Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
An introduction to macroeconomic objectives
-
Macroeconomic objectives are the main goals that a government tries to achieve in the wider economy to keep the economy stable and growing
-
Successfully meeting the objectives helps improve living standards and create a strong business environment
-
Macroeconomic objectives usually include
-
Economic growth – increasing the total output of goods and services in the country (measured by GDP)
-
Low unemployment – making sure most people who want to work can find a job
-
Low and stable inflation – keeping prices from rising too quickly
-
Low unemployment
-
The target unemployment rate for many economies is between 2-5%
-
In December 2022 the unemployment rate in the USA was 3.7% and in Singapore it was 2.6%
-
-
Low unemployment rates like this are close to the full employment level of labour
-
There will always be a level of frictional, seasonal and structural unemployment
-
This makes it impossible to achieve 100% employment
-
-
Different economies have different unemployment rates that are considered to be close to the full employment level of labour
-
E.g. Japan’s level is about 2.5% while India’s is about 5.7%
-
-
There is an increased emphasis on the unemployment rate within different sections of the population
-
E.g. Youth unemployment, ethnic/racial unemployment by group
-
In 2021, black unemployment in the UK was 11% and white unemployment was 4.%
-
-
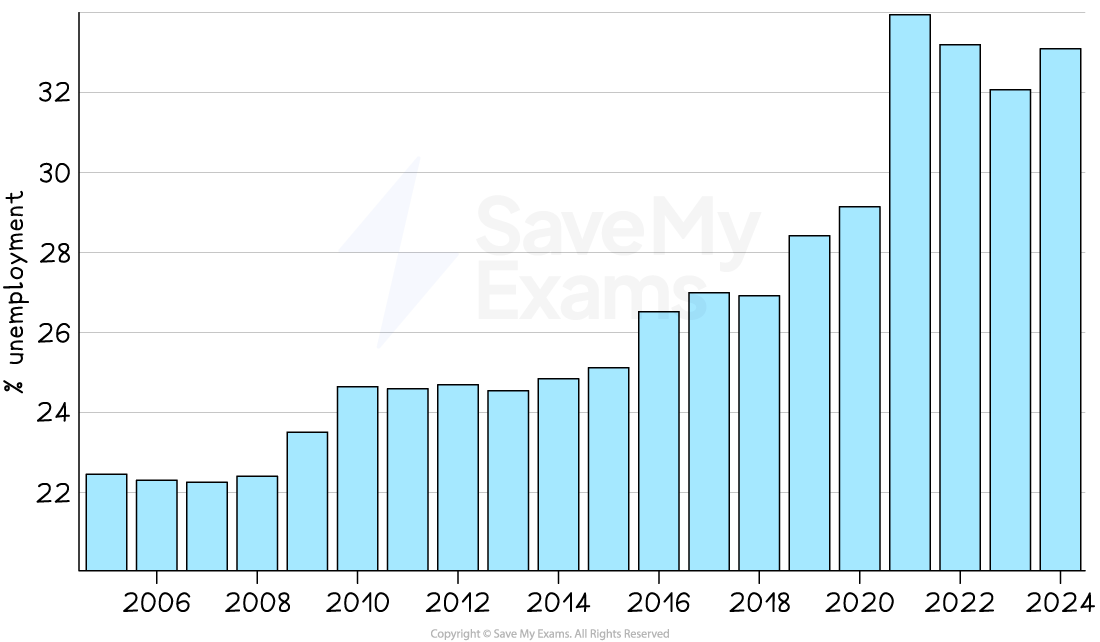
-
Unemployment tends to be inversely proportional to real GDP growth
-
When real GDP increases, unemployment falls
-
When real GDP decreases, unemployment rises
-
Impact on business activity
-
Higher employment levels mean more people have income to spend, which increases consumer demand for goods and services
-
Lower unemployment reduces the availability of labour, making it harder for firms to recruit – this may push up wage costs
-
High employment increases business confidence, encouraging firms to invest and expand
-
In areas or sectors with high unemployment, demand may fall, leading to lower sales and possible business closures
-
Businesses may be able to recruit workers more cheaply during periods of high unemployment, improving labour cost competitiveness
Low and stable inflation
-
Many economies have a target inflation rate of 2% using the Consumer Price Index (CPI)
-
A low and stable rate of inflation is desirable, as it is a symptom of economic growth
-
The different causes of inflation (cost push or demand pull) require different policy responses from the Government
-
Demand-side policies ease demand pull inflation
-
Supply-side policies ease cost push inflation
-
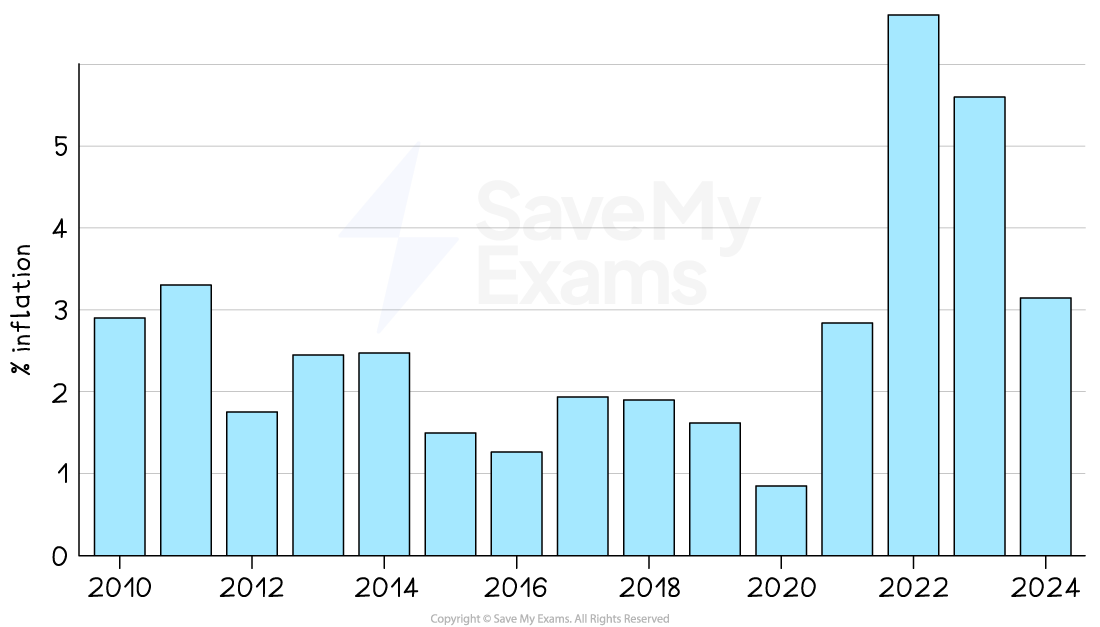
-
In the UK, a significant deviation from the target of 2% would not be considered stable
-
An inflation ratea of 3% is considered to be unstable, eroding household purchasing power
-
By October 2022 the inflation rate in Australia had risen to 6.59%
-
-
A low and stable rate of inflation is important as it
-
Allows firms to confidently plan for future investment
-
Offers price stability to consumers
-
Impact on business activity
-
Low and stable inflation helps businesses plan ahead with greater confidence in costs and pricing strategies
-
High inflation increases input costs (e.g., wages, raw materials), reducing profit margins unless firms can raise prices
-
Unstable inflation creates uncertainty, making it harder to budget, forecast, or make investment decisions
-
Inflation may erode consumer purchasing power, reducing demand for non-essential goods and services
-
In countries with high inflation, businesses may face pressure to increase wages, which can increase overall operational costs
Economic growth
-
Economic growth is a central macroeconomic aim of most governments
-
Many developed nations have an annual target rate of 2-3%
-
This is considered to be sustainable growth
-
Growth at this rate is less likely to cause excessive demand pull inflation
-
-
Politicians use the economic growth rate as a measure of the effectiveness of their policies and leadership
-
Economic growth has positive impacts on confidence, consumption, investment, employment, incomes, living standards and government budgets
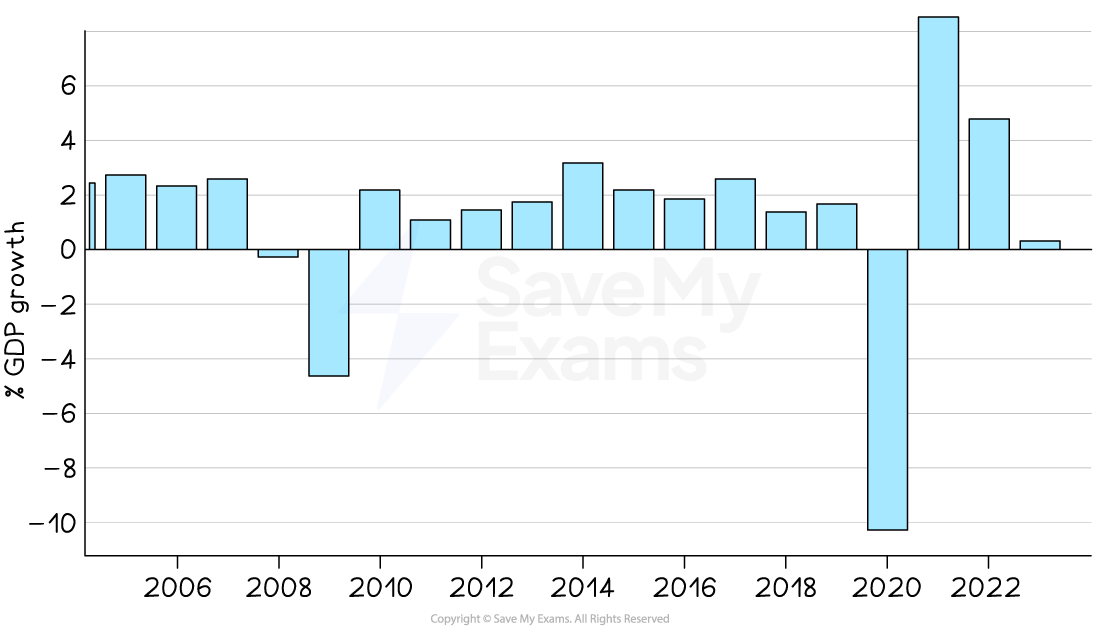
Economic growth trends in the UK since 1998
1998 – 2007
-
Steady growth fluctuating between 2-4%
2008 – 2015
-
Global financial crisis followed by a rapid bounce back due to government intervention – and then steady growth
2016 – 2019
-
Gradual disinflation possibly due to future expectations regarding the impact of the Brexit vote
2020 – 2021
-
Covid resulted in significant economic slumps on a global basis during 2020
-
These created a deep recession (short-lived due to government intervention)
-
-
Many economies rebounded in 2021
2022 – 2025
-
Supply chain issues due to Covid and Brexit continued
-
Increases in the interest rate reduced the level of economic activity
Impact on business activity
-
Growth boosts consumer incomes and spending power, increasing demand for most goods and services
-
Rising demand encourages businesses to expand capacity, hire more workers, and invest in new products or technology
-
Economic booms can lead to higher profits for firms, improving shareholder returns and business sustainability
-
High growth can also cause overheating, leading to labour shortages or inflationary pressures, which may affect input costs
-
A lack of growth (or recession) can lead to lower consumer confidence, reduced investment, and declining business revenues
