Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
Factors determining location and relocation
-
Choosing a good production location can have significant impacts on a business.
-
A range of factors influence the location a business chooses for production or where it chooses to relocate
Factors affecting business location

Proximity to the market
-
This refers to how close the business is to its target customers
-
Being near the market can reduce transport costs and make it easier for customers to access the business
Proximity to labour
-
This means being located near areas where skilled and qualified workers are available
-
Businesses often choose locations with a strong local workforce to make it easier to recruit the right people and run operations efficiently
Proximity to materials
-
This refers to how close a business is to the raw materials or supplies it needs
-
Being near materials helps reduce transportation costs and ensures a steady supply
Proximity to competitors
-
Some businesses choose to locate near competitors to attract the same customer base or to offer something different
-
Others may avoid locating near competitors to reduce direct competition
The nature of the business activity
-
Different types of businesses have different location needs based on what they do
-
For example, a manufacturing plant may need large space and delivery access, while a law firm may need a smaller, more central office
-
E.g. A factory needs room for machinery and deliveries, while a law office needs a professional, easy-to-access location
-
Infrastructure
-
This includes transport links and electronic networks like internet connections
-
Good transport is essential for businesses that deliver physical goods
-
Fast and reliable internet access is key for online businesses
-
E.g. An online fashion retailer needs a location close to the motorway for quick delivery and fast service, helping it compete in the market
Local, national and international location decisions
-
When a business chooses where to locate, the scale of that decision can be local, national or international
1. Local location decisions
-
Local location decisions involve choosing where in a particular town or city to place the business, such as in the city centre, on an industrial estate or near transport links
-
E.g. A hair salon might choose a busy high street over a quiet side road to attract walk-in customers
-
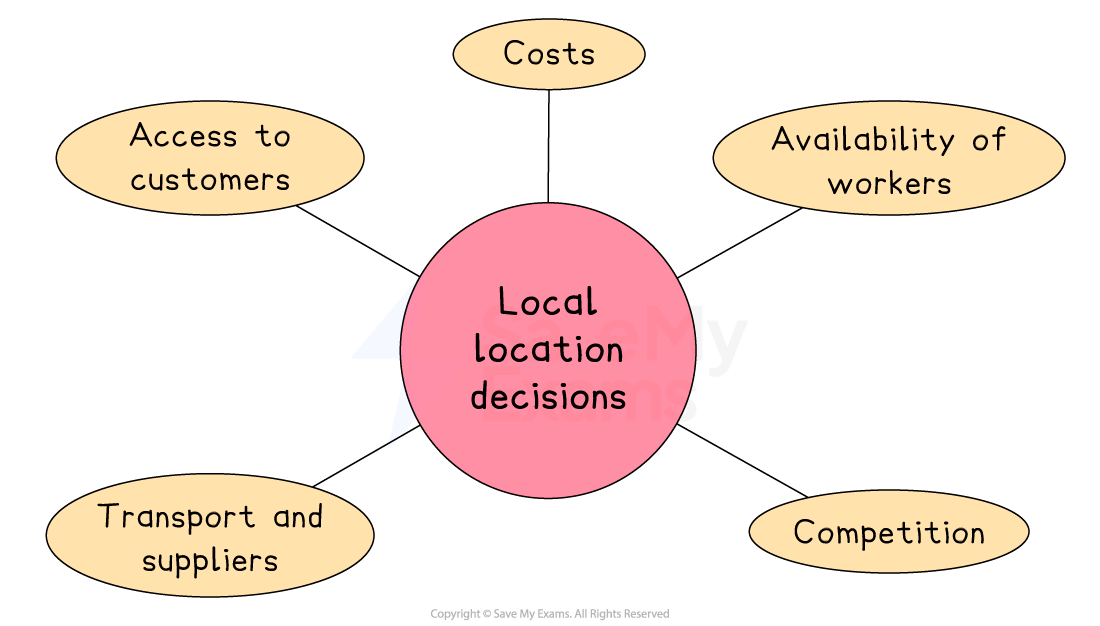
Key factors affecting local location decisions
-
Access to customers
-
Retail shops often choose high footfall areas like shopping centres to attract more sales
-
Major Turkish retail brands, for example, locate their flagship stores on İstiklal Caddesi, a busy shopping street in Istanbul.
-
-
-
Availability of workers
-
Businesses benefit from locating near skilled or affordable labour
-
Hi-tech firms choose business parks around MIT in the USA to access a strong pool of computing graduates
-
-
-
Costs
-
Rent and business rates can vary widely even within one town or city
-
Retail space on Berlin’s Kurfürstendamm is expensive, but nearby Prenzlauer Berg offers more affordable options
-
-
-
Competition
-
Locating near rivals can create a customer hub but may also reduce market share
-
Hatton Garden in London is home to many high-end jewellery and gold businesses, attracting specialist customers.
-
-
-
Transport and suppliers
-
Good transport links are essential for service and delivery-based businesses
-
Logistics firms favour northern Calais due to its excellent road, rail and ferry connections.
-
-
2. National location decisions
-
National location decisions involve choosing which part of a country to set up or expand a business
-
E.g. A call centre might choose a city in the north of the UK to benefit from lower wages and government support.
-
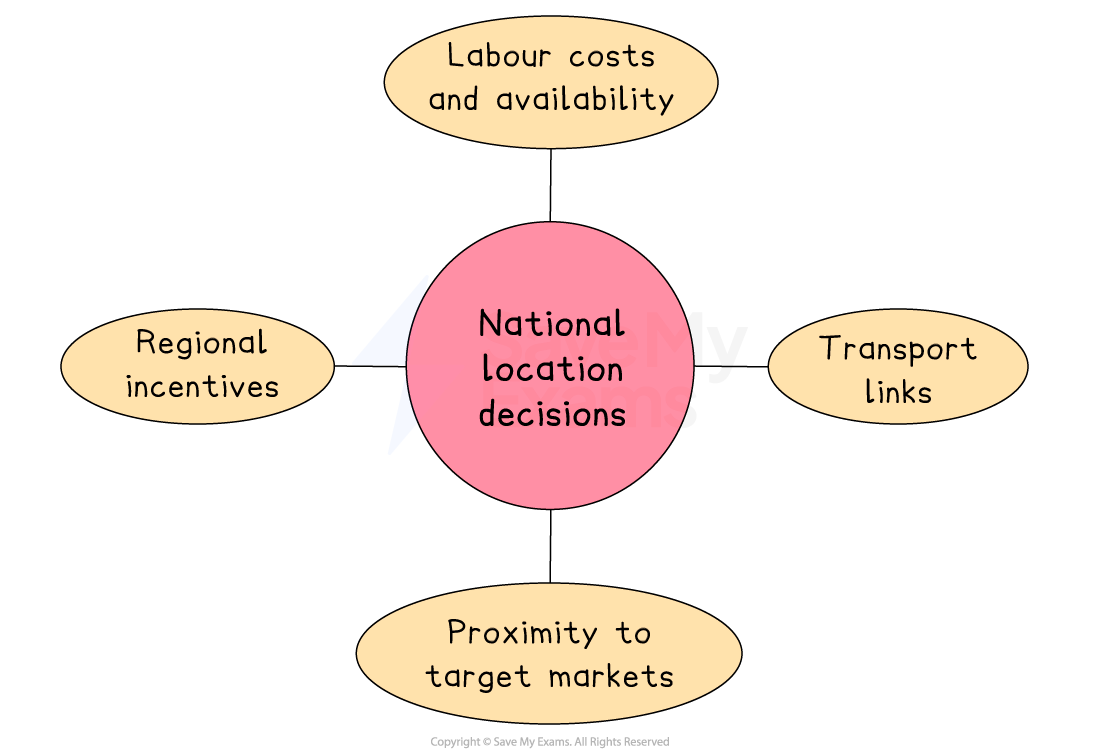
Key factors affecting national location decisions
-
Regional incentives
-
Governments may offer grants or tax breaks to attract businesses to poorer areas, aiming to reduce unemployment and support local economies
-
E.g. The Welsh Government has funded companies locating in places like Cardiff and Swansea
-
-
-
Labour costs and availability
-
Wages and skills vary by region
-
Cities may offer highly skilled workers at higher wages, while rural areas may be cheaper but with fewer qualified employees
-
E.g. In India, major cities like Bangalore and Delhi have more skilled workers than rural regions
-
-
-
Proximity to target markets
-
Locating near areas with high demand helps reduce delivery costs and respond better to local preferences
-
E.g. Mexican food firms often base themselves near large cities like Mexico City or Guadalajara to reach more consumers
-
-
-
Transport links
-
Good access to roads, ports, railways or airports helps cut delivery times and transport costs, especially for goods-based businesses
-
E.g. The Netherlands attracts many distribution centres due to Rotterdam port and a strong road and rail network
-
-
3. International location decisions
-
International location decisions relate to a business considering moving or expanding to another country
-
E.g. A European clothing brand might open a factory in Vietnam to reduce production costs and sell to Asian markets
-
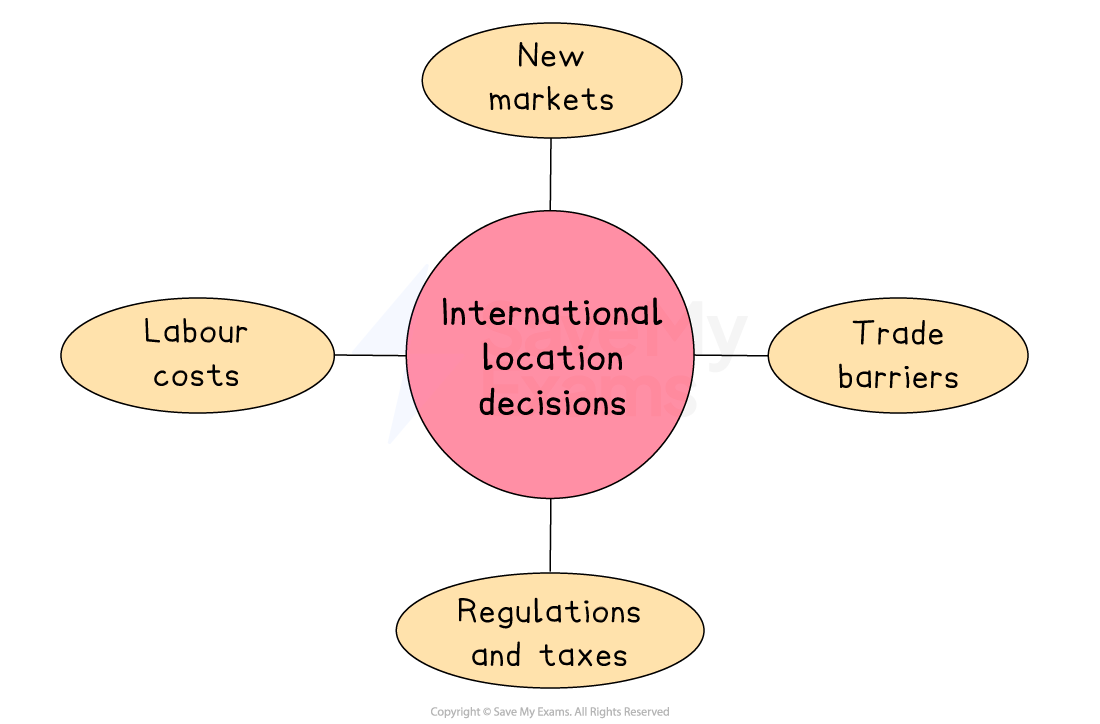
Key factors affecting international location decisions
-
Labour costs
-
Businesses may locate in countries where wages are lower to reduce production costs, especially in labour-intensive sectors like textiles or electronics
-
However, they must weigh up lower wages against possible lower skill levels, productivity and working conditions
-
E.g. Zara and H&M outsource production to countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, where labour is much cheaper than in Europe or North America
-
-
-
New markets
-
Expanding abroad helps businesses access new customers, particularly in growing economies
-
This boosts sales and market share, especially if the home market is saturated
-
Being based locally also helps firms better understand customer behaviour and respond quickly to demand
-
E.g. McDonald’s has entered Asian and African markets to tap into rising incomes and growing demand for Western food
-
-
-
Regulations and taxes
-
Some countries offer lower tax rates and simpler business laws, making them attractive for international firms
-
These benefits can raise profits but must be balanced with maintaining ethical standards
-
E.g. Ireland’s low corporate tax and EU access have attracted major tech firms like Google and Facebook
-
-
-
Trade barriers
-
Locating within a country can help businesses avoid tariffs, quotas or other trade restrictions
-
This is vital for exporters and also improves delivery times and local relationships
-
E.g. Toyota has built factories in the US and UK to avoid import tariffs and bet
-
-
