Resources and operational decisions
-
Operational decisions are impacted by, and have an impact on, business resources
-
Business resources include:
-
Capital
-
Employees, including contractors
-
Property and land
-
Machinery and equipment, including IT hardware
-
Intellectual property such as patents
-
Databases and key software and hardware
-
-
When operational decisions are made, care needs to be taken to ensure that the appropriate resources are in place or that adequate plans are made to ensure that they will be in place when needed
-
This may involve
-
Purchasing new facilities, such as land or property
-
Investing in new production equipment or hardware
-
Hiring new workers or training existing staff
-
Obtaining legal protection for inventions
-
Updating systems to ensure information is up-to-date and complete
-
-
-
Without the appropriate resources, operations decisions may be delayed or require significant amendment
-
This may impact on the operations function’s ability to achieve its overall targets and limit its contribution to achieving business objectives
-
Information technology and operational decisions
-
Businesses are increasingly using a range of technologies to automate production processes
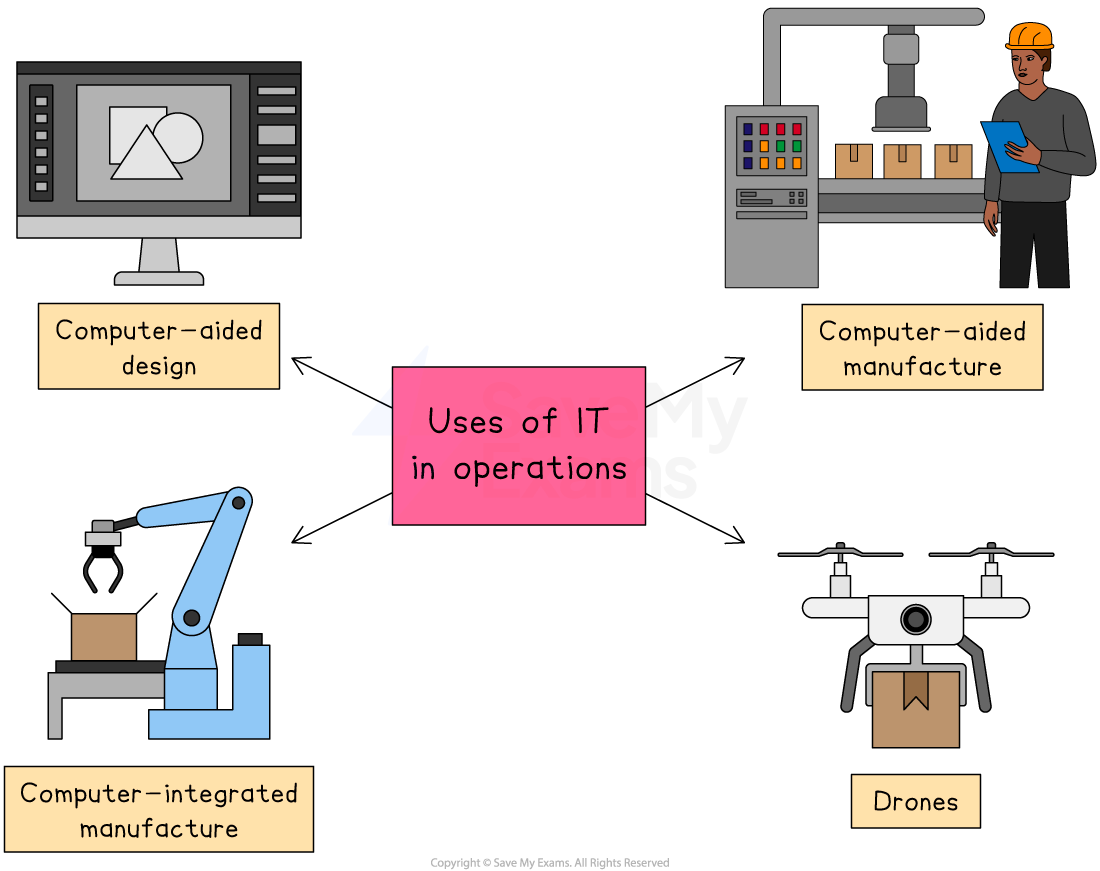
1. Computer-aided design (CAD)
-
The process of digitally creating design simulations of products in 2D or 3D
-
It can also include the use of computer software to create mapping processes for industrial machinery, e.g. the movements required by a robotic arm in a television factory
Evaluating the use of CAD
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
2. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM)
-
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is the use of computers to assist in operations of a manufacturing plant, such as production processes, planning, management, transportation and storage
-
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the complete automation of a manufacturing plant, with all processes functioning under computer control with digital information tying them together
Evaluating the use of CAM and CIM
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
3. Drones
-
Unpiloted aircraft are being used to carry out an increasing range of business tasks, including package delivery, photography and security
-
E.g. Large agriculture businesses use drones to spot failing crops and areas of concern in large fields, mapping boundaries and even applying pesticides
-
Evaluation of IT in operations
-
The installation and maintenance of IT technology in production is likely to incur significant costs
-
Purchasing IT hardware and software may require external finance, such as loans which will need to be repaid with interest
-
Employees will need training in order to safely and effectively operate technology
-
Down time as technology is installed and workers are trained, it impacts output levels
-
-
Businesses must be sure that this capital expenditure is outweighed by gains in productivity and improvements in quality and flexibility
-
Higher levels of productivity may only be achieved with high levels of output
-
Automation usually works best in the manufacture of standardised products
-
Flexibility in production refers to how easy it is to install machinery and switch to different machinery which is required to manufacture different products (known as retooling)
-
The most flexible technology is also likely to be the most costly
-
-
Artificial intelligence and operational decisions
-
Artificial intelligence can be used in a range of ways to enhance business operations
-
In financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies, AI systems can identify customers’ financial and behavioural patterns to identify potential instances of fraud
-
In grocery retail, AI systems can be used to monitor and control storage environments, such as freezers, to ensure that products are kept in optimum conditions
-
In manufacturing, AI can be used to schedule upgrades and maintenance to reduce the amount of production down time
-
-
Robots are programmed to collect information from their environment using sensors and use artificial intelligence (AI) to improve production performance
-
E.g. Hotel chain Yotel employs ‘robotic staff’ that can move around anywhere in the hotels, carrying guests’ luggage, delivering laundry, cleaning rooms and making coffee
-
Business uses of robots
-
Manufacturing
-
In manufacturing and assembly lines, robots can increase productivity and accuracy
-
-
Logistics
-
Warehouses and logistics businesses can use robots to move and transport goods
-
-
Agriculture
-
In agriculture, tasks such as planting, harvesting and spraying crops can be carried out by robots
-
-
Medicine
-
In medicine robots can be used in surgical procedures to increase precision and reduce the risk of errors
-
-
Entertainment
-
Robots can be sold as toys or used in amusement parks to provide entertainment
-
-
Dangerous tasks
-
Remote-controlled robots can be programmed to carry out hazardous testing and R&D processes
-
The use of robots in particular presents a range of advantages and disadvantages related to productivity, quality and flexibility
-
Evaluating the use of robots in operations
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
The need for flexibility
-
Businesses should have the flexibility to change output volumes, timescales and product specifications for several reasons
-
The level of demand can change with little warning
-
Supplies may become unavailable
-
Customers may delay orders or require rapid delivery of orders
-
Customers may demand variations to products
-
-
Flexibility can be improved in a number of ways
-
Outsourcing some production to trusted manufacturers
-
Employing multi-skilled workers and investing in their training and development
-
Holding buffer stock to ensure increased demand can be met
-
Investing in advanced machinery that is capable of mass customisation
-
Investing in buildings and land to extend production premises
-
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be asked to analyse the impact of IT and AI on a business. Their contribution to improving flexibility should be one of your key arguments – the case study may give you some ideas on how the business in question could apply them.
Process innovation
-
Process innovation involves identifying new ways to organise and carry out production processes
-
In recent years, organisations have made some notable improvements production processes that have improved productive efficiency
-
Examples of process innovation
|
Amazon |
IKEA |
UK Passport and Borders Agency |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
