The need for operations planning
-
Operations planning is the process of organising all the resources and activities needed to produce goods or services efficiently
-
It ensures that the right products are made, at the right time, in the right quantity and using the right resources
-
Benefits of operations planning
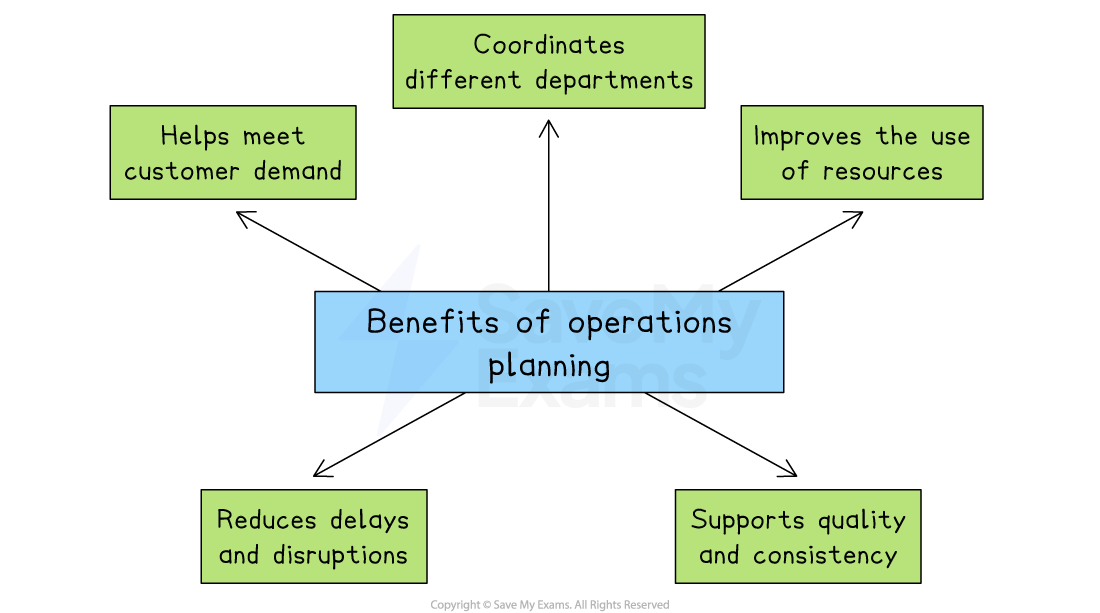
-
Meet customer demand
-
Planning helps businesses produce the correct quantity of goods to match expected demand
-
Without it, a business might make too little, causing stock shortages and lost sales,or too much, leading to waste and higher costs
-
-
-
Improve the use of resources
-
Operations planning ensures that staff, machinery and materials are used efficiently
-
It helps avoid wasted time, overuse of equipment, or running out of stock during production
-
-
-
Coordination of departments
-
Good planning allows production, purchasing, finance, and marketing to work together
-
E.g. Marketing can give sales forecasts, finance can set budgets and production can schedule output to meet targets
-
-
-
Reduces delays and disruptions
-
Planning helps identify potential problems early, such as a shortage of raw materials or a machine breakdown
-
Solutions can be prepared in advance, reducing the risk of disruption
-
-
-
Supports quality and consistency
-
Operations planning includes setting clear standards for quality, timing and workflows
-
This ensures that products or services are delivered consistently to meet customer expectations
-
-
An introduction to network diagrams
-
A network diagram is a visual planning tool used in operations management to help organise and schedule tasks in a project
-
It shows the order in which activities must be completed and how long each one is expected to take
Example network analysis

-
A network diagram must always start and end on a single node
-
Lines must not cross and must only be assigned to activities
How network diagrams help operations planning
-
Network diagrams improve time management by helping managers identify the critical path, the shortest time needed to complete a project
-
They highlight task dependencies by showing which activities must be completed before others can begin, helping to avoid mistakes and delays
-
-
Network diagrams support efficient resource allocation by showing when people, machines, or materials will be needed, reducing idle time and bottlenecks
-
They improve decision-making by making it easier to adjust plans if there are unexpected delays or changes to deadlines
-
Elements of network diagrams
Node
-
A node is a circle that represents a point in time where an activity either starts or finishes
-
Each node is split into three sections
-
The left half of the circle shows the activity number
-
The top right section shows the earliest start time (EST)—the earliest point an activity can begin, based on the completion of the previous activity
-
The bottom right section shows the latest finish time (LFT)—the latest time by which the previous activity must be completed without delaying the project
-
Activities
-
An activity is a task or process within a project that takes time to complete
-
Activities are shown on a network diagram as a line linking two nodes
-
Above the line, you will usually find either a letter or a short description of the activity
-
Duration
-
The duration is the length of time required to complete an activity
-
This is shown below the activity line and is usually measured in time units such as hours or days
Dummy activities
-
A dummy activity is an activity that has a weight of zero
-
Dummies are not assigned names (letters)
-
Dummies are represented by dotted lines
-
Where a dummy activity is used
-
To ensure each activity has a unique pair of start and end nodes
-
E.g. In the activity network below, activity D has immediate predecessors B and C
-
B and C cannot both start at event (node) 1 and end at event (node) 2 (this would not be a unique pair)
-
a dummy activity is used so that B has start and end pair (1, 3) and C has a start and end pair (1, 2)
-
-

-
When there is a split of immediate predecessors
-
E.g. In the activity network below, activity D has immediate predecessors B and C
-
Activity E only has B as an immediate predecessor
-
A dummy activity is used to show that D depends on both B and C
-
-

Using network diagrams for critical path analysis
1. Calculating earliest start times (EST)
-
Working forward from Node 1, it is possible to calculate the Earliest Start Time for each activity by adding the duration of each task

-
The EST for each activity is placed in the top right of each node
-
Node 1 is the starting point of the project and where both Activity A and Activity B begin
-
Activity A and Activity B are independent processes
-
Activity A has a duration of 2 days and its earliest start time (EST) is 0 days
-
Activity B has a duration of 3 days and its EST is also 0 days
-
Activity C and Activity D both begin at Node 2 and are dependent upon the completion of Activity A but are independent from each other
-
Activity C has a duration of 3 days and its EST is 2 days
-
Activity D has a duration of 5 days and its EST is also 2 days
-
-
-
Activity E begins at Node 3
-
Activity E has a duration of 4 days and its EST is 3 days
-
-
Activity F begins at Node 4
-
Activity F has a duration of 2 days and its EST is 5 days
-
-
Activity G begins at Node 5
-
Activity G has a duration of 1 day and its EST is 7 days
-
-
Activity H begins at Node 6
-
Activity H has a duration of 3 days and its EST is 7 days
-
-
Node 7 is the end point of the project
2. Calculating latest finish times (LFT)
-
Working backwards from Node 7, it is now possible to calculate the Latest Finish Time (LFT) for each activity by subtracting the duration of each task
