Business_A-level_Cie
-
business-and-its-environment
enterprise6 主题 -
business-structure6 主题
-
size-of-business3 主题
-
business-objectives3 主题
-
stakeholders-in-a-business2 主题
-
external-influences-on-business12 主题
-
political-influences
-
legal-influences
-
economic-influences
-
economic-government-macroeconomic-objectives
-
economic-government-policies
-
social-influences
-
the-impact-of-corporate-social-responsibility
-
demographic-influences
-
technology-competitors-and-suppliers
-
international-trade
-
the-impact-of-multinationals
-
environmental-influences
-
political-influences
-
business-strategy10 主题
-
human-resource-managementhuman-resource-management-hrm8 主题
-
motivation4 主题
-
management2 主题
-
organisational-structure5 主题
-
business-communication5 主题
-
leadership2 主题
-
human-resource-strategy3 主题
-
marketingthe-nature-of-marketing7 主题
-
market-research3 主题
-
the-marketing-mix6 主题
-
marketing-analysis5 主题
-
marketing-strategy3 主题
-
operations-managementthe-nature-of-operations3 主题
-
inventory-management2 主题
-
capacity-utilisation-and-outsourcing1 主题
-
location-and-scale2 主题
-
quality-management1 主题
-
operations-strategy4 主题
-
finance-and-accountingbusiness-finance2 主题
-
sources-of-finance3 主题
-
forecasting-and-managing-cash-flows1 主题
-
costs4 主题
-
budgets1 主题
-
financial-statements4 主题
-
analysing-published-accounts6 主题
-
investment-appraisal2 主题
approaches-to-costing
An introduction to costing
-
Businesses can choose how to calculate the costs of manufacturing products, accounting for
-
Direct costs, such as raw materials, components and direct labour
-
Indirect costs, including overheads such as rent, rates, selling costs and administration expenses
-
-
Two of the most commonly used methods are
-
Full costing
-
This method allocates all costs, direct and indirect, equally across all products a business manufactures
-
-
Contribution costing
-
This method allocates only direct costs to products manufactured by a business
-
Indirect costs are covered and profits generated by contribution
-
-
The principles of full costing
-
If a business manufactures one type of product, full costing can be used to allocate all costs, direct and indirect, equally across all products
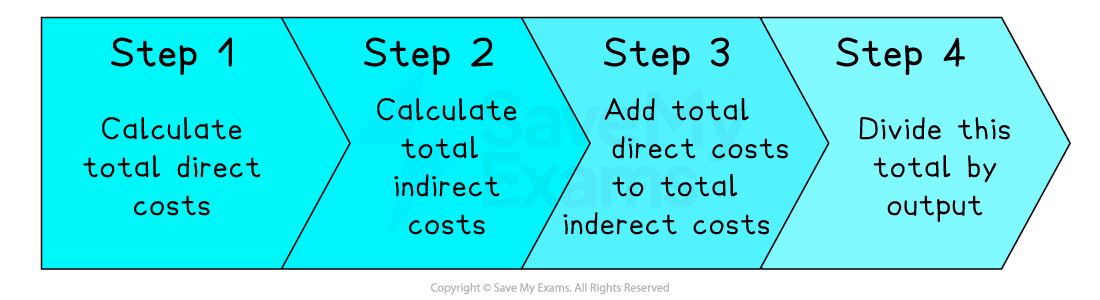
Stages in full Costing
Worked Example
Luftig Soft Drinks Gmbh uses full costing to determine the cost of manufacturing each bottle it produces.
In 2023 it manufactured 455,000 bottles of soft drink, and recorded the following costs:
Total Direct Costs €52,300
Total Indirect Costs €120,600
Calculate the full cost of producing each bottle of soft drink.
(2)
Step 1: Add total direct costs to total indirect costs
(1)
Step 2: Divide total costs by output
(1)
-
When a business manufactures more than one product, it needs to decide how to allocate indirect costs across the range of products
-
Each product may incur a different proportion of indirect costs
-
E.g. they may require more workers, machinery or factory space, or may be manufactured in greater volumes
-
-
These decisions are unlikely to be straightforward and should remain constant over time
-
Inappropriate allocation of costs can lead to incorrect pri
-
-
