer feedback, regular audits and process checks to improve quality at every stage, from sourcing its raw materials to final packaging
Impact on the business
|
Area |
Impact |
|---|---|
|
Product quality |
|
|
Operational efficiency |
|
|
Customer trust |
|
|
Employee engagement |
|
The importance of benchmarking
-
Benchmarking involves a business comparing its quality and performance with market leaders within the same industry
1. Internal benchmarking
-
Comparison of different functions within a business, such as finance or marketing
-
Performance
-
Comparison of key performance indicators such as labour productivity or labour turnover rates
-
-
Process
-
Comparison of business operations and processes such as call centre queue times or delivery times
-
-
2. External benchmarking
-
Comparison of key performance indicators, such as the number of product recalls, against those of market leaders in an industry
Evaluating benchmarking
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
