An introduction to legal influences
-
Legal factors are laws and regulations that businesses must follow for a range of reasons, including:
-
To protect consumers from harmful substances
-
To protect consumers from misinformation
-
To ensure that businesses operate ethically
-
To ensure that business competition is healthy for society and does not become harmful or destructive
-
-
Governments use laws to guide how businesses behave
-
This helps protect workers, consumers, and the wider economy
-
-
The main areas of legal influence are shown on the diagram below
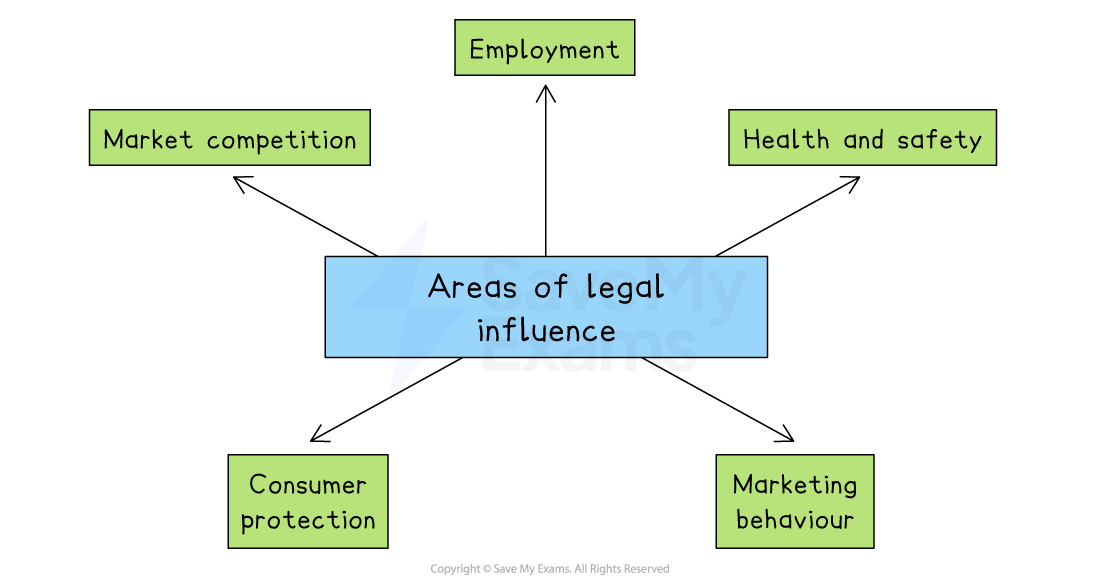
Employment law
-
Employee protection legislation prevents exploitation of workers
-
It covers areas including
-
Pay and working conditions
-
Equality of employment rights for marginalised groups (e.g. those with disabilities) to avoid discrimination
-
The right to belong to a trade union and take industrial action
-
Contracts and termination of employment
-
Health and safety of employees and contractors
-
|
Area of law |
Typical coverage |
Impact on business |
|---|---|---|
|
Pay and working conditions |
|
|
|
Equality of employment rights |
|
|
|
Right to belong to a trade union and take industrial action |
|
|
|
Contracts and termination of employment |
|
|
Health and safety law
-
Health and safety law is intended to protect the physical and mental wellbeing of employees and contractors
-
Laws in different countries typically cover
-
Provision of adequate rest periods
-
Acceptable workplace temperature and noise levels
-
Provision of safety equipment
-
Hygienic, safe and sanitary conditions
-
Manageable workloads
-
Safety procedures and equipment, e.g., fire exits and first aid kits
-
-
To comply with health and safety laws, businesses need to
-
Train and supervise staff properly on how to work safely
-
Adjust working hours and ensure proper rest is taken
-
Arrange manuals, signage, and legally required safety documentation
-
Purchase and maintain personal protective equipment and safety tools
-
Create and follow a health and safety policy or code of practice
-
-
Serious breaches of health and safety laws can lead to investigations, fines or prosecution.
-
Poor health and safety practices can also cause accidents, reduce staff morale and damage a business’s reputation
-
Case Study
IronForge Engineering Ltd
IronForge operates a busy metal fabrication plant. Workers often complain about
-
High indoor temperatures
-
Loud machinery with no hearing protection
-
Lack of proper safety gear when cutting and welding
-
Long shifts without proper breaks

Scenario
After a serious accident where a worker was injured by a falling object, the business was reported to the local health and safety authority
The company was ordered to
-
Install proper ventilation and provide ear protection
-
Reduce shift lengths and allow more frequent rest breaks
-
Provide hard hats, gloves, and protective clothing
-
Develop a written health and safety policy
-
Train all workers in equipment safety and emergency procedures
Impact
While the improvements increased costs at first, the business
-
Avoided prosecution
-
Saw fewer accidents and reduced staff turnover
-
Gained a better reputation with clients and employees
Marketing behaviour
-
Laws regulate marketing behaviour and protect consumers from unfair, misleading or harmful practices
-
They ensure that businesses advertise products truthfully, responsibly and ethically
-
Marketing strategies must comply with legal standards in areas such as
-
Advertising content
-
Data protection
-
Pricing and promotions
-
Comparisons with competitors
-
-
Failure to follow these laws can lead to fines, legal action or reputational damage
Areas of marketing law
|
Type of law |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
False or misleading advertising |
|
|
Use of personal data in marketing |
|
|
Advertising to children |
|
|
Unfair pricing |
|
|
Comparative and competitive advertising |
|
Consumer law
-
Consumer protection laws defend the rights of buyers and ensure that businesses act fairly, safely, and honestly
-
These laws create trust in the market by making sure that products sold meet certain standards and that consumers are not misled
-
Laws often cover
-
Product safety
-
Accuracy of information
-
Unfair contracts
-
Refunds or returns
-
Online and distance purchases
-
-
If businesses fail to follow these laws, they can face legal action, financial penalties or reputational damage
Areas of consumer law
|
Type of law |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Product safety |
|
|
Right to information |
|
|
Right to refunds, repairs or replacements |
|
|
Protection against unfair contract terms |
|
|
Online and distance selling |
|
Competition law
-
Competition law helps ensure markets are open, fair and competitive
-
Powerful companies are prevented from using their position to dominate the market
-
Competition law can
-
Prevent price fixing and unfair collusion
-
Stop mergers or takeovers that reduce market competition
-
Ban abuse of monopoly power
-
-
If a company breaks competition law, it may face heavy fines, restrictions or forced break-up of business operations
Laws affecting market competition
|
Type of law |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Ban on price fixing and <span class=”popovers” data-content=”Where a group of busine |
