Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
economic-influences
How government might intervene to help businesses and encourage enterprise
-
Governments often intervene in the economy to:
-
Promote economic growth
-
Create jobs
-
Encourage innovation and enterprise
-
Increase international competitiveness
-
-
By helping businesses, especially start-ups and small firms, governments aim to build a strong and stable economy
Ways governments support businesses and encourage enterprise
|
Support |
What it involves |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Finance |
|
|
|
Training and education |
|
|
|
Infrastructure investment |
|
|
|
Cutting red tape |
|
|
|
Export and trade support |
|
|
How government might intervene to constrain business activity
-
Governments also have a duty to protect the public, the environment, and the economy
-
They may limit or control certain business activities that are seen as harmful, unfair, or against the wider interests of society
-
-
These interventions can increase business costs, limit certain actions or block business plans altogether
Examples of government interventions
|
Intervention |
What it involves |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Legal regulation |
|
|
|
Competition law enforcement |
|
|
|
Taxation policy |
|
|
|
Planning and zoning controls |
|
|
|
Trade restrictions |
|
|
How government might deal with market failure
-
Market failure happens when the free market fails to allocate resources efficiently or fairly
-
This happens when the market does not produce the right amount of goods and services or does so in a way that is unfair or harmful to society
-
Some goods or services are underprovided (like healthcare or education)
-
Others are overproduced, causing harm (like pollution or drugs)
-
Not everyone can access what they need (like clean water or housing)
-
Ways governments correct market failure
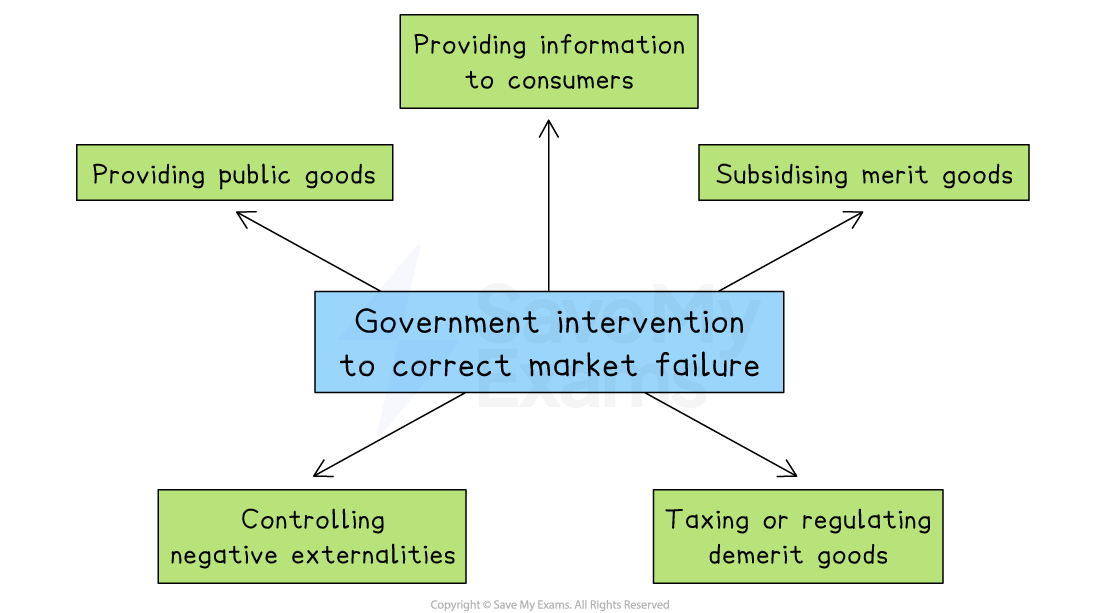
Solutions to market failure
1. Providing public goods
-
Public goods, like street lighting or national defence, wouldn’t be provided by private firms because there’s no way to make a profit
-
The government funds and provides these directly using tax revenue
-
E.g. Most countries provide publicly funded defence, as private business would be able to charge individuals to stay safe from attack
-
2. Subsidising merit goods
-
Merit goods (like education or vaccines) are under-consumed in a free market because people may not understand their full benefits
-
Governments subsidise these goods or provide them for free to encourage greater use
-
E.g. Ghana’s government introduced free secondary education to ensure that more young people stay in school and contribute to economic development
-
3. Taxing or regulating demerit goods
-
Demerit goods, like tobacco or sugary drinks, are over-consumed because consumers ignore or underestimate the harm they cause
-
Governments introduce taxes or regulations to reduce consumption and raise awareness
-
E.g. Mexico introduced a sugar tax in 2014 to tackle rising obesity levels; soft drink sales dropped as a result
-
4. Controlling negative externalities
-
Negative externalities occur when businesses cause harm to others, like air or water pollution
-
Governments enforce regulations, set limits or fine businesses for pollution and environmental damage
-
E.g. China has introduced stricter emissions controls and shut down high-polluting factories to reduce air pollution in major cities like Beijing
-
5. Providing information to consumers
-
Consumers often lack full information to make good choices about, for example, health, finance or environmental impact
-
Governments can launch public awareness campaigns or require businesses to label products clearly
-
E.g. In Chile, food packaging must carry clear warning labels for high sugar, salt, or fat content to help consumers make informed choices
-
