Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
international-trade
An introduction to international influences
-
International trade is the exchange of goods and services across national borders
-
Exporting is the selling of goods or services from the home country to a customer in another country
-
E.g. A UK chocolate manufacturer ships bars to supermarkets in Germany
-
-
Importing is buying goods or services from producers in another country for use or resale at home
-
E.g. A Mexican furniture shop sells flat-pack desks manufactured by a producer in Poland
-
-
-
Exports generate extra sales revenue for businesses selling their goods abroad
-
Imports result in money leaving the country, which generates extra revenue for foreign businesses
Trends in international trade
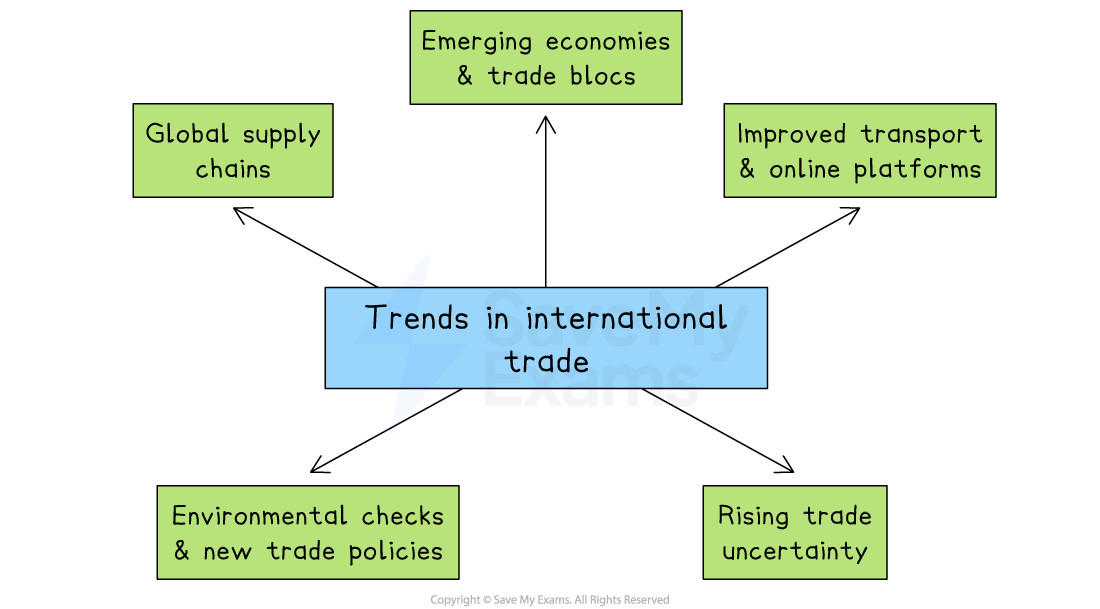
Global supply chains and digital services
-
Many products are made in several countries before they reach the customer.
-
E.g. A smartphone can be designed in the United States, use chips from Taiwan, be assembled in Vietnam and sold around the world
-
Emerging economies and trade blocs
-
China, India and Mexico now produce much of the world’s manufactured goods
-
Trade blocs like the EU and USMCA lower tariffs for members, but businesses must follow each bloc’s rules
Improved transport and online platforms
-
Container ships and air freight make international delivery faster and cheaper
-
Even small firms can sell online to customers in other countries
Environmental checks and new trade policies
-
Customers and governments examine carbon footprints, working conditions and data security before buying or approving goods
-
New trade rules encourage firms to adjust their supply chains to meet these higher standards and reduce risk
Rising trade uncertainty
-
Exchange rates, tariffs and political tensions change more often, making international trade less predictable
-
E.g. The USA has recently applied high levels of tariffs to a wide range of consumer goods manufactured in China
-
-
This encourages firms to develop more flexible supply chains
Benefits of increased international trade
|
Benefit |
Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Larger customer base |
|
|
Economies of scale |
|
|
Lower input costs |
|
|
Risk spreading |
|
|
Access to new ideas and technology |
|
The importance of international trade links
-
International trade links, such as shared markets, digital agreements and transport routes, lower barriers to trade and reduce risk when trading internationally
-
They can help managers make decisions, including
-
Where to source supplies
-
Where to produce
-
How to distribute goods or services
-
International trade links and business decisions
|
International trade link |
How it shapes business decisions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The impact of trade agreements on business
-
International trade agreements set the ground rules for buying and selling across borders
-
By lowering tariffs, standardising product rules or protecting foreign investors, these agreements reduce risk and cost for firms
-
-
As a result, managers decide where to locate factories, how to price products and which new markets to enter based on the protection and opportunities each agreement offers
Examples of trade agreements
|
Trade agreement |
Example |
How it shapes business decisions |
|---|---|---|
|
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) |
|
|
|
Customs unions and common markets |
|
|
|
Global trade rules |
|
|
The role of technology in international trade
-
Technology removes many barriers, such as distance, paperwork and payment difficulties, that once limited international trade
Uses of technology in international trade
|
Technology |
Explanation |
How it helps firms trade across borders |
|---|---|---|
|
Mobile payment systems |
|
|
|
Digital sales platforms |
|
|
|
Cloud collaboration & digital freight tools |
|
|
|
Blockchain for trade finance and traceability |
|
|
|
Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications |
|
|
